M Tanveer
Machine learning techniques for the Schizophrenia diagnosis: A comprehensive review and future research directions
Jan 16, 2023Abstract:Schizophrenia (SCZ) is a brain disorder where different people experience different symptoms, such as hallucination, delusion, flat-talk, disorganized thinking, etc. In the long term, this can cause severe effects and diminish life expectancy by more than ten years. Therefore, early and accurate diagnosis of SCZ is prevalent, and modalities like structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI), functional MRI (fMRI), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and electroencephalogram (EEG) assist in witnessing the brain abnormalities of the patients. Moreover, for accurate diagnosis of SCZ, researchers have used machine learning (ML) algorithms for the past decade to distinguish the brain patterns of healthy and SCZ brains using MRI and fMRI images. This paper seeks to acquaint SCZ researchers with ML and to discuss its recent applications to the field of SCZ study. This paper comprehensively reviews state-of-the-art techniques such as ML classifiers, artificial neural network (ANN), deep learning (DL) models, methodological fundamentals, and applications with previous studies. The motivation of this paper is to benefit from finding the research gaps that may lead to the development of a new model for accurate SCZ diagnosis. The paper concludes with the research finding, followed by the future scope that directly contributes to new research directions.
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in Cognitive Decline: A Review of Technical Aspects and Applications
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:In the human brain, essential iron molecules for proper neurological functioning exist in transferrin (tf) and ferritin (Fe3) forms. However, its unusual increment manifests iron overload, which reacts with hydrogen peroxide. This reaction will generate hydroxyl radicals, and irons higher oxidation states. Further, this reaction causes tissue damage or cognitive decline in the brain and also leads to neurodegenerative diseases. The susceptibility difference due to iron overload within the volume of interest (VOI) responsible for field perturbation of MRI and can benefit in estimating the neural disorder. The quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) technique can estimate susceptibility alteration and assist in quantifying the local tissue susceptibility differences. It has attracted many researchers and clinicians to diagnose and detect neural disorders such as Parkinsons, Alzheimers, Multiple Sclerosis, and aging. The paper presents a systematic review illustrating QSM fundamentals and its processing steps, including phase unwrapping, background field removal, and susceptibility inversion. Using QSM, the present work delivers novel predictive biomarkers for various neural disorders. It can strengthen new researchers fundamental knowledge and provides insight into its applicability for cognitive decline disclosure. The paper discusses the future scope of QSM processing stages and their applications in identifying new biomarkers for neural disorders.
Lightweight 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Schizophrenia diagnosis using MRI Images and Ensemble Bagging Classifier
Nov 05, 2022
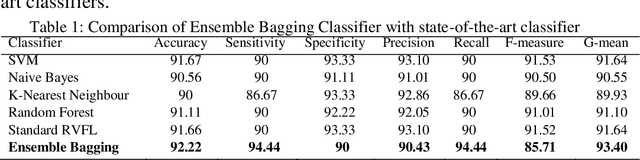


Abstract:Structural alterations have been thoroughly investigated in the brain during the early onset of schizophrenia (SCZ) with the development of neuroimaging methods. The objective of the paper is an efficient classification of SCZ in 2 different classes: Cognitive Normal (CN), and SCZ using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. This paper proposed a lightweight 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) based framework for SCZ diagnosis using MRI images. In the proposed model, lightweight 3D CNN is used to extract both spatial and spectral features simultaneously from 3D volume MRI scans, and classification is done using an ensemble bagging classifier. Ensemble bagging classifier contributes to preventing overfitting, reduces variance, and improves the model's accuracy. The proposed algorithm is tested on datasets taken from three benchmark databases available as open-source: MCICShare, COBRE, and fBRINPhase-II. These datasets have undergone preprocessing steps to register all the MRI images to the standard template and reduce the artifacts. The model achieves the highest accuracy 92.22%, sensitivity 94.44%, specificity 90%, precision 90.43%, recall 94.44%, F1-score 92.39% and G-mean 92.19% as compared to the current state-of-the-art techniques. The performance metrics evidenced the use of this model to assist the clinicians for automatic accurate diagnosis of SCZ.
Identification of Chimera using Machine Learning
Jan 16, 2020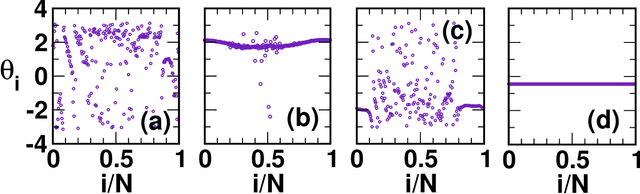
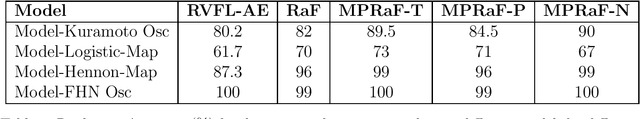
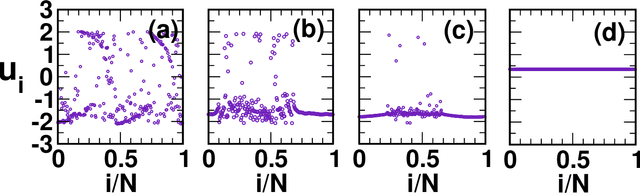
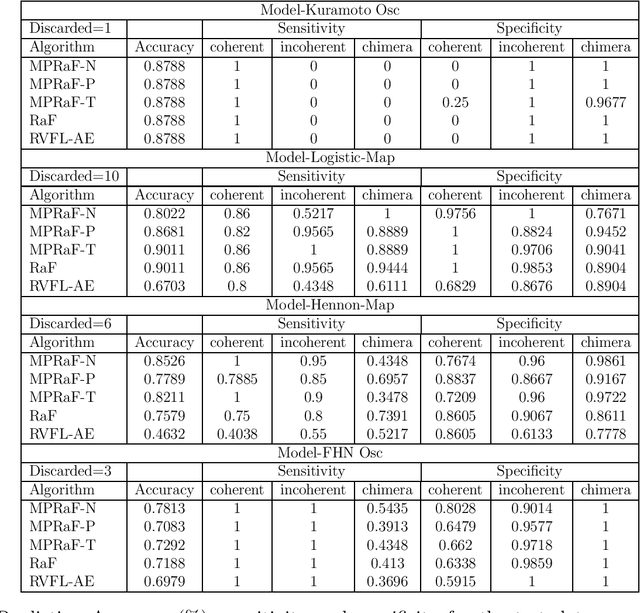
Abstract:Coupled dynamics on the network models have been tremendously helpful in getting insight into complex spatiotemporal dynamical patterns of a wide variety of large-scale real-world complex systems. Chimera, a state of coexistence of incoherence and coherence, is one of such patterns arising in identically coupled oscillators, which has recently drawn tremendous attention due to its peculiar nature and wide applicability, specially in neuroscience. The identification of chimera is a challenging problem due to ambiguity in its appearance. We present a distinctive approach to identify and characterize the chimera state using machine learning techniques, namely random forest, oblique random forests via multi-surface proximal support vector machines (MPRaF-T, P, N) and sparse pre-trained / auto-encoder based random vector functional link neural network (RVFL-AE). We demonstrate high accuracy in identifying the coherent, incoherent and chimera states from given spatial profiles. We validate this approach for different time-continuous and time discrete coupled dynamics on networks. This work provides a direction for employing machine learning techniques to identify dynamical patterns arising due to the interaction among non-linear units on large-scale, and for characterizing complex spatio-temporal phenomena in real-world systems for various applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge