Liyi Xiao
Learning Reinforced Attentional Representation for End-to-End Visual Tracking
Aug 28, 2019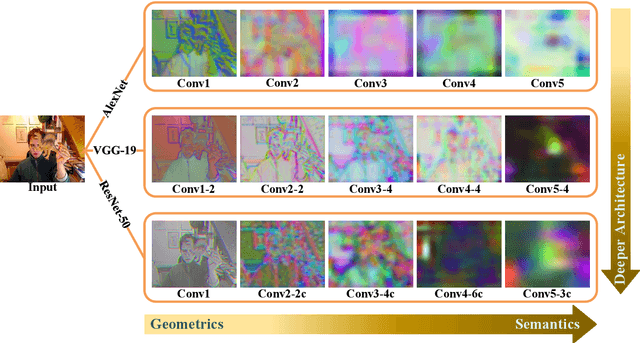
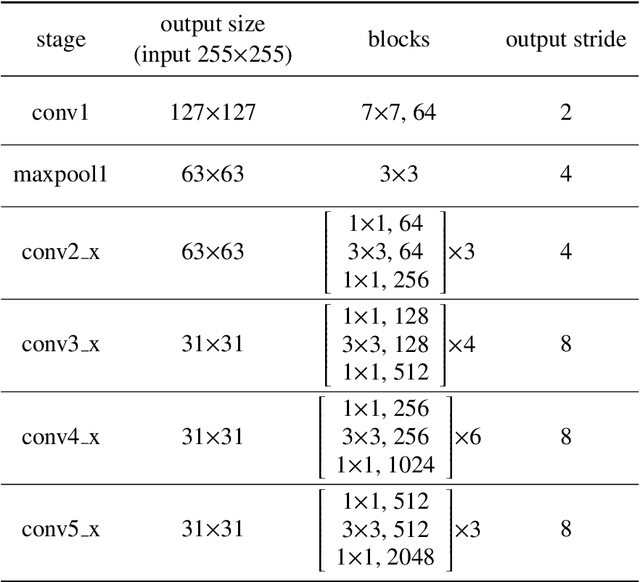
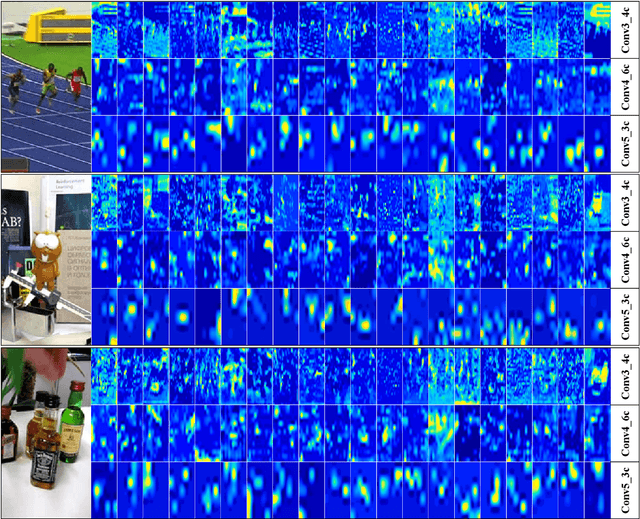
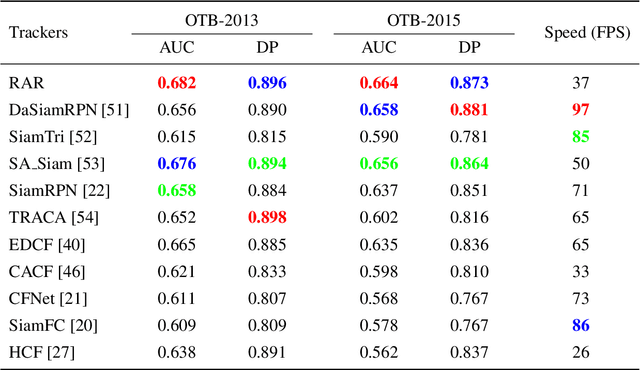
Abstract:Despite the fact that tremendous advances have been made by numerous recent tracking approaches in the last decade, how to achieve high-performance visual tracking is still an open problem. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end network model to learn reinforced attentional representation for accurate target object discrimination and localization. We utilize a novel hierarchical attentional module with long short-term memory and multi-layer perceptrons to leverage both inter- and intra-frame attention to effectively facilitate visual pattern emphasis. Moreover, we incorporate a contextual attentional correlation filter into the backbone network to make our model be trained in an end-to-end fashion. Our proposed approach not only takes full advantage of informative geometries and semantics, but also updates correlation filters online without the backbone network fine-tuning to enable adaptation of target appearance variations. Extensive experiments conducted on several popular benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed approach while remaining computational efficiency.
Learning Cascaded Siamese Networks for High Performance Visual Tracking
May 08, 2019



Abstract:Visual tracking is one of the most challenging computer vision problems. In order to achieve high performance visual tracking in various negative scenarios, a novel cascaded Siamese network is proposed and developed based on two different deep learning networks: a matching subnetwork and a classification subnetwork. The matching subnetwork is a fully convolutional Siamese network. According to the similarity score between the exemplar image and the candidate image, it aims to search possible object positions and crop scaled candidate patches. The classification subnetwork is designed to further evaluate the cropped candidate patches and determine the optimal tracking results based on the classification score. The matching subnetwork is trained offline and fixed online, while the classification subnetwork performs stochastic gradient descent online to learn more target-specific information. To improve the tracking performance further, an effective classification subnetwork update method based on both similarity and classification scores is utilized for updating the classification subnetwork. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in recent benchmarks.
Siamese Attentional Keypoint Network for High Performance Visual Tracking
Apr 23, 2019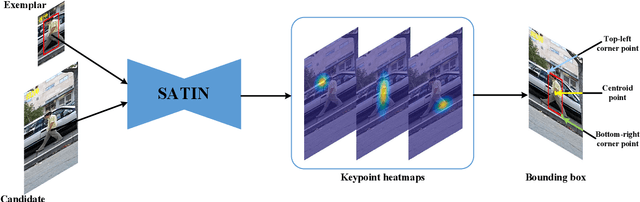
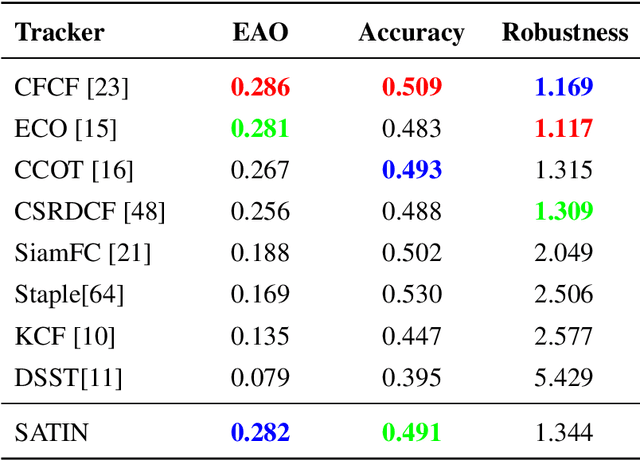
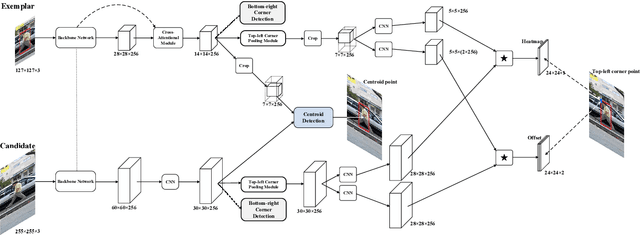
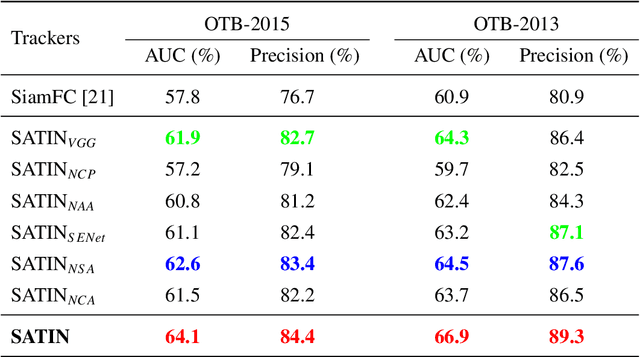
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate impacts of three main aspects of visual tracking, i.e., the backbone network, the attentional mechanism and the detection component, and propose a Siamese Attentional Keypoint Network, dubbed SATIN, to achieve efficient tracking and accurate localization. Firstly, a new Siamese lightweight hourglass network is specifically designed for visual tracking. It takes advantage of the benefits of the repeated bottom-up and top-down inference to capture more global and local contextual information at multiple scales. Secondly, a novel cross-attentional module is utilized to leverage both channel-wise and spatial intermediate attentional information, which enhance both discriminative and localization capabilities of feature maps. Thirdly, a keypoints detection approach is invented to track any target object by detecting the top-left corner point, the centroid point and the bottom-right corner point of its bounding box. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to propose this approach. Therefore, our SATIN tracker not only has a strong capability to learn more effective object representations, but also computational and memory storage efficiency, either during the training or testing stage. Without bells and whistles, experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on several recent benchmark datasets, at speeds far exceeding the frame-rate requirement.
High Performance Visual Tracking with Circular and Structural Operators
Oct 13, 2018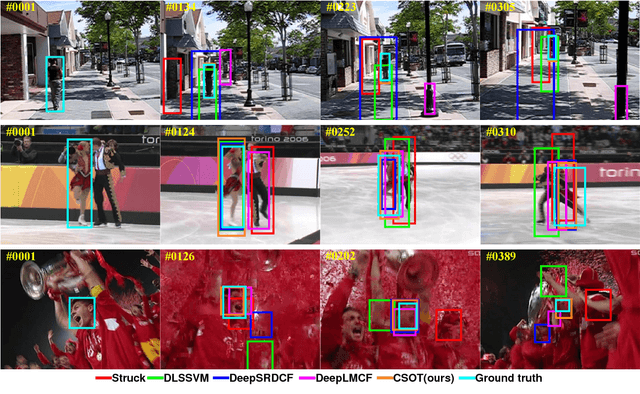
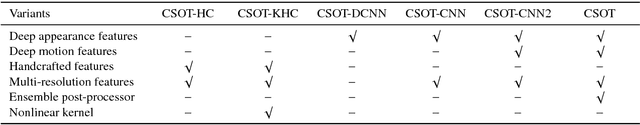
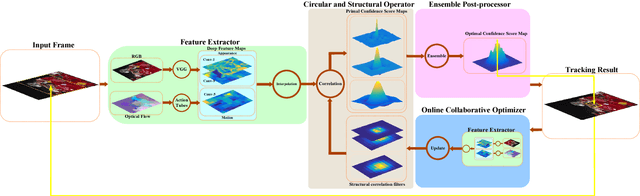

Abstract:In this paper, a novel circular and structural operator tracker (CSOT) is proposed for high performance visual tracking, it not only possesses the powerful discriminative capability of SOSVM but also efficiently inherits the superior computational efficiency of DCF. Based on the proposed circular and structural operators, a set of primal confidence score maps can be obtained by circular correlating feature maps with their corresponding structural correlation filters. Furthermore, an implicit interpolation is applied to convert the multi-resolution feature maps to the continuous domain and make all primal confidence score maps have the same spatial resolution. Then, we exploit an efficient ensemble post-processor based on relative entropy, which can coalesce primal confidence score maps and create an optimal confidence score map for more accurate localization. The target is localized on the peak of the optimal confidence score map. Besides, we introduce a collaborative optimization strategy to update circular and structural operators by iteratively training structural correlation filters, which significantly reduces computational complexity and improves robustness. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in mean AUC scores of 71.5% and 69.4% on the OTB-2013 and OTB-2015 benchmarks respectively, and obtains a third-best expected average overlap (EAO) score of 29.8% on the VOT-2017 benchmark.
A Complementary Tracking Model with Multiple Features
Jul 19, 2018Abstract:Discriminative Correlation Filters based tracking algorithms exploiting conventional handcrafted features have achieved impressive results both in terms of accuracy and robustness. Template handcrafted features have shown excellent performance, but they perform poorly when the appearance of target changes rapidly such as fast motions and fast deformations. In contrast, statistical handcrafted features are insensitive to fast states changes, but they yield inferior performance in the scenarios of illumination variations and background clutters. In this work, to achieve an efficient tracking performance, we propose a novel visual tracking algorithm, named MFCMT, based on a complementary ensemble model with multiple features, including Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOGs), Color Names (CNs) and Color Histograms (CHs). Additionally, to improve tracking results and prevent targets drift, we introduce an effective fusion method by exploiting relative entropy to coalesce all basic response maps and get an optimal response. Furthermore, we suggest a simple but efficient update strategy to boost tracking performance. Comprehensive evaluations are conducted on two tracking benchmarks demonstrate and the experimental results demonstrate that our method is competitive with numerous state-of-the-art trackers. Our tracker achieves impressive performance with faster speed on these benchmarks.
Large Margin Structured Convolution Operator for Thermal Infrared Object Tracking
Jul 19, 2018



Abstract:Compared with visible object tracking, thermal infrared (TIR) object tracking can track an arbitrary target in total darkness since it cannot be influenced by illumination variations. However, there are many unwanted attributes that constrain the potentials of TIR tracking, such as the absence of visual color patterns and low resolutions. Recently, structured output support vector machine (SOSVM) and discriminative correlation filter (DCF) have been successfully applied to visible object tracking, respectively. Motivated by these, in this paper, we propose a large margin structured convolution operator (LMSCO) to achieve efficient TIR object tracking. To improve the tracking performance, we employ the spatial regularization and implicit interpolation to obtain continuous deep feature maps, including deep appearance features and deep motion features, of the TIR targets. Finally, a collaborative optimization strategy is exploited to significantly update the operators. Our approach not only inherits the advantage of the strong discriminative capability of SOSVM but also achieves accurate and robust tracking with higher-dimensional features and more dense samples. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to incorporate the advantages of DCF and SOSVM for TIR object tracking. Comprehensive evaluations on two thermal infrared tracking benchmarks, i.e. VOT-TIR2015 and VOT-TIR2016, clearly demonstrate that our LMSCO tracker achieves impressive results and outperforms most state-of-the-art trackers in terms of accuracy and robustness with sufficient frame rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge