Luo Cheng
SL-CBM: Enhancing Concept Bottleneck Models with Semantic Locality for Better Interpretability
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) is crucial for building transparent and trustworthy machine learning systems, especially in high-stakes domains. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) have emerged as a promising ante-hoc approach that provides interpretable, concept-level explanations by explicitly modeling human-understandable concepts. However, existing CBMs often suffer from poor locality faithfulness, failing to spatially align concepts with meaningful image regions, which limits their interpretability and reliability. In this work, we propose SL-CBM (CBM with Semantic Locality), a novel extension that enforces locality faithfulness by generating spatially coherent saliency maps at both concept and class levels. SL-CBM integrates a 1x1 convolutional layer with a cross-attention mechanism to enhance alignment between concepts, image regions, and final predictions. Unlike prior methods, SL-CBM produces faithful saliency maps inherently tied to the model's internal reasoning, facilitating more effective debugging and intervention. Extensive experiments on image datasets demonstrate that SL-CBM substantially improves locality faithfulness, explanation quality, and intervention efficacy while maintaining competitive classification accuracy. Our ablation studies highlight the importance of contrastive and entropy-based regularization for balancing accuracy, sparsity, and faithfulness. Overall, SL-CBM bridges the gap between concept-based reasoning and spatial explainability, setting a new standard for interpretable and trustworthy concept-based models.
ReactDiff: Fundamental Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Diffusion Model
Oct 06, 2025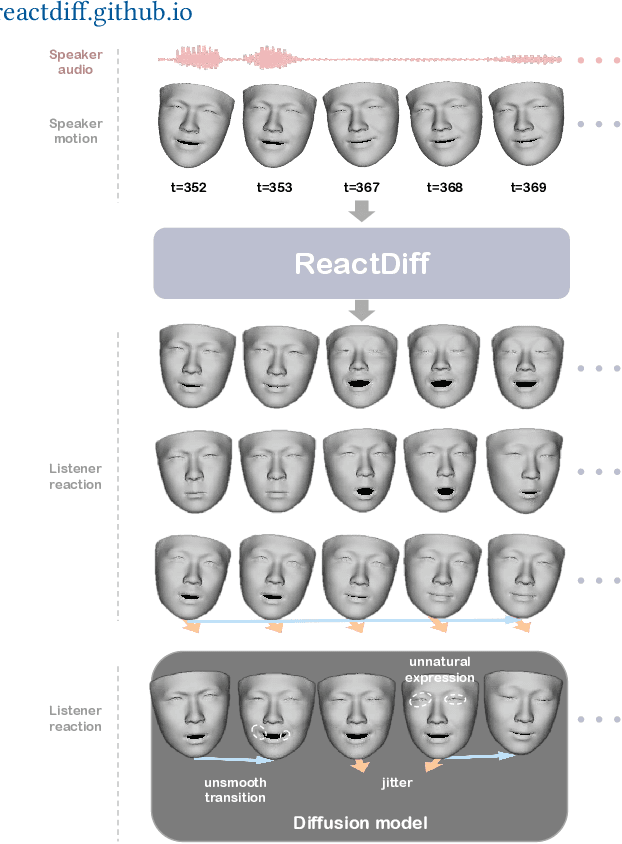
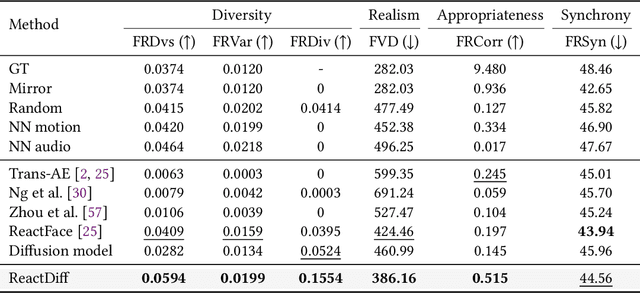
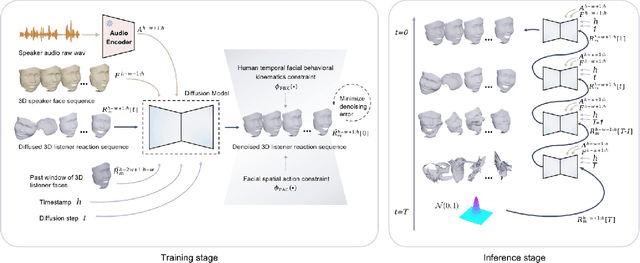
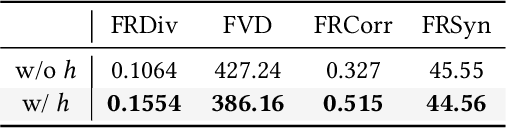
Abstract:The automatic generation of diverse and human-like facial reactions in dyadic dialogue remains a critical challenge for human-computer interaction systems. Existing methods fail to model the stochasticity and dynamics inherent in real human reactions. To address this, we propose ReactDiff, a novel temporal diffusion framework for generating diverse facial reactions that are appropriate for responding to any given dialogue context. Our key insight is that plausible human reactions demonstrate smoothness, and coherence over time, and conform to constraints imposed by human facial anatomy. To achieve this, ReactDiff incorporates two vital priors (spatio-temporal facial kinematics) into the diffusion process: i) temporal facial behavioral kinematics and ii) facial action unit dependencies. These two constraints guide the model toward realistic human reaction manifolds, avoiding visually unrealistic jitters, unstable transitions, unnatural expressions, and other artifacts. Extensive experiments on the REACT2024 dataset demonstrate that our approach not only achieves state-of-the-art reaction quality but also excels in diversity and reaction appropriateness.
Eidos: Efficient, Imperceptible Adversarial 3D Point Clouds
May 23, 2024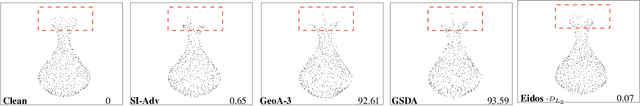
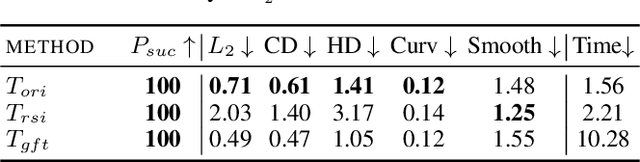
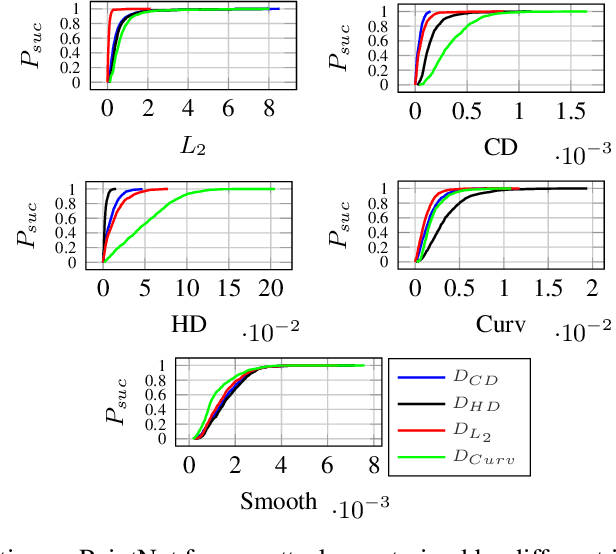
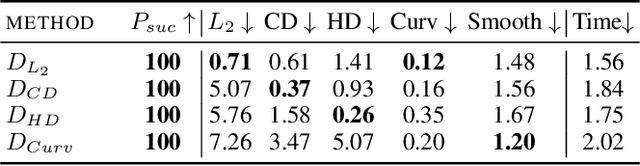
Abstract:Classification of 3D point clouds is a challenging machine learning (ML) task with important real-world applications in a spectrum from autonomous driving and robot-assisted surgery to earth observation from low orbit. As with other ML tasks, classification models are notoriously brittle in the presence of adversarial attacks. These are rooted in imperceptible changes to inputs with the effect that a seemingly well-trained model ends up misclassifying the input. This paper adds to the understanding of adversarial attacks by presenting Eidos, a framework providing Efficient Imperceptible aDversarial attacks on 3D pOint cloudS. Eidos supports a diverse set of imperceptibility metrics. It employs an iterative, two-step procedure to identify optimal adversarial examples, thereby enabling a runtime-imperceptibility trade-off. We provide empirical evidence relative to several popular 3D point cloud classification models and several established 3D attack methods, showing Eidos' superiority with respect to efficiency as well as imperceptibility.
Both Efficiency and Effectiveness! A Large Scale Pre-ranking Framework in Search System
Apr 05, 2023



Abstract:In the realm of search systems, multi-stage cascade architecture is a prevalent method, typically consisting of sequential modules such as matching, pre-ranking, and ranking. It is generally acknowledged that the model used in the pre-ranking stage must strike a balance between efficacy and efficiency. Thus, the most commonly employed architecture is the representation-focused vector product based model. However, this architecture lacks effective interaction between the query and document, resulting in a reduction in the effectiveness of the search system. To address this issue, we present a novel pre-ranking framework called RankDFM. Our framework leverages DeepFM as the backbone and employs a pairwise training paradigm to learn the ranking of videos under a query. The capability of RankDFM to cross features provides significant improvement in offline and online A/B testing performance. Furthermore, we introduce a learnable feature selection scheme to optimize the model and reduce the time required for online inference, equivalent to a tree model. Currently, RankDFM has been deployed in the search system of a shortvideo App, providing daily services to hundreds of millions users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge