Alexandre Duarte
SelfReDepth: Self-Supervised Real-Time Depth Restoration for Consumer-Grade Sensors
Jun 05, 2024Abstract:Depth maps produced by consumer-grade sensors suffer from inaccurate measurements and missing data from either system or scene-specific sources. Data-driven denoising algorithms can mitigate such problems. However, they require vast amounts of ground truth depth data. Recent research has tackled this limitation using self-supervised learning techniques, but it requires multiple RGB-D sensors. Moreover, most existing approaches focus on denoising single isolated depth maps or specific subjects of interest, highlighting a need for methods to effectively denoise depth maps in real-time dynamic environments. This paper extends state-of-the-art approaches for depth-denoising commodity depth devices, proposing SelfReDepth, a self-supervised deep learning technique for depth restoration, via denoising and hole-filling by inpainting full-depth maps captured with RGB-D sensors. The algorithm targets depth data in video streams, utilizing multiple sequential depth frames coupled with color data to achieve high-quality depth videos with temporal coherence. Finally, SelfReDepth is designed to be compatible with various RGB-D sensors and usable in real-time scenarios as a pre-processing step before applying other depth-dependent algorithms. Our results demonstrate our approach's real-time performance on real-world datasets. They show that it outperforms state-of-the-art denoising and restoration performance at over 30fps on Commercial Depth Cameras, with potential benefits for augmented and mixed-reality applications.
* 13pp, 5 figures, 1 table
Power Modeling for Effective Datacenter Planning and Compute Management
Mar 22, 2021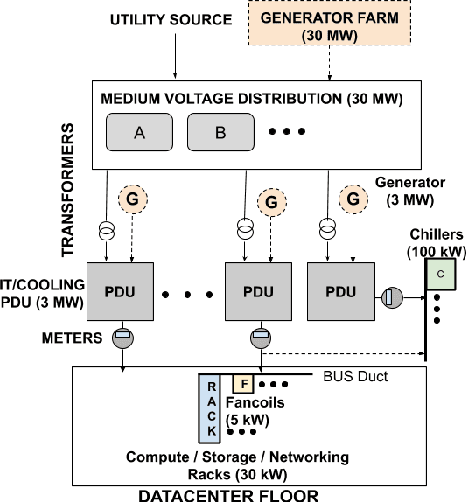
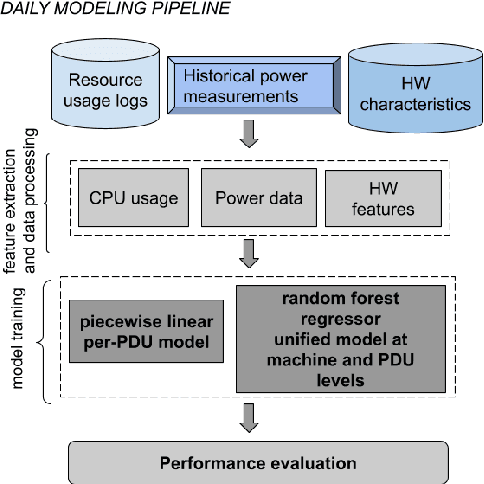
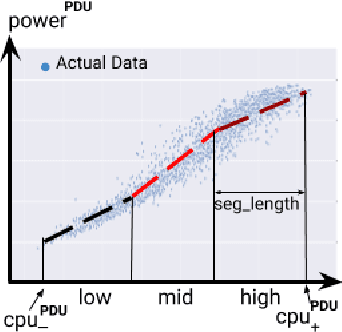
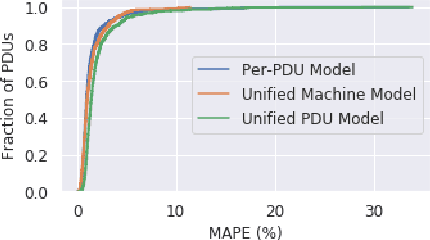
Abstract:Datacenter power demand has been continuously growing and is the key driver of its cost. An accurate mapping of compute resources (CPU, RAM, etc.) and hardware types (servers, accelerators, etc.) to power consumption has emerged as a critical requirement for major Web and cloud service providers. With the global growth in datacenter capacity and associated power consumption, such models are essential for important decisions around datacenter design and operation. In this paper, we discuss two classes of statistical power models designed and validated to be accurate, simple, interpretable and applicable to all hardware configurations and workloads across hyperscale datacenters of Google fleet. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest scale power modeling study of this kind, in both the scope of diverse datacenter planning and real-time management use cases, as well as the variety of hardware configurations and workload types used for modeling and validation. We demonstrate that the proposed statistical modeling techniques, while simple and scalable, predict power with less than 5% Mean Absolute Percent Error (MAPE) for more than 95% diverse Power Distribution Units (more than 2000) using only 4 features. This performance matches the reported accuracy of the previous started-of-the-art methods, while using significantly less features and covering a wider range of use cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge