Linyan Yang
Attr-Int: A Simple and Effective Entity Alignment Framework for Heterogeneous Knowledge Graphs
Oct 17, 2024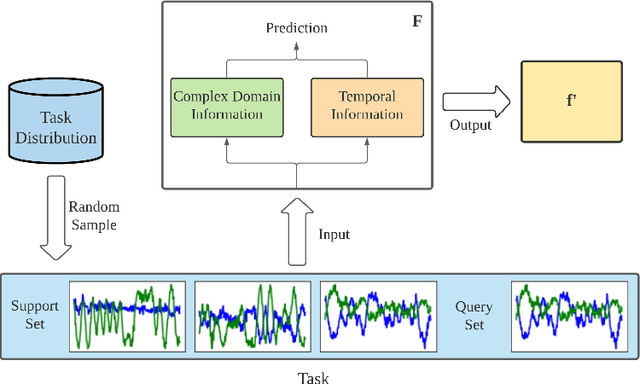
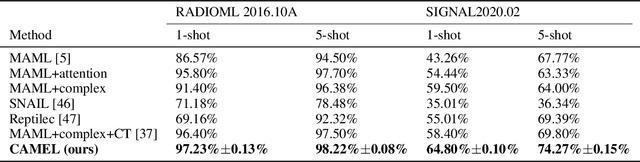

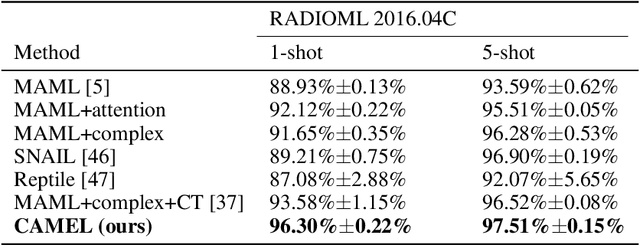
Abstract:Entity alignment (EA) refers to the task of linking entities in different knowledge graphs (KGs). Existing EA methods rely heavily on structural isomorphism. However, in real-world KGs, aligned entities usually have non-isomorphic neighborhood structures, which paralyses the application of these structure-dependent methods. In this paper, we investigate and tackle the problem of entity alignment between heterogeneous KGs. First, we propose two new benchmarks to closely simulate real-world EA scenarios of heterogeneity. Then we conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the performance of representative EA methods on the new benchmarks. Finally, we propose a simple and effective entity alignment framework called Attr-Int, in which innovative attribute information interaction methods can be seamlessly integrated with any embedding encoder for entity alignment, improving the performance of existing entity alignment techniques. Experiments demonstrate that our framework outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on two new benchmarks.
MICDrop: Masking Image and Depth Features via Complementary Dropout for Domain-Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Aug 29, 2024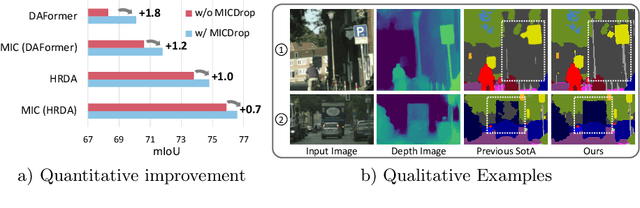
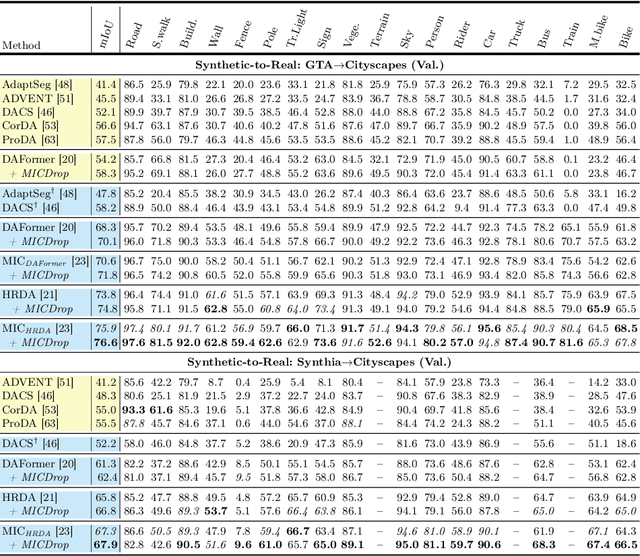
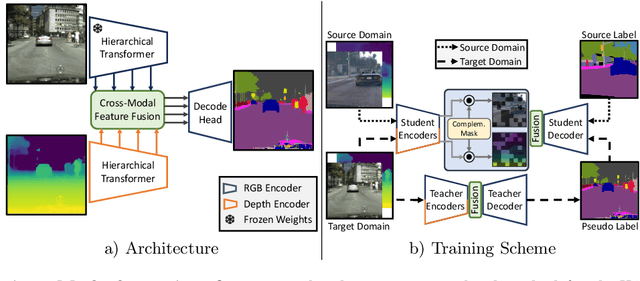

Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is the task of bridging the domain gap between a labeled source domain, e.g., synthetic data, and an unlabeled target domain. We observe that current UDA methods show inferior results on fine structures and tend to oversegment objects with ambiguous appearance. To address these shortcomings, we propose to leverage geometric information, i.e., depth predictions, as depth discontinuities often coincide with segmentation boundaries. We show that naively incorporating depth into current UDA methods does not fully exploit the potential of this complementary information. To this end, we present MICDrop, which learns a joint feature representation by masking image encoder features while inversely masking depth encoder features. With this simple yet effective complementary masking strategy, we enforce the use of both modalities when learning the joint feature representation. To aid this process, we propose a feature fusion module to improve both global as well as local information sharing while being robust to errors in the depth predictions. We show that our method can be plugged into various recent UDA methods and consistently improve results across standard UDA benchmarks, obtaining new state-of-the-art performances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge