Longsheng Wei
Multimodal Image Matching based on Frequency-domain Information of Local Energy Response
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Complicated nonlinear intensity differences, nonlinear local geometric distortions, noises and rotation transformation are main challenges in multimodal image matching. In order to solve these problems, we propose a method based on Frequency-domain Information of Local Energy Response called FILER. The core of FILER is the local energy response model based on frequency-domain information, which can overcome the effect of nonlinear intensity differences. To improve the robustness to local nonlinear geometric distortions and noises, we design a new edge structure enhanced feature detector and convolutional feature weighted descriptor, respectively. In addition, FILER overcomes the sensitivity of the frequency-domain information to the rotation angle and achieves rotation invariance. Extensive experiments multimodal image pairs show that FILER outperforms other state-of-the-art algorithms and has good robustness and universality.
Learning Scene-specific Object Detectors Based on a Generative-Discriminative Model with Minimal Supervision
Mar 13, 2018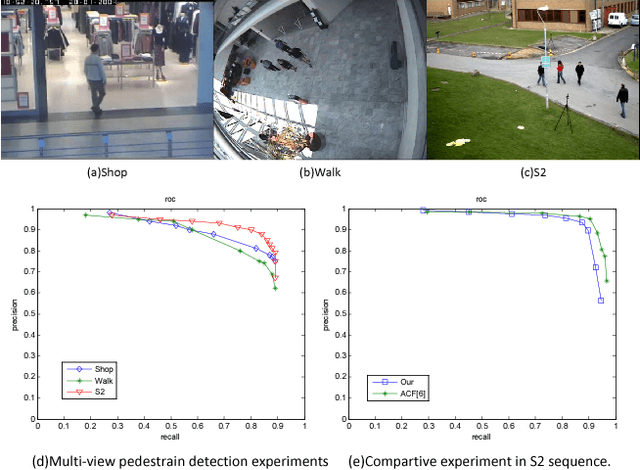
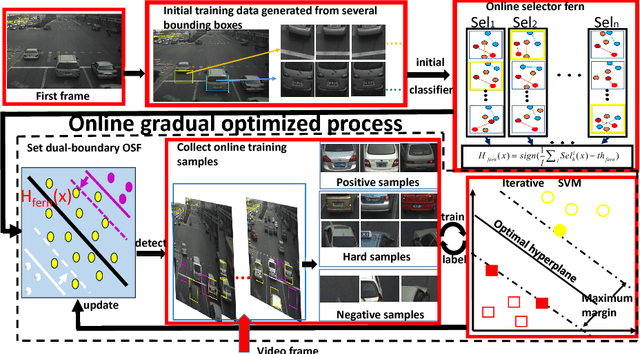
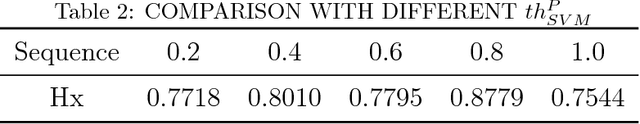
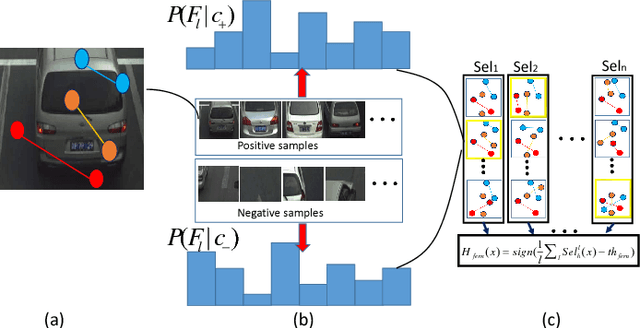
Abstract:One object class may show large variations due to diverse illuminations, backgrounds and camera viewpoints. Traditional object detection methods often perform worse under unconstrained video environments. To address this problem, many modern approaches model deep hierarchical appearance representations for object detection. Most of these methods require a timeconsuming training process on large manual labelling sample set. In this paper, the proposed framework takes a remarkably different direction to resolve the multi-scene detection problem in a bottom-up fashion. First, a scene-specific objector is obtained from a fully autonomous learning process triggered by marking several bounding boxes around the object in the first video frame via a mouse. Here the human labeled training data or a generic detector are not needed. Second, this learning process is conveniently replicated many times in different surveillance scenes and results in particular detectors under various camera viewpoints. Thus, the proposed framework can be employed in multi-scene object detection applications with minimal supervision. Obviously, the initial scene-specific detector, initialized by several bounding boxes, exhibits poor detection performance and is difficult to improve with traditional online learning algorithm. Consequently, we propose Generative-Discriminative model to partition detection response space and assign each partition an individual descriptor that progressively achieves high classification accuracy. A novel online gradual optimized process is proposed to optimize the Generative-Discriminative model and focus on the hard samples.Experimental results on six video datasets show our approach achieves comparable performance to robust supervised methods, and outperforms the state of the art self-learning methods under varying imaging conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge