Luise Poustka
Comparison of marker-less 2D image-based methods for infant pose estimation
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:There are increasing efforts to automate clinical methods for early diagnosis of developmental disorders, among them the General Movement Assessment (GMA), a video-based tool to classify infant motor functioning. Optimal pose estimation is a crucial part of the automated GMA. In this study we compare the performance of available generic- and infant-pose estimators, and the choice of viewing angle for optimal recordings, i.e., conventional diagonal view used in GMA vs. top-down view. For this study, we used 4500 annotated video-frames from 75 recordings of infant spontaneous motor functions from 4 to 26 weeks. To determine which available pose estimation method and camera angle yield the best pose estimation accuracy on infants in a GMA related setting, the distance to human annotations as well as the percentage of correct key-points (PCK) were computed and compared. The results show that the best performing generic model trained on adults, ViTPose, also performs best on infants. We see no improvement from using specialized infant-pose estimators over the generic pose estimators on our own infant dataset. However, when retraining a generic model on our data, there is a significant improvement in pose estimation accuracy. The pose estimation accuracy obtained from the top-down view is significantly better than that obtained from the diagonal view, especially for the detection of the hip key-points. The results also indicate only limited generalization capabilities of infant-pose estimators to other infant datasets, which hints that one should be careful when choosing infant pose estimators and using them on infant datasets which they were not trained on. While the standard GMA method uses a diagonal view for assessment, pose estimation accuracy significantly improves using a top-down view. This suggests that a top-down view should be included in recording setups for automated GMA research.
Automatic rating of incomplete hippocampal inversions evaluated across multiple cohorts
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:Incomplete Hippocampal Inversion (IHI), sometimes called hippocampal malrotation, is an atypical anatomical pattern of the hippocampus found in about 20% of the general population. IHI can be visually assessed on coronal slices of T1 weighted MR images, using a composite score that combines four anatomical criteria. IHI has been associated with several brain disorders (epilepsy, schizophrenia). However, these studies were based on small samples. Furthermore, the factors (genetic or environmental) that contribute to the genesis of IHI are largely unknown. Large-scale studies are thus needed to further understand IHI and their potential relationships to neurological and psychiatric disorders. However, visual evaluation is long and tedious, justifying the need for an automatic method. In this paper, we propose, for the first time, to automatically rate IHI. We proceed by predicting four anatomical criteria, which are then summed up to form the IHI score, providing the advantage of an interpretable score. We provided an extensive experimental investigation of different machine learning methods and training strategies. We performed automatic rating using a variety of deep learning models (conv5-FC3, ResNet and SECNN) as well as a ridge regression. We studied the generalization of our models using different cohorts and performed multi-cohort learning. We relied on a large population of 2,008 participants from the IMAGEN study, 993 and 403 participants from the QTIM/QTAB studies as well as 985 subjects from the UKBiobank. We showed that deep learning models outperformed a ridge regression. We demonstrated that the performances of the conv5-FC3 network were at least as good as more complex networks while maintaining a low complexity and computation time. We showed that training on a single cohort may lack in variability while training on several cohorts improves generalization.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2024:016
Deep learning empowered sensor fusion to improve infant movement classification
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:There is a recent boom in the development of AI solutions to facilitate and enhance diagnostic procedures for established clinical tools. To assess the integrity of the developing nervous system, the Prechtl general movement assessment (GMA) is recognized for its clinical value in diagnosing neurological impairments in early infancy. GMA has been increasingly augmented through machine learning approaches intending to scale-up its application, circumvent costs in the training of human assessors and further standardize classification of spontaneous motor patterns. Available deep learning tools, all of which are based on single sensor modalities, are however still considerably inferior to that of well-trained human assessors. These approaches are hardly comparable as all models are designed, trained and evaluated on proprietary/silo-data sets. With this study we propose a sensor fusion approach for assessing fidgety movements (FMs) comparing three different sensor modalities (pressure, inertial, and visual sensors). Various combinations and two sensor fusion approaches (late and early fusion) for infant movement classification were tested to evaluate whether a multi-sensor system outperforms single modality assessments. The performance of the three-sensor fusion (classification accuracy of 94.5\%) was significantly higher than that of any single modality evaluated, suggesting the sensor fusion approach is a promising avenue for automated classification of infant motor patterns. The development of a robust sensor fusion system may significantly enhance AI-based early recognition of neurofunctions, ultimately facilitating automated early detection of neurodevelopmental conditions.
Facilitating deep acoustic phenotyping: A basic coding scheme of infant vocalisations preluding computational analysis, machine learning and clinical reasoning
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Theoretical background: early verbal development is not yet fully understood, especially in its formative phase. Research question: can a reliable, easy-to-use coding scheme for the classification of early infant vocalizations be defined that is applicable as a basis for further analysis of language development? Methods: in a longitudinal study of 45 neurotypical infants, we analyzed vocalizations of the first 4 months of life. Audio segments were assigned to 5 classes: (1) Voiced and (2) Voiceless vocalizations; (3) Defined signal; (4) Non-target; (5) Nonassignable. Results: Two female coders with different experience achieved high agreement without intensive training. Discussion and Conclusion: The reliable scheme can be used in research and clinical settings for efficient coding of infant vocalizations, as a basis for detailed manual and machine analyses.
Infant movement classification through pressure distribution analysis -- added value for research and clinical implementation
Jul 26, 2022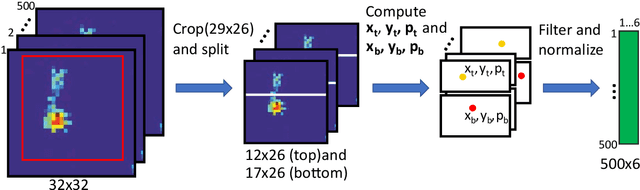
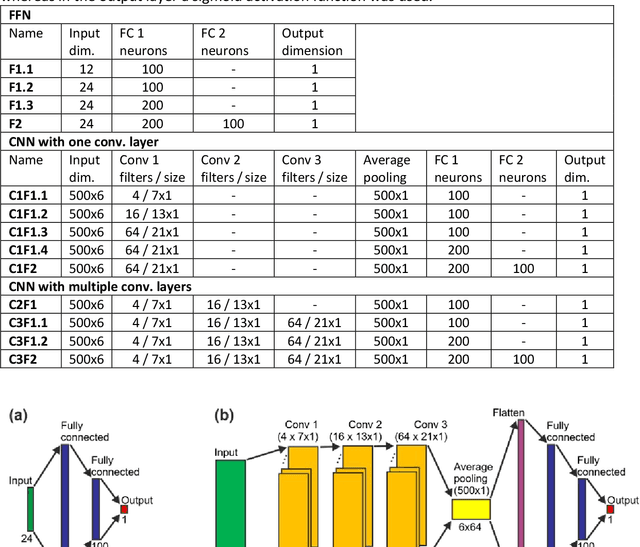
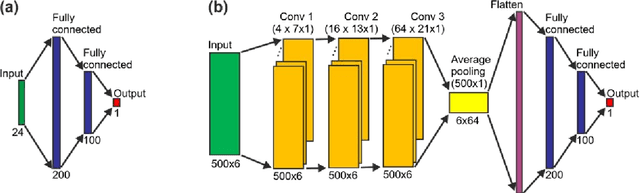
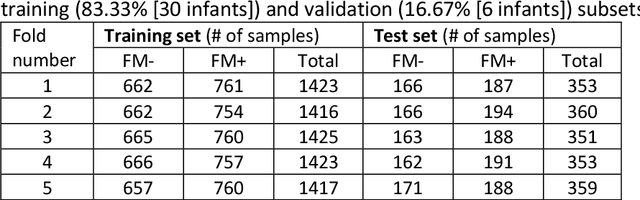
Abstract:In recent years, numerous automated approaches complementing the human Prechtl's general movements assessment (GMA) were developed. Most approaches utilised RGB or RGB-D cameras to obtain motion data, while a few employed accelerometers or inertial measurement units. In this paper, within a prospective longitudinal infant cohort study applying a multimodal approach for movement tracking and analyses, we examined for the first time the performance of pressure sensors for classifying an infant general movements pattern, the fidgety movements. We developed an algorithm to encode movements with pressure data from a 32x32 grid mat with 1024 sensors. Multiple neural network architectures were investigated to distinguish presence vs. absence of the fidgety movements, including the feed-forward networks (FFNs) with manually defined statistical features and the convolutional neural networks (CNNs) with learned features. The CNN with multiple convolutional layers and learned features outperformed the FFN with manually defined statistical features, with classification accuracy of $81.4\%$ and $75.6\%$, respectively. We compared the pros and cons of the pressure sensing approach to the video-based and inertial motion senor-based approaches for analysing infant movements. The non-intrusive, extremely easy-to-use pressure sensing approach has great potential for efficient large-scaled movement data acquisition across cites and for application in busy daily clinical routines for evaluating infant neuromotor functions. The pressure sensors can be combined with other sensor modalities to enhance infant movement analyses in research and practice, as proposed in our multimodal sensor fusion model.
Open video data sharing in developmental and behavioural science
Jul 22, 2022
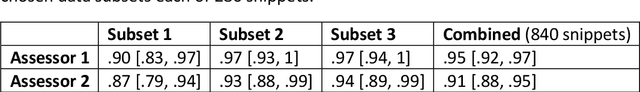
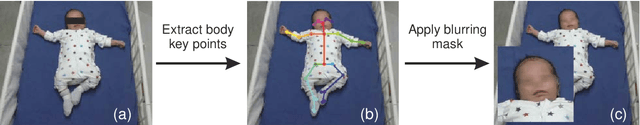

Abstract:Video recording is a widely used method for documenting infant and child behaviours in research and clinical practice. Video data has rarely been shared due to ethical concerns of confidentiality, although the need of shared large-scaled datasets remains increasing. This demand is even more imperative when data-driven computer-based approaches are involved, such as screening tools to complement clinical assessments. To share data while abiding by privacy protection rules, a critical question arises whether efforts at data de-identification reduce data utility? We addressed this question by showcasing the Prechtl's general movements assessment (GMA), an established and globally practised video-based diagnostic tool in early infancy for detecting neurological deficits, such as cerebral palsy. To date, no shared expert-annotated large data repositories for infant movement analyses exist. Such datasets would massively benefit training and recalibration of human assessors and the development of computer-based approaches. In the current study, sequences from a prospective longitudinal infant cohort with a total of 19451 available general movements video snippets were randomly selected for human clinical reasoning and computer-based analysis. We demonstrated for the first time that pseudonymisation by face-blurring video recordings is a viable approach. The video redaction did not affect classification accuracy for either human assessors or computer vision methods, suggesting an adequate and easy-to-apply solution for sharing movement video data. We call for further explorations into efficient and privacy rule-conforming approaches for deidentifying video data in scientific and clinical fields beyond movement assessments. These approaches shall enable sharing and merging stand-alone video datasets into large data pools to advance science and public health.
Nonlinear functional mapping of the human brain
Sep 08, 2015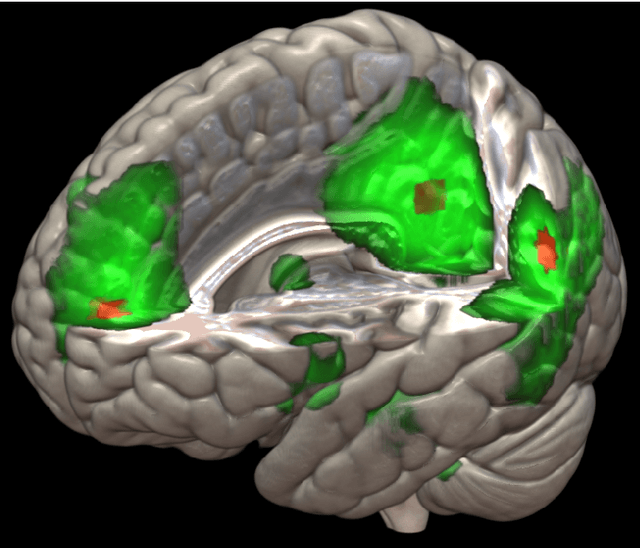
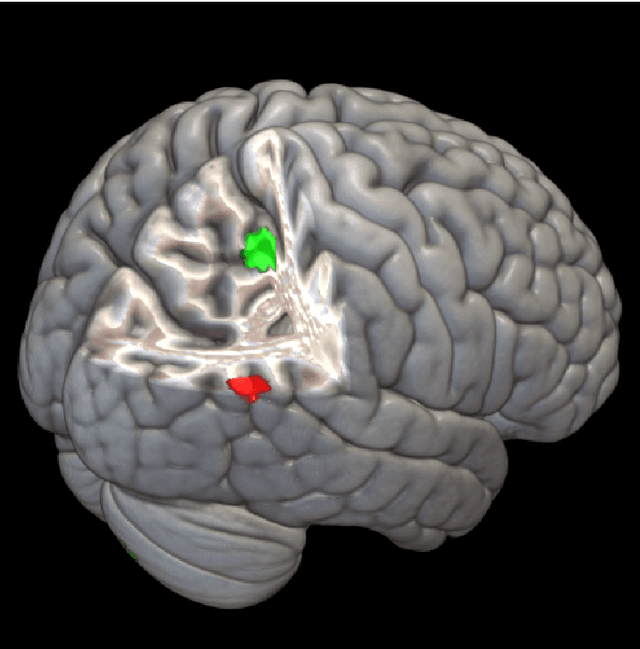
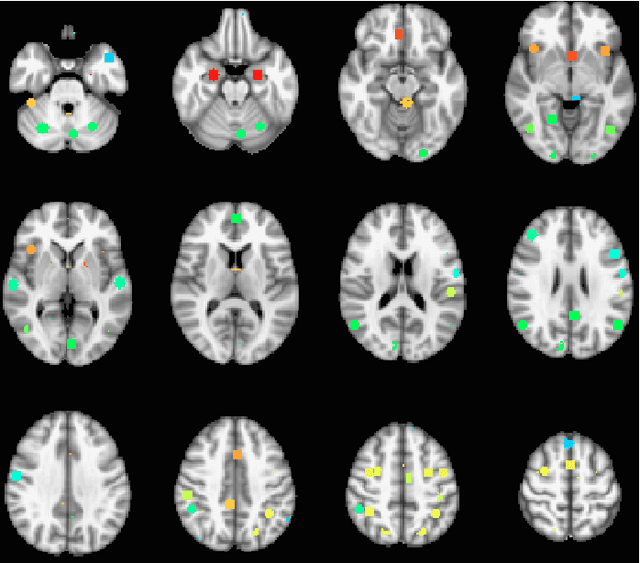
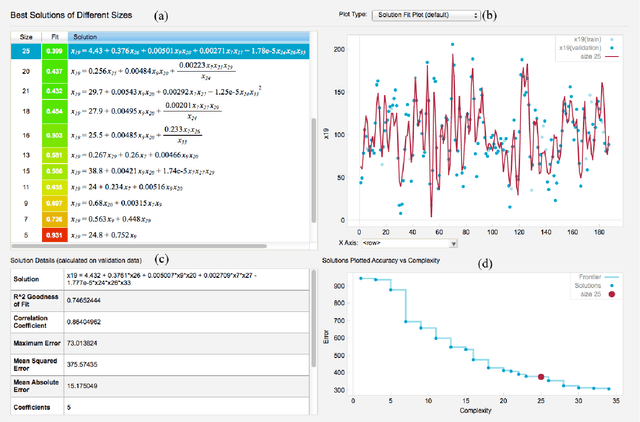
Abstract:The field of neuroimaging has truly become data rich, and novel analytical methods capable of gleaning meaningful information from large stores of imaging data are in high demand. Those methods that might also be applicable on the level of individual subjects, and thus potentially useful clinically, are of special interest. In the present study, we introduce just such a method, called nonlinear functional mapping (NFM), and demonstrate its application in the analysis of resting state fMRI from a 242-subject subset of the IMAGEN project, a European study of adolescents that includes longitudinal phenotypic, behavioral, genetic, and neuroimaging data. NFM employs a computational technique inspired by biological evolution to discover and mathematically characterize interactions among ROI (regions of interest), without making linear or univariate assumptions. We show that statistics of the resulting interaction relationships comport with recent independent work, constituting a preliminary cross-validation. Furthermore, nonlinear terms are ubiquitous in the models generated by NFM, suggesting that some of the interactions characterized here are not discoverable by standard linear methods of analysis. We discuss one such nonlinear interaction in the context of a direct comparison with a procedure involving pairwise correlation, designed to be an analogous linear version of functional mapping. We find another such interaction that suggests a novel distinction in brain function between drinking and non-drinking adolescents: a tighter coupling of ROI associated with emotion, reward, and interoceptive processes such as thirst, among drinkers. Finally, we outline many improvements and extensions of the methodology to reduce computational expense, complement other analytical tools like graph-theoretic analysis, and allow for voxel level NFM to eliminate the necessity of ROI selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge