Liping Lu
ARTEMIS: Autoregressive End-to-End Trajectory Planning with Mixture of Experts for Autonomous Driving
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:This paper presents ARTEMIS, an end-to-end autonomous driving framework that combines autoregressive trajectory planning with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE). Traditional modular methods suffer from error propagation, while existing end-to-end models typically employ static one-shot inference paradigms that inadequately capture the dynamic changes of the environment. ARTEMIS takes a different method by generating trajectory waypoints sequentially, preserves critical temporal dependencies while dynamically routing scene-specific queries to specialized expert networks. It effectively relieves trajectory quality degradation issues encountered when guidance information is ambiguous, and overcomes the inherent representational limitations of singular network architectures when processing diverse driving scenarios. Additionally, we use a lightweight batch reallocation strategy that significantly improves the training speed of the Mixture-of-Experts model. Through experiments on the NAVSIM dataset, ARTEMIS exhibits superior competitive performance, achieving 87.0 PDMS and 83.1 EPDMS with ResNet-34 backbone, demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on multiple metrics.
CHARMS: Cognitive Hierarchical Agent with Reasoning and Motion Styles
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:To address the current challenges of low intelligence and simplistic vehicle behavior modeling in autonomous driving simulation scenarios, this paper proposes the Cognitive Hierarchical Agent with Reasoning and Motion Styles (CHARMS). The model can reason about the behavior of other vehicles like a human driver and respond with different decision-making styles, thereby improving the intelligence and diversity of the surrounding vehicles in the driving scenario. By introducing the Level-k behavioral game theory, the paper models the decision-making process of human drivers and employs deep reinforcement learning to train the models with diverse decision styles, simulating different reasoning approaches and behavioral characteristics. Building on the Poisson cognitive hierarchy theory, this paper also presents a novel driving scenario generation method. The method controls the proportion of vehicles with different driving styles in the scenario using Poisson and binomial distributions, thus generating controllable and diverse driving environments. Experimental results demonstrate that CHARMS not only exhibits superior decision-making capabilities as ego vehicles, but also generates more complex and diverse driving scenarios as surrounding vehicles. We will release code for CHARMS at https://github.com/WUTAD-Wjy/CHARMS.
CLIP-SENet: CLIP-based Semantic Enhancement Network for Vehicle Re-identification
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Vehicle re-identification (Re-ID) is a crucial task in intelligent transportation systems (ITS), aimed at retrieving and matching the same vehicle across different surveillance cameras. Numerous studies have explored methods to enhance vehicle Re-ID by focusing on semantic enhancement. However, these methods often rely on additional annotated information to enable models to extract effective semantic features, which brings many limitations. In this work, we propose a CLIP-based Semantic Enhancement Network (CLIP-SENet), an end-to-end framework designed to autonomously extract and refine vehicle semantic attributes, facilitating the generation of more robust semantic feature representations. Inspired by zero-shot solutions for downstream tasks presented by large-scale vision-language models, we leverage the powerful cross-modal descriptive capabilities of the CLIP image encoder to initially extract general semantic information. Instead of using a text encoder for semantic alignment, we design an adaptive fine-grained enhancement module (AFEM) to adaptively enhance this general semantic information at a fine-grained level to obtain robust semantic feature representations. These features are then fused with common Re-ID appearance features to further refine the distinctions between vehicles. Our comprehensive evaluation on three benchmark datasets demonstrates the effectiveness of CLIP-SENet. Our approach achieves new state-of-the-art performance, with 92.9% mAP and 98.7% Rank-1 on VeRi-776 dataset, 90.4% Rank-1 and 98.7% Rank-5 on VehicleID dataset, and 89.1% mAP and 97.9% Rank-1 on the more challenging VeRi-Wild dataset.
ConvoyLLM: Dynamic Multi-Lane Convoy Control Using LLMs
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a novel method for multi-lane convoy formation control that uses large language models (LLMs) to tackle coordination challenges in dynamic highway environments. Each connected and autonomous vehicle in the convoy uses a knowledge-driven approach to make real-time adaptive decisions based on various scenarios. Our method enables vehicles to dynamically perform tasks, including obstacle avoidance, convoy joining/leaving, and escort formation switching, all while maintaining the overall convoy structure. We design a Interlaced formation control strategy based on locally dynamic distributed graphs, ensuring the convoy remains stable and flexible. We conduct extensive experiments in the SUMO simulation platform across multiple traffic scenarios, and the results demonstrate that the proposed method is effective, robust, and adaptable to dynamic environments. The code is available at: https://github.com/chuduanfeng/ConvoyLLM.
EPN: An Ego Vehicle Planning-Informed Network for Target Trajectory Prediction
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Trajectory prediction plays a crucial role in improving the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles, serving as an intermediate link between perception and planning. However, due to the highly dynamic and multimodal nature of the task, accurately predicting the future trajectory of a target vehicle remains a significant challenge. To address these challenges, we propose an Ego vehicle Planning-informed Network (EPN) for multimodal trajectory prediction. Current trajectory prediction methods typically use the historical trajectory and vehicle attributes as inputs, focusing primarily on how historical information influences the future trajectory of the target vehicle. In real-world driving scenarios, however, the future trajectory of a vehicle is influenced not only by its own historical data but also by the behavior of other vehicles on the road. To address this, we incorporate the future planned trajectory of the ego vehicle as an additional input to simulate the mutual influence between the ego vehicle's planned trajectory and the predicted trajectory of the target vehicle. Furthermore, to tackle the challenges of intention ambiguity and large prediction errors often encountered in methods based on driving intentions, we propose a target's endpoint prediction module. This module first predicts the possible endpoints of the target vehicle, then refines these predictions through a correction mechanism, and finally generates a complete multimodal predicted trajectory based on the corrected endpoints. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to other trajectory prediction methods, EPN achieves an average reduction of 34.9%, 30.7%, and 30.4% in RMSE, ADE, and FDE evaluation metrics on the NGSIM dataset, and an average reduction of 64.6%, 64.5%, and 64.3% in RMSE, ADE, and FDE on the HighD dataset. These results highlight the strong performance of EPN in trajectory prediction.
Multi-Agent Trajectory Prediction with Difficulty-Guided Feature Enhancement Network
Jul 29, 2024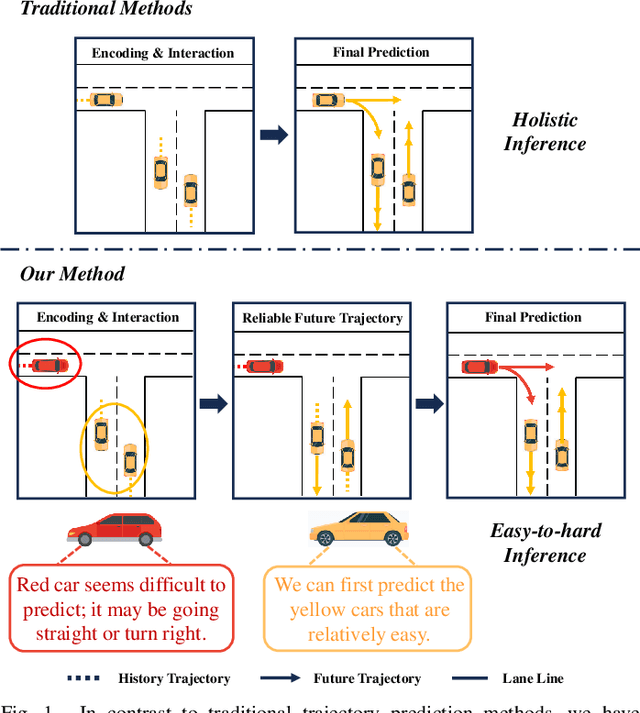
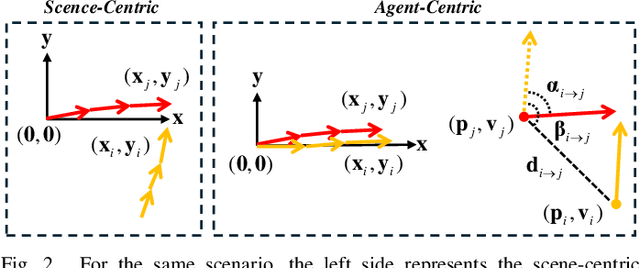
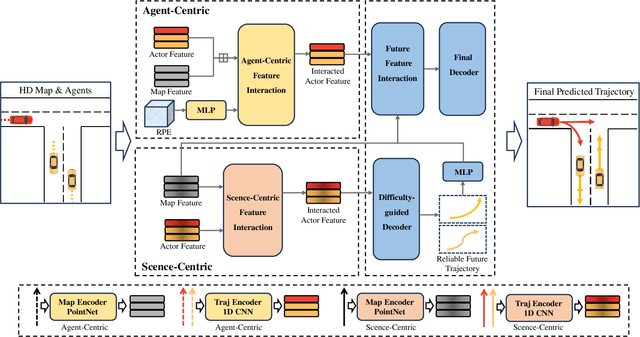
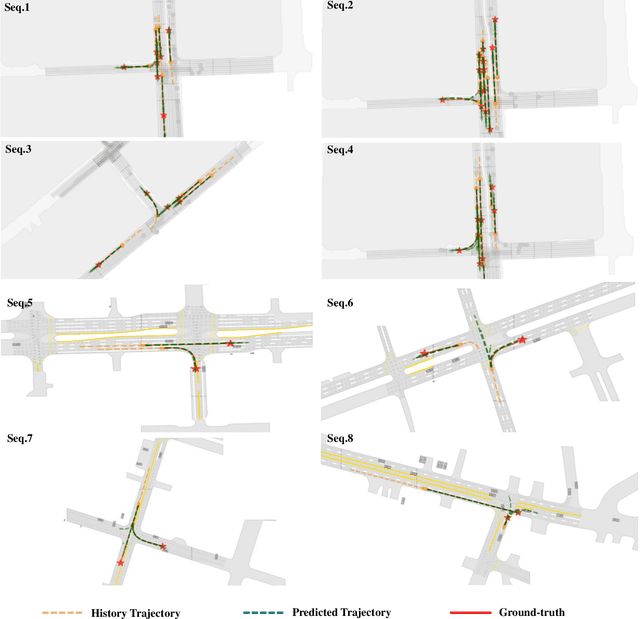
Abstract:Trajectory prediction is crucial for autonomous driving as it aims to forecast the future movements of traffic participants. Traditional methods usually perform holistic inference on the trajectories of agents, neglecting the differences in prediction difficulty among agents. This paper proposes a novel Difficulty-Guided Feature Enhancement Network (DGFNet), which leverages the prediction difficulty differences among agents for multi-agent trajectory prediction. Firstly, we employ spatio-temporal feature encoding and interaction to capture rich spatio-temporal features. Secondly, a difficulty-guided decoder is used to control the flow of future trajectories into subsequent modules, obtaining reliable future trajectories. Then, feature interaction and fusion are performed through the future feature interaction module. Finally, the fused agent features are fed into the final predictor to generate the predicted trajectory distributions for multiple participants. Experimental results demonstrate that our DGFNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Argoverse 1\&2 motion forecasting benchmarks. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of each module. Moreover, compared with SOTA methods, our method balances trajectory prediction accuracy and real-time inference speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge