Manraj Singh Grover
Automated Speech Scoring System Under The Lens: Evaluating and interpreting the linguistic cues for language proficiency
Nov 30, 2021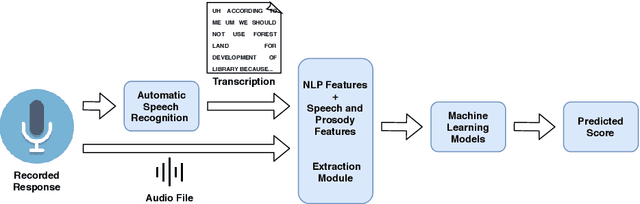
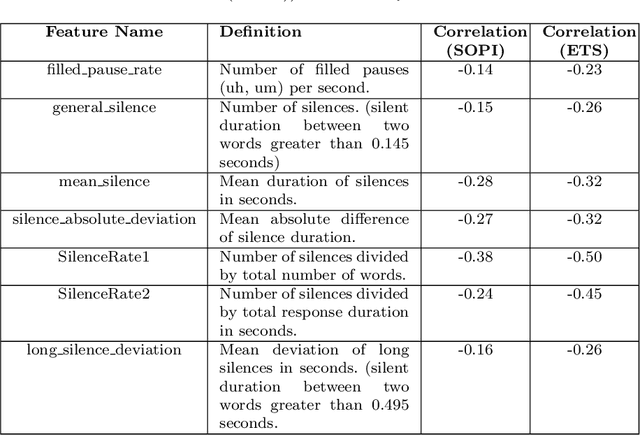
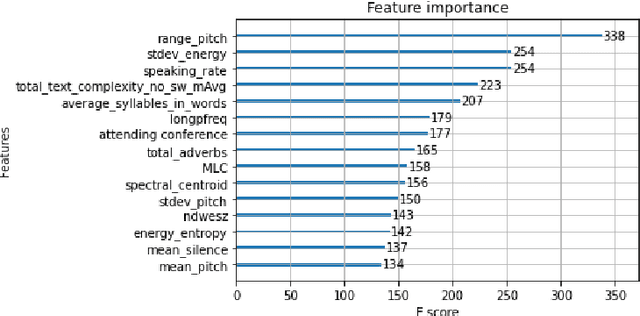
Abstract:English proficiency assessments have become a necessary metric for filtering and selecting prospective candidates for both academia and industry. With the rise in demand for such assessments, it has become increasingly necessary to have the automated human-interpretable results to prevent inconsistencies and ensure meaningful feedback to the second language learners. Feature-based classical approaches have been more interpretable in understanding what the scoring model learns. Therefore, in this work, we utilize classical machine learning models to formulate a speech scoring task as both a classification and a regression problem, followed by a thorough study to interpret and study the relation between the linguistic cues and the English proficiency level of the speaker. First, we extract linguist features under five categories (fluency, pronunciation, content, grammar and vocabulary, and acoustic) and train models to grade responses. In comparison, we find that the regression-based models perform equivalent to or better than the classification approach. Second, we perform ablation studies to understand the impact of each of the feature and feature categories on the performance of proficiency grading. Further, to understand individual feature contributions, we present the importance of top features on the best performing algorithm for the grading task. Third, we make use of Partial Dependence Plots and Shapley values to explore feature importance and conclude that the best performing trained model learns the underlying rubrics used for grading the dataset used in this study.
audino: A Modern Annotation Tool for Audio and Speech
Jun 09, 2020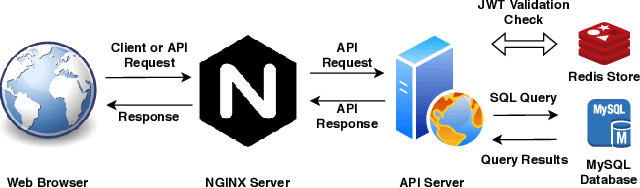
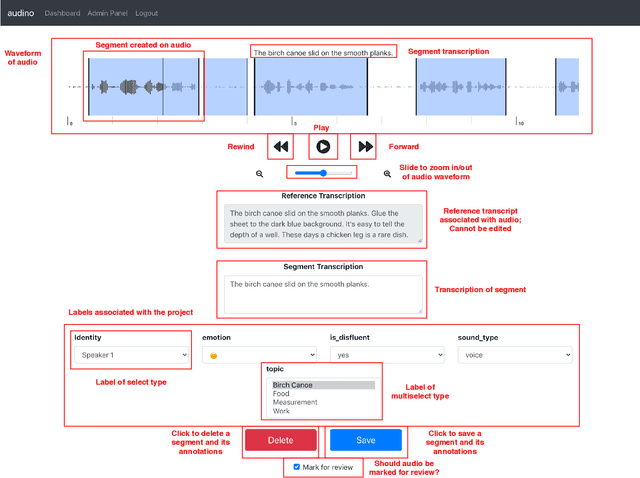
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a collaborative and modern annotation tool for audio and speech: audino. The tool allows annotators to define and describe temporal segmentation in audios. These segments can be labelled and transcribed easily using a dynamically generated form. An admin can centrally control user roles and project assignment through the admin dashboard. The dashboard also enables describing labels and their values. The annotations can easily be exported in JSON format for further processing. The tool allows audio data to be uploaded and assigned to a user through a key-based API. The flexibility available in the annotation tool enables annotation for Speech Scoring, Voice Activity Detection (VAD), Speaker Diarisation, Speaker Identification, Speech Recognition, Emotion Recognition tasks and more. The MIT open source license allows it to be used for academic and commercial projects.
Multi-modal Automated Speech Scoring using Attention Fusion
May 17, 2020



Abstract:In this study, we propose a novel multi-modal end-to-end neural approach for automated assessment of non-native English speakers' spontaneous speech using attention fusion. The pipeline employs Bi-directional Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks and Bi-directional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks to encode acoustic and lexical cues from spectrograms and transcriptions, respectively. Attention fusion is performed on these learned predictive features to learn complex interactions between different modalities before final scoring. We compare our model with strong baselines and find combined attention to both lexical and acoustic cues significantly improves the overall performance of the system. Further, we present a qualitative and quantitative analysis of our model.
Universal EEG Encoder for Learning Diverse Intelligent Tasks
Nov 26, 2019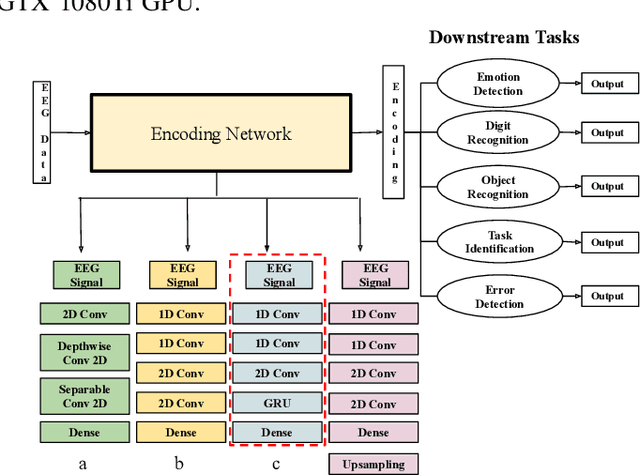
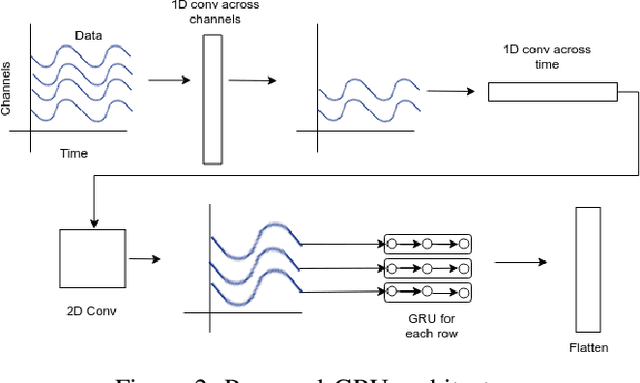
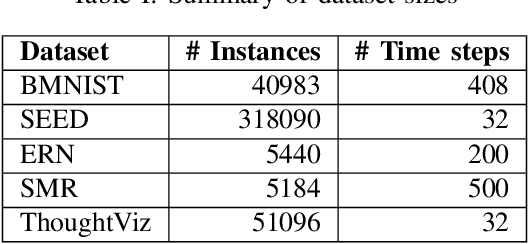
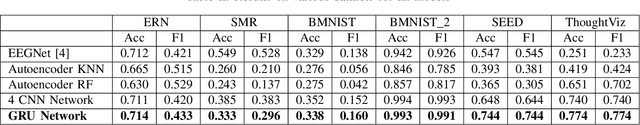
Abstract:Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) have become very popular with Electroencephalography (EEG) being one of the most commonly used signal acquisition techniques. A major challenge in BCI studies is the individualistic analysis required for each task. Thus, task-specific feature extraction and classification are performed, which fails to generalize to other tasks with similar time-series EEG input data. To this end, we design a GRU-based universal deep encoding architecture to extract meaningful features from publicly available datasets for five diverse EEG-based classification tasks. Our network can generate task and format-independent data representation and outperform the state of the art EEGNet architecture on most experiments. We also compare our results with CNN-based, and Autoencoder networks, in turn performing local, spatial, temporal and unsupervised analysis on the data.
Text2FaceGAN: Face Generation from Fine Grained Textual Descriptions
Nov 26, 2019
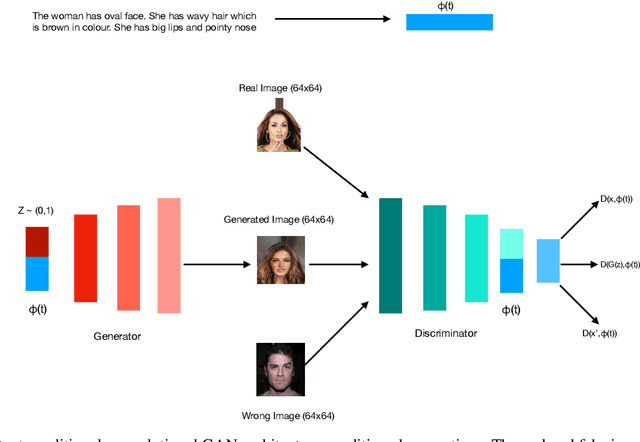

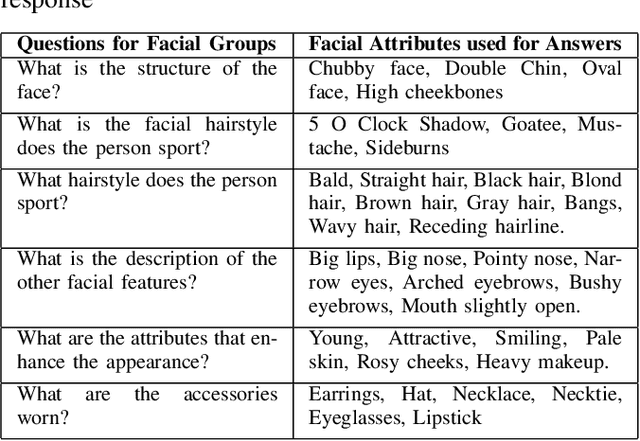
Abstract:Powerful generative adversarial networks (GAN) have been developed to automatically synthesize realistic images from text. However, most existing tasks are limited to generating simple images such as flowers from captions. In this work, we extend this problem to the less addressed domain of face generation from fine-grained textual descriptions of face, e.g., "A person has curly hair, oval face, and mustache". We are motivated by the potential of automated face generation to impact and assist critical tasks such as criminal face reconstruction. Since current datasets for the task are either very small or do not contain captions, we generate captions for images in the CelebA dataset by creating an algorithm to automatically convert a list of attributes to a set of captions. We then model the highly multi-modal problem of text to face generation as learning the conditional distribution of faces (conditioned on text) in same latent space. We utilize the current state-of-the-art GAN (DC-GAN with GAN-CLS loss) for learning conditional multi-modality. The presence of more fine-grained details and variable length of the captions makes the problem easier for a user but more difficult to handle compared to the other text-to-image tasks. We flipped the labels for real and fake images and added noise in discriminator. Generated images for diverse textual descriptions show promising results. In the end, we show how the widely used inceptions score is not a good metric to evaluate the performance of generative models used for synthesizing faces from text.
A Hitchhiker's Guide On Distributed Training of Deep Neural Networks
Oct 28, 2018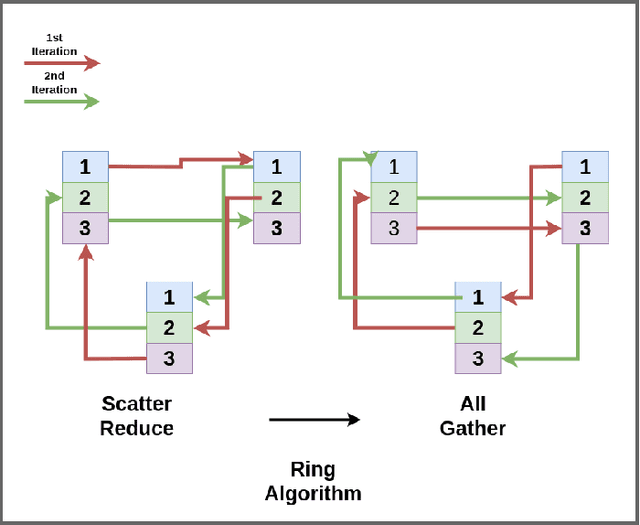
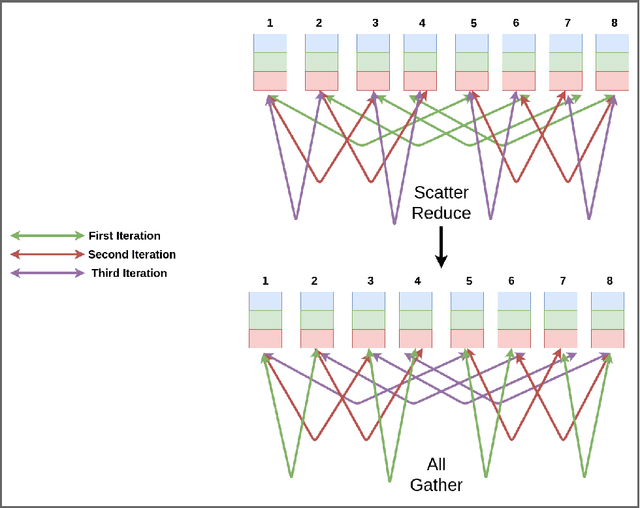
Abstract:Deep learning has led to tremendous advancements in the field of Artificial Intelligence. One caveat however is the substantial amount of compute needed to train these deep learning models. Training a benchmark dataset like ImageNet on a single machine with a modern GPU can take upto a week, distributing training on multiple machines has been observed to drastically bring this time down. Recent work has brought down ImageNet training time to a time as low as 4 minutes by using a cluster of 2048 GPUs. This paper surveys the various algorithms and techniques used to distribute training and presents the current state of the art for a modern distributed training framework. More specifically, we explore the synchronous and asynchronous variants of distributed Stochastic Gradient Descent, various All Reduce gradient aggregation strategies and best practices for obtaining higher throughout and lower latency over a cluster such as mixed precision training, large batch training and gradient compression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge