Mahya Shahbazi
Power Modeling for Effective Datacenter Planning and Compute Management
Mar 22, 2021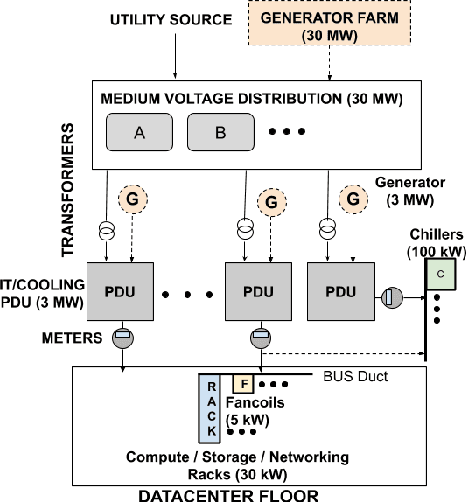
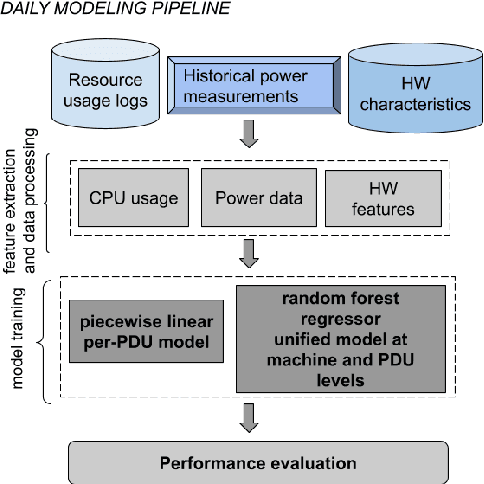
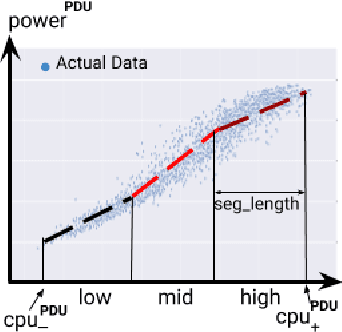
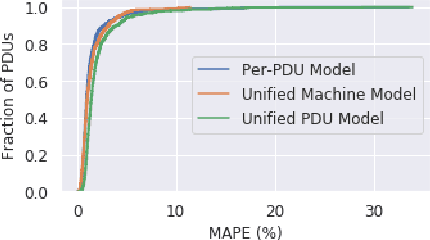
Abstract:Datacenter power demand has been continuously growing and is the key driver of its cost. An accurate mapping of compute resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) and hardware types (servers, accelerators, etc.) to power consumption has emerged as a critical requirement for major Web and cloud service providers. With the global growth in datacenter capacity and associated power consumption, such models are essential for important decisions around datacenter design and operation. In this paper, we discuss two classes of statistical power models designed and validated to be accurate, simple, interpretable and applicable to all hardware configurations and workloads across hyperscale datacenters of Google fleet. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest scale power modeling study of this kind, in both the scope of diverse datacenter planning and real-time management use cases, as well as the variety of hardware configurations and workload types used for modeling and validation. We demonstrate that the proposed statistical modeling techniques, while simple and scalable, predict power with less than 5% Mean Absolute Percent Error (MAPE) for more than 95% diverse Power Distribution Units (more than 2000) using only 4 features. This performance matches the reported accuracy of the previous started-of-the-art methods, while using significantly less features and covering a wider range of use cases.
Hybrid Robotic-assisted Frameworks for Endomicroscopy Scanning in Retinal Surgeries
Sep 15, 2019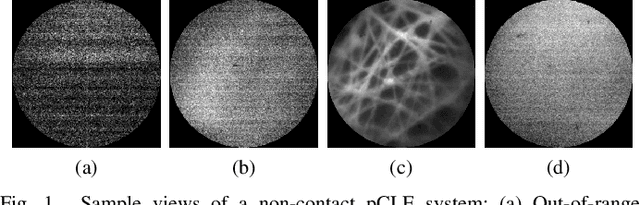
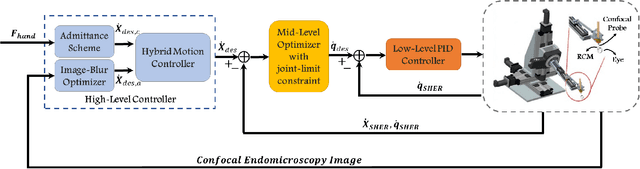
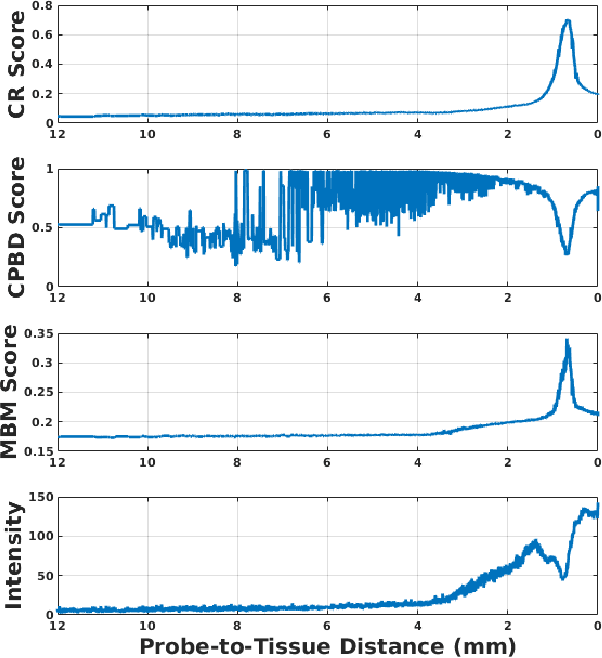
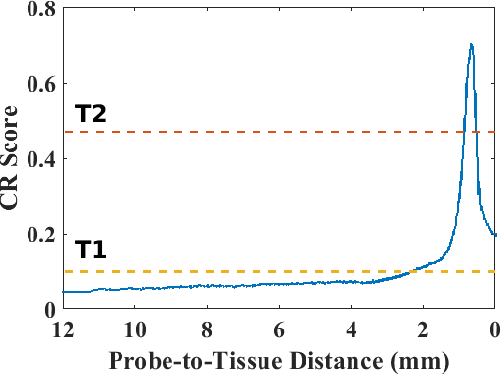
Abstract:High-resolution real-time imaging at cellular levelin retinal surgeries is very challenging due to extremely confinedspace within the eyeball and lack of appropriate modalities.Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (pCLE) system,which has a small footprint and provides highly-magnified im-ages, can be a potential imaging modality for improved diagnosis.The ability to visualize in cellular-level the retinal pigmentepithelium and the chorodial blood vessels underneath canprovide useful information for surgical outcomes in conditionssuch as retinal detachment. However, the adoption of pCLE islimited due to narrow field of view and micron-level range offocus. The physiological tremor of surgeons' hand also deterioratethe image quality considerably and leads to poor imaging results. In this paper, a novel image-based hybrid motion controlapproach is proposed to mitigate challenges of using pCLEin retinal surgeries. The proposed framework enables sharedcontrol of the pCLE probe by a surgeon to scan the tissueprecisely without hand tremors and an auto-focus image-basedcontrol algorithm that optimizes quality of pCLE images. Thecontrol strategy is deployed on two semi-autonomous frameworks: cooperative and teleoperated. Both frameworks consist of theSteady-Hand Eye Robot (SHER), whose end-effector holds thepCLE probe...
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge