Marco Law
Segmentation of Pulmonary Opacification in Chest CT Scans of COVID-19 Patients
Jul 08, 2020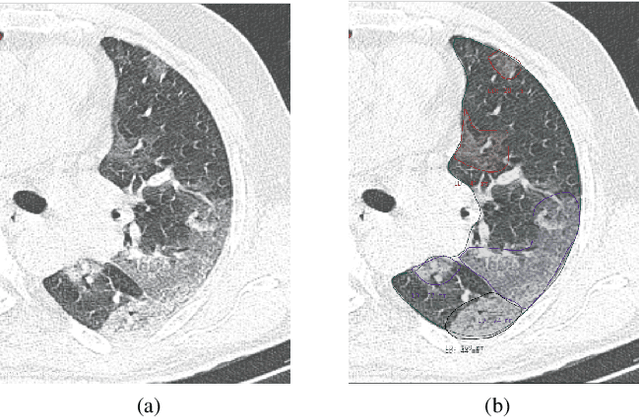
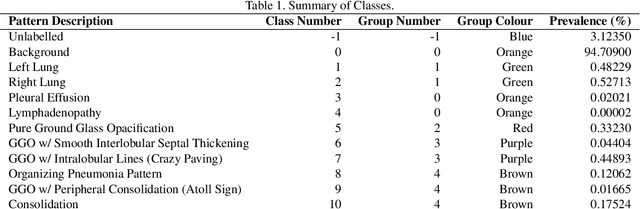
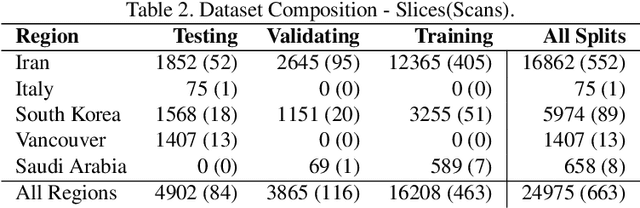
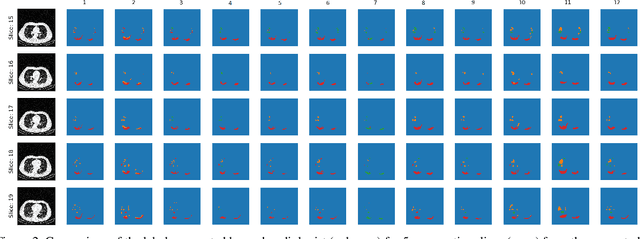
Abstract:The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has rapidly spread into a global pandemic. A form of pneumonia, presenting as opacities with in a patient's lungs, is the most common presentation associated with this virus, and great attention has gone into how these changes relate to patient morbidity and mortality. In this work we provide open source models for the segmentation of patterns of pulmonary opacification on chest Computed Tomography (CT) scans which have been correlated with various stages and severities of infection. We have collected 663 chest CT scans of COVID-19 patients from healthcare centers around the world, and created pixel wise segmentation labels for nearly 25,000 slices that segment 6 different patterns of pulmonary opacification. We provide open source implementations and pre-trained weights for multiple segmentation models trained on our dataset. Our best model achieves an opacity Intersection-Over-Union score of 0.76 on our test set, demonstrates successful domain adaptation, and predicts the volume of opacification within 1.7\% of expert radiologists. Additionally, we present an analysis of the inter-observer variability inherent to this task, and propose methods for appropriate probabilistic approaches.
A Weakly Supervised Consistency-based Learning Method for COVID-19 Segmentation in CT Images
Jul 07, 2020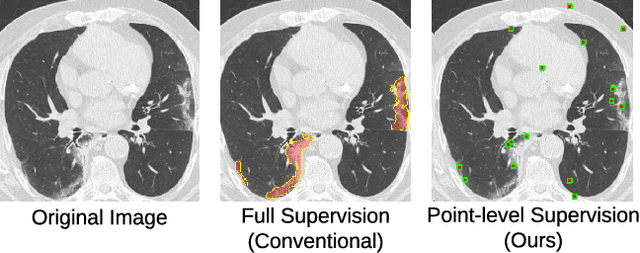

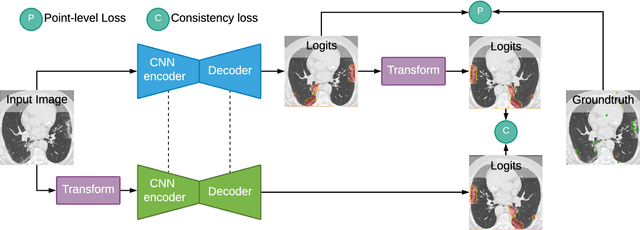
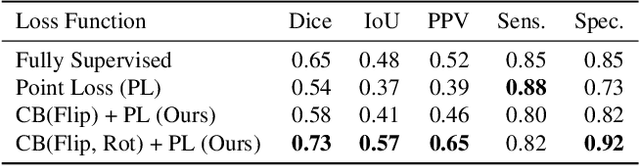
Abstract:Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has spread aggressively across the world causing an existential health crisis. Thus, having a system that automatically detects COVID-19 in tomography (CT) images can assist in quantifying the severity of the illness. Unfortunately, labelling chest CT scans requires significant domain expertise, time, and effort. We address these labelling challenges by only requiring point annotations, a single pixel for each infected region on a CT image. This labeling scheme allows annotators to label a pixel in a likely infected region, only taking 1-3 seconds, as opposed to 10-15 seconds to segment a region. Conventionally, segmentation models train on point-level annotations using the cross-entropy loss function on these labels. However, these models often suffer from low precision. Thus, we propose a consistency-based (CB) loss function that encourages the output predictions to be consistent with spatial transformations of the input images. The experiments on 3 open-source COVID-19 datasets show that this loss function yields significant improvement over conventional point-level loss functions and almost matches the performance of models trained with full supervision with much less human effort. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/IssamLaradji/covid19_weak_supervision}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge