Longbin Li
Multi-Behavior Sequential Modeling with Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network for E-Commerce Recommendation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:User interactions on e-commerce platforms are inherently diverse, involving behaviors such as clicking, favoriting, adding to cart, and purchasing. The transitions between these behaviors offer valuable insights into user-item interactions, serving as a key signal for un- derstanding evolving preferences. Consequently, there is growing interest in leveraging multi-behavior data to better capture user intent. Recent studies have explored sequential modeling of multi- behavior data, many relying on transformer-based architectures with polynomial time complexity. While effective, these approaches often incur high computational costs, limiting their applicability in large-scale industrial systems with long user sequences. To address this challenge, we propose the Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network (TGA), a linear-complexity approach for modeling multi-behavior transitions. Unlike traditional trans- formers that treat all behavior pairs equally, TGA constructs a structured sparse graph by identifying informative transitions from three perspectives: (a) item-level transitions, (b) category-level transitions, and (c) neighbor-level transitions. Built upon the structured graph, TGA employs a transition-aware graph Attention mechanism that jointly models user-item interactions and behav- ior transition types, enabling more accurate capture of sequential patterns while maintaining computational efficiency. Experiments show that TGA outperforms all state-of-the-art models while sig- nificantly reducing computational cost. Notably, TGA has been deployed in a large-scale industrial production environment, where it leads to impressive improvements in key business metrics.
ReaSeq: Unleashing World Knowledge via Reasoning for Sequential Modeling
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Industrial recommender systems face two fundamental limitations under the log-driven paradigm: (1) knowledge poverty in ID-based item representations that causes brittle interest modeling under data sparsity, and (2) systemic blindness to beyond-log user interests that constrains model performance within platform boundaries. These limitations stem from an over-reliance on shallow interaction statistics and close-looped feedback while neglecting the rich world knowledge about product semantics and cross-domain behavioral patterns that Large Language Models have learned from vast corpora. To address these challenges, we introduce ReaSeq, a reasoning-enhanced framework that leverages world knowledge in Large Language Models to address both limitations through explicit and implicit reasoning. Specifically, ReaSeq employs explicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning via multi-agent collaboration to distill structured product knowledge into semantically enriched item representations, and latent reasoning via Diffusion Large Language Models to infer plausible beyond-log behaviors. Deployed on Taobao's ranking system serving hundreds of millions of users, ReaSeq achieves substantial gains: >6.0% in IPV and CTR, >2.9% in Orders, and >2.5% in GMV, validating the effectiveness of world-knowledge-enhanced reasoning over purely log-driven approaches.
RecGPT Technical Report
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems are among the most impactful applications of artificial intelligence, serving as critical infrastructure connecting users, merchants, and platforms. However, most current industrial systems remain heavily reliant on historical co-occurrence patterns and log-fitting objectives, i.e., optimizing for past user interactions without explicitly modeling user intent. This log-fitting approach often leads to overfitting to narrow historical preferences, failing to capture users' evolving and latent interests. As a result, it reinforces filter bubbles and long-tail phenomena, ultimately harming user experience and threatening the sustainability of the whole recommendation ecosystem. To address these challenges, we rethink the overall design paradigm of recommender systems and propose RecGPT, a next-generation framework that places user intent at the center of the recommendation pipeline. By integrating large language models (LLMs) into key stages of user interest mining, item retrieval, and explanation generation, RecGPT transforms log-fitting recommendation into an intent-centric process. To effectively align general-purpose LLMs to the above domain-specific recommendation tasks at scale, RecGPT incorporates a multi-stage training paradigm, which integrates reasoning-enhanced pre-alignment and self-training evolution, guided by a Human-LLM cooperative judge system. Currently, RecGPT has been fully deployed on the Taobao App. Online experiments demonstrate that RecGPT achieves consistent performance gains across stakeholders: users benefit from increased content diversity and satisfaction, merchants and the platform gain greater exposure and conversions. These comprehensive improvement results across all stakeholders validates that LLM-driven, intent-centric design can foster a more sustainable and mutually beneficial recommendation ecosystem.
Simple but Efficient: A Multi-Scenario Nearline Retrieval Framework for Recommendation on Taobao
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:In recommendation systems, the matching stage is becoming increasingly critical, serving as the upper limit for the entire recommendation process. Recently, some studies have started to explore the use of multi-scenario information for recommendations, such as model-based and data-based approaches. However, the matching stage faces significant challenges due to the need for ultra-large-scale retrieval and meeting low latency requirements. As a result, the methods applied at this stage (collaborative filtering and two-tower models) are often designed to be lightweight, hindering the full utilization of extensive information. On the other hand, the ranking stage features the most sophisticated models with the strongest scoring capabilities, but due to the limited screen size of mobile devices, most of the ranked results may not gain exposure or be displayed. In this paper, we introduce an innovative multi-scenario nearline retrieval framework. It operates by harnessing ranking logs from various scenarios through Flink, allowing us to incorporate finely ranked results from other scenarios into our matching stage in near real-time. Besides, we propose a streaming scoring module, which selects a crucial subset from the candidate pool. Implemented on the "Guess You Like" (homepage of the Taobao APP), China's premier e-commerce platform, our method has shown substantial improvements-most notably, a 5% uptick in product transactions. Furthermore, the proposed approach is not only model-free but also highly efficient, suggesting it can be quickly implemented in diverse scenarios and demonstrate promising performance.
Graph Contrastive Learning with Multi-Objective for Personalized Product Retrieval in Taobao Search
Jul 10, 2023Abstract:In e-commerce search, personalized retrieval is a crucial technique for improving user shopping experience. Recent works in this domain have achieved significant improvements by the representation learning paradigm, e.g., embedding-based retrieval (EBR) and collaborative filtering (CF). EBR methods do not sufficiently exploit the useful collaborative signal and are difficult to learn the representations of long-tail item well. Graph-based CF methods improve personalization by modeling collaborative signal within the user click graph. However, existing Graph-based methods ignore user's multiple behaviours, such as click/purchase and the relevance constraint between user behaviours and items.In this paper, we propose a Graph Contrastive Learning with Multi-Objective (GCL-MO) collaborative filtering model, which solves the problems of weak relevance and incomplete personalization in e-commerce search. Specifically, GCL-MO builds a homogeneous graph of items and then optimizes a multi-objective function of personalization and relevance. Moreover, we propose a modified contrastive loss for multi-objectives graph learning, which avoids the mutual suppression among positive samples and thus improves the generalization and robustness of long-tail item representations. These learned item embeddings are then used for personalized retrieval by constructing an efficient offline-to-online inverted table. GCL-MO outperforms the online collaborative filtering baseline in both offline/online experimental metrics and shows a significant improvement in the online A/B testing of Taobao search.
Rethinking the Role of Pre-ranking in Large-scale E-Commerce Searching System
May 23, 2023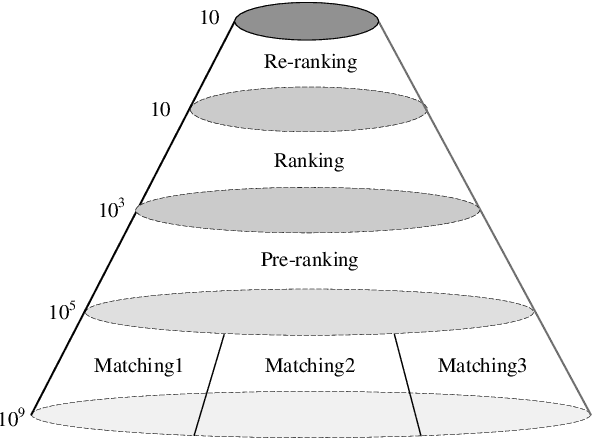
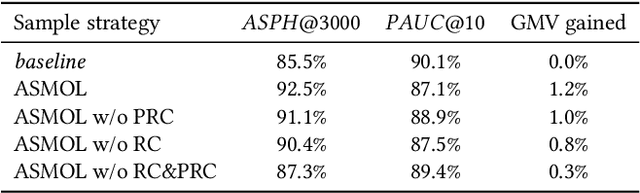
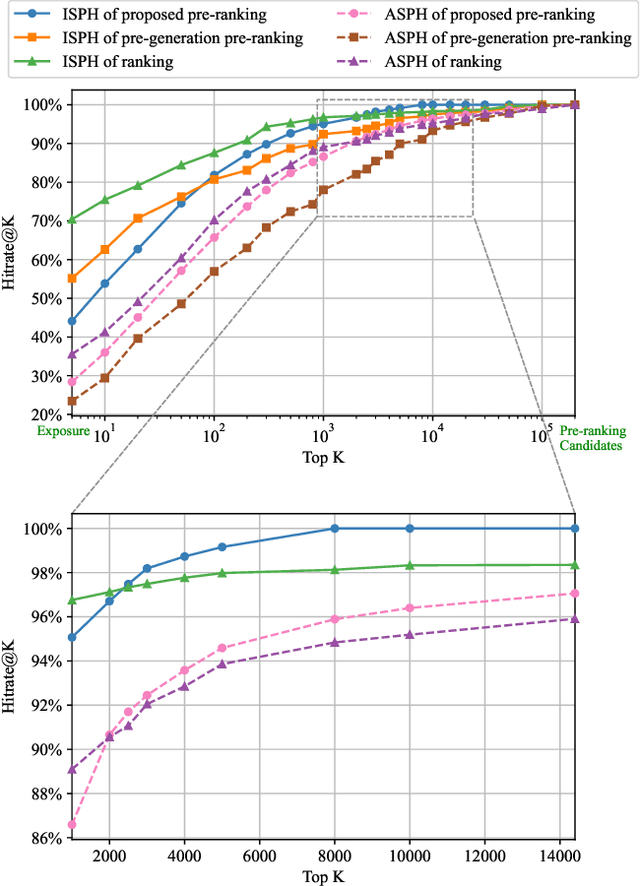
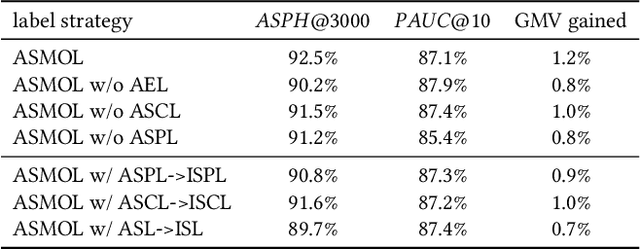
Abstract:E-commerce search systems such as Taobao Search, the largest e-commerce searching system in China, aim at providing users with the most preferred items (e.g., products). Due to the massive data and limited time for response, a typical industrial ranking system consists of three or more modules, including matching, pre-ranking, and ranking. The pre-ranking is widely considered a mini-ranking module, as it needs to rank hundreds of times more items than the ranking under limited latency. Existing researches focus on building a lighter model that imitates the ranking model. As such, the metric of a pre-ranking model follows the ranking model using Area Under ROC (AUC) for offline evaluation. However, such a metric is inconsistent with online A/B tests in practice, so engineers have to perform costly online tests to reach a convincing conclusion. In our work, we rethink the role of the pre-ranking. We argue that the primary goal of the pre-ranking stage is to return an optimal unordered set rather than an ordered list of items because it is the ranking that determines the final exposures. Since AUC measures the quality of an ordered item list, it is not suitable for evaluating the quality of the output unordered set. This paper proposes a new evaluation metric called All-Scenario Hitrate (ASH) for pre-ranking. ASH is proven effective in the offline evaluation and consistent with online A/B tests based on numerous experiments in Taobao Search. We also introduce an all-scenario-based multi-objective learning framework (ASMOL), which improves the ASH significantly. Surprisingly, the new pre-ranking model can outperforms the ranking model when outputting thousands of items. The phenomenon validates that the pre-ranking stage should not imitate the ranking blindly. With the improvements in ASH consistently translating to online improvement, it makes a 1.2% GMV improvement on Taobao Search.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge