Maja Vukovic
CoSiNES: Contrastive Siamese Network for Entity Standardization
Jun 05, 2023Abstract:Entity standardization maps noisy mentions from free-form text to standard entities in a knowledge base. The unique challenge of this task relative to other entity-related tasks is the lack of surrounding context and numerous variations in the surface form of the mentions, especially when it comes to generalization across domains where labeled data is scarce. Previous research mostly focuses on developing models either heavily relying on context, or dedicated solely to a specific domain. In contrast, we propose CoSiNES, a generic and adaptable framework with Contrastive Siamese Network for Entity Standardization that effectively adapts a pretrained language model to capture the syntax and semantics of the entities in a new domain. We construct a new dataset in the technology domain, which contains 640 technical stack entities and 6,412 mentions collected from industrial content management systems. We demonstrate that CoSiNES yields higher accuracy and faster runtime than baselines derived from leading methods in this domain. CoSiNES also achieves competitive performance in four standard datasets from the chemistry, medicine, and biomedical domains, demonstrating its cross-domain applicability.
Partitioning Cloud-based Microservices (via Deep Learning)
Sep 29, 2021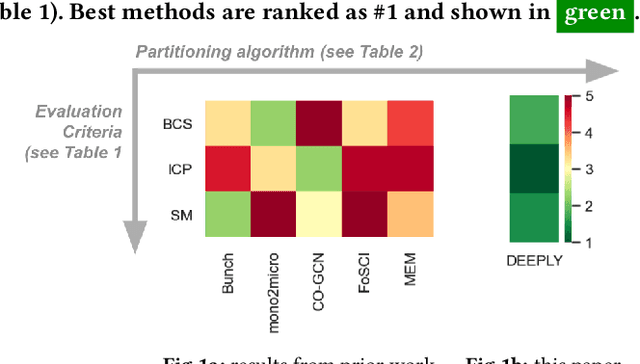

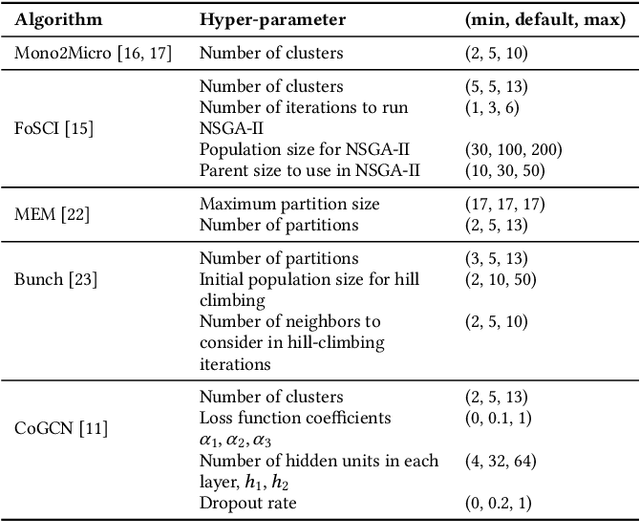
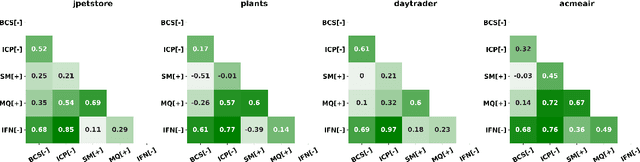
Abstract:Cloud-based software has many advantages. When services are divided into many independent components, they are easier to update. Also, during peak demand, it is easier to scale cloud services (just hire more CPUs). Hence, many organizations are partitioning their monolithic enterprise applications into cloud-based microservices. Recently there has been much work using machine learning to simplify this partitioning task. Despite much research, no single partitioning method can be recommended as generally useful. More specifically, those prior solutions are "brittle''; i.e. if they work well for one kind of goal in one dataset, then they can be sub-optimal if applied to many datasets and multiple goals. In order to find a generally useful partitioning method, we propose DEEPLY. This new algorithm extends the CO-GCN deep learning partition generator with (a) a novel loss function and (b) some hyper-parameter optimization. As shown by our experiments, DEEPLY generally outperforms prior work (including CO-GCN, and others) across multiple datasets and goals. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report in SE of such stable hyper-parameter optimization. To aid reuse of this work, DEEPLY is available on-line at https://bit.ly/2WhfFlB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge