Maksim Bolonkin
Automatic Long-Term Deception Detection in Group Interaction Videos
May 15, 2019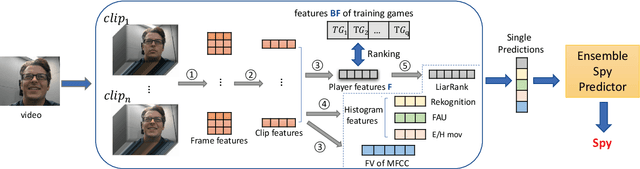
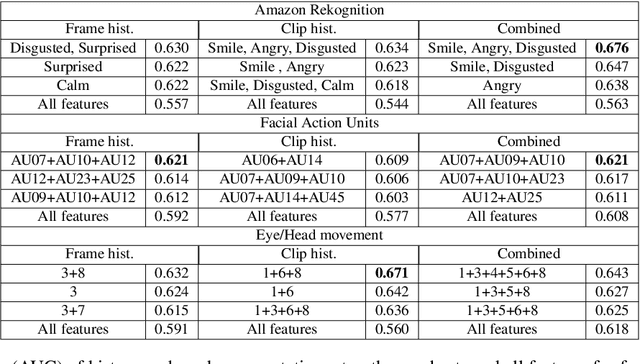
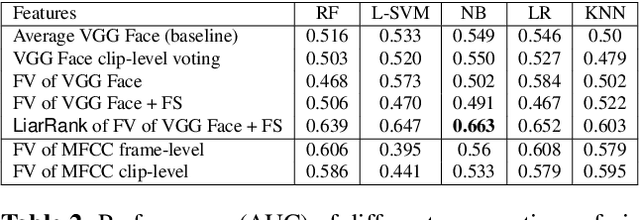
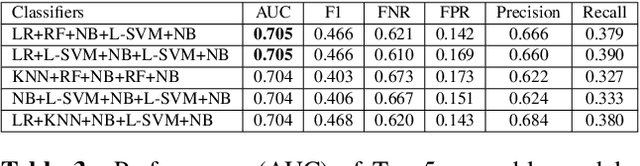
Abstract:Most work on automated deception detection (ADD) in video has two restrictions: (i) it focuses on a video of one person, and (ii) it focuses on a single act of deception in a one or two minute video. In this paper, we propose a new ADD framework which captures long term deception in a group setting. We study deception in the well-known Resistance game (like Mafia and Werewolf) which consists of 5-8 players of whom 2-3 are spies. Spies are deceptive throughout the game (typically 30-65 minutes) to keep their identity hidden. We develop an ensemble predictive model to identify spies in Resistance videos. We show that features from low-level and high-level video analysis are insufficient, but when combined with a new class of features that we call LiarRank, produce the best results. We achieve AUCs of over 0.70 in a fully automated setting. Our demo can be found at http://home.cs.dartmouth.edu/~mbolonkin/scan/demo/
VideoMCC: a New Benchmark for Video Comprehension
Jun 16, 2017
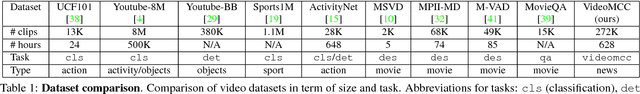
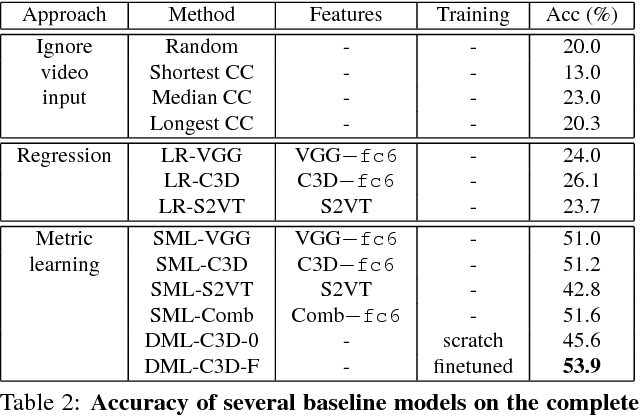
Abstract:While there is overall agreement that future technology for organizing, browsing and searching videos hinges on the development of methods for high-level semantic understanding of video, so far no consensus has been reached on the best way to train and assess models for this task. Casting video understanding as a form of action or event categorization is problematic as it is not fully clear what the semantic classes or abstractions in this domain should be. Language has been exploited to sidestep the problem of defining video categories, by formulating video understanding as the task of captioning or description. However, language is highly complex, redundant and sometimes ambiguous. Many different captions may express the same semantic concept. To account for this ambiguity, quantitative evaluation of video description requires sophisticated metrics, whose performance scores are typically hard to interpret by humans. This paper provides four contributions to this problem. First, we formulate Video Multiple Choice Caption (VideoMCC) as a new well-defined task with an easy-to-interpret performance measure. Second, we describe a general semi-automatic procedure to create benchmarks for this task. Third, we publicly release a large-scale video benchmark created with an implementation of this procedure and we include a human study that assesses human performance on our dataset. Finally, we propose and test a varied collection of approaches on this benchmark for the purpose of gaining a better understanding of the new challenges posed by video comprehension.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge