Luca La Fisca
User Preferences for Large Language Model versus Template-Based Explanations of Movie Recommendations: A Pilot Study
Sep 10, 2024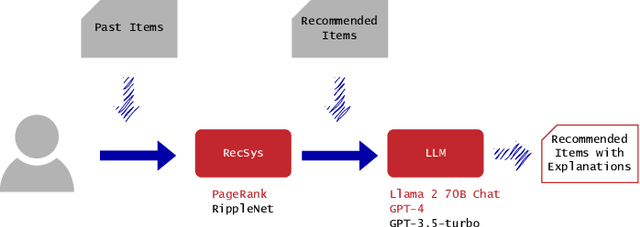
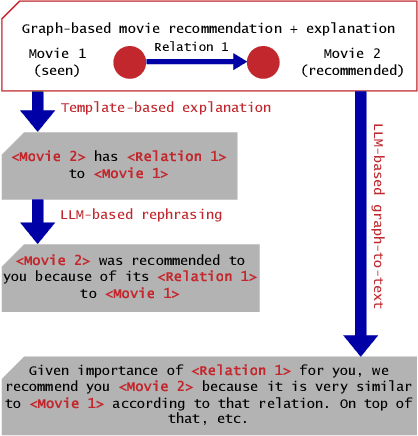

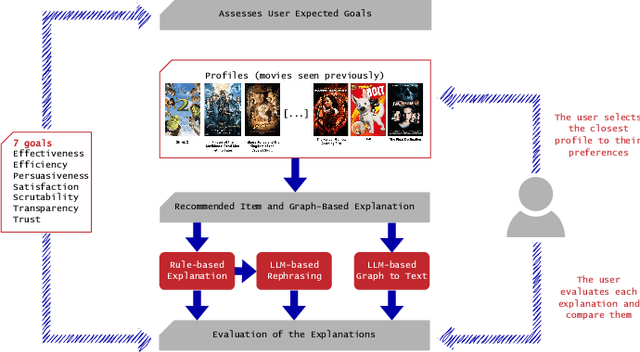
Abstract:Recommender systems have become integral to our digital experiences, from online shopping to streaming platforms. Still, the rationale behind their suggestions often remains opaque to users. While some systems employ a graph-based approach, offering inherent explainability through paths associating recommended items and seed items, non-experts could not easily understand these explanations. A popular alternative is to convert graph-based explanations into textual ones using a template and an algorithm, which we denote here as ''template-based'' explanations. Yet, these can sometimes come across as impersonal or uninspiring. A novel method would be to employ large language models (LLMs) for this purpose, which we denote as ''LLM-based''. To assess the effectiveness of LLMs in generating more resonant explanations, we conducted a pilot study with 25 participants. They were presented with three explanations: (1) traditional template-based, (2) LLM-based rephrasing of the template output, and (3) purely LLM-based explanations derived from the graph-based explanations. Although subject to high variance, preliminary findings suggest that LLM-based explanations may provide a richer and more engaging user experience, further aligning with user expectations. This study sheds light on the potential limitations of current explanation methods and offers promising directions for leveraging large language models to improve user satisfaction and trust in recommender systems.
Where Is My Mind ? Predicting Visual Attention from Brain Activity
Jan 11, 2022



Abstract:Visual attention estimation is an active field of research at the crossroads of different disciplines: computer vision, artificial intelligence and medicine. One of the most common approaches to estimate a saliency map representing attention is based on the observed images. In this paper, we show that visual attention can be retrieved from EEG acquisition. The results are comparable to traditional predictions from observed images, which is of great interest. For this purpose, a set of signals has been recorded and different models have been developed to study the relationship between visual attention and brain activity. The results are encouraging and comparable with other approaches estimating attention with other modalities. The codes and dataset considered in this paper have been made available at \url{https://figshare.com/s/3e353bd1c621962888ad} to promote research in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge