Manuel Muehlig
Modeling and Simulation of a Multi Robot System Architecture
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:A Multi Robot System (MRS) is the infrastructure of an intelligent cyberphysical system, where the robots understand the need of the human, and hence cooperate together to fulfill this need. Modeling an MRS is a crucial aspect of designing the proper system architecture, because this model can be used to simulate and measure the performance of the proposed architecture. However, an MRS solution architecture modeling is a very difficult problem, as it contains many dependent behaviors that dynamically change due to the current status of the overall system. In this paper, we introduce a general purpose MRS case study, where the humans initiate requests that are achieved by the available robots. These requests require different plans that use the current capabilities of the available robots. After proposing an architecture that defines the solution components, three steps are followed. First is modeling these components via Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) language. BPMN provides a graphical notation to precisely represent the behaviors of every component, which is an essential need to model the solution. Second is to simulate these components behaviors and interaction in form of software agents. Java Agent DEvelopment (JADE) middleware has been used to develop and simulate the proposed model. JADE is based on a reactive agent approach, therefore it can dynamically represent the interaction among the solution components. Finally is to analyze the performance of the solution by defining a number of quantitative measurements, which can be obtained while simulating the system model in JADE middleware, therefore the solution can be analyzed and compared to another architecture.
Designing Interaction for Multi-agent Cooperative System in an Office Environment
Feb 15, 2020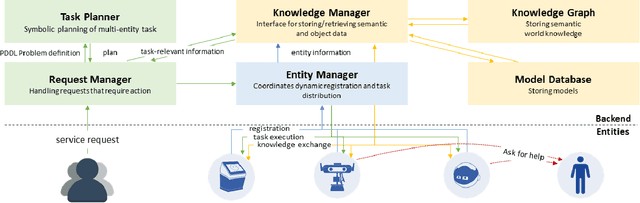
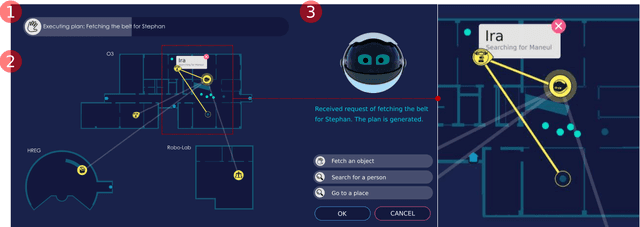
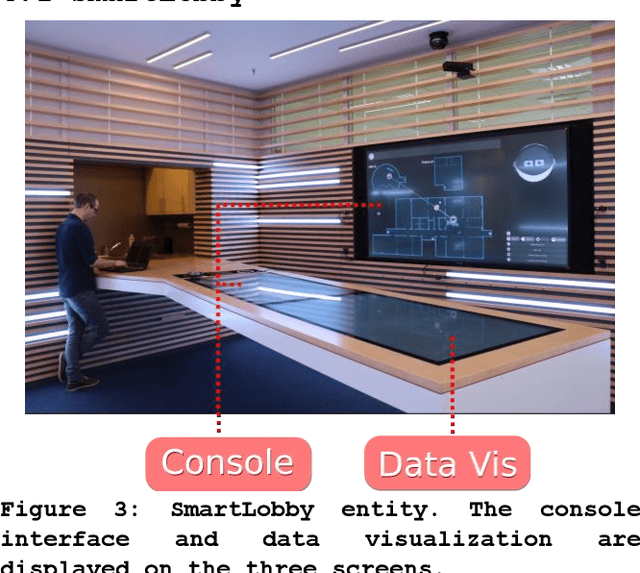

Abstract:Future intelligent system will involve very various types of artificial agents, such as mobile robots, smart home infrastructure or personal devices, which share data and collaborate with each other to execute certain tasks.Designing an efficient human-machine interface, which can support users to express needs to the system, supervise the collaboration progress of different entities and evaluate the result, will be challengeable. This paper presents the design and implementation of the human-machine interface of Intelligent Cyber-Physical system (ICPS),which is a multi-entity coordination system of robots and other smart devices in a working environment. ICPS gathers sensory data from entities and then receives users' command, then optimizes plans to utilize the capability of different entities to serve people. Using multi-model interaction methods, e.g. graphical interfaces, speech interaction, gestures and facial expressions, ICPS is able to receive inputs from users through different entities, keep users aware of the progress and accomplish the task efficiently
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge