Linghao Han
Underwater Ranker: Learn Which Is Better and How to Be Better
Aug 14, 2022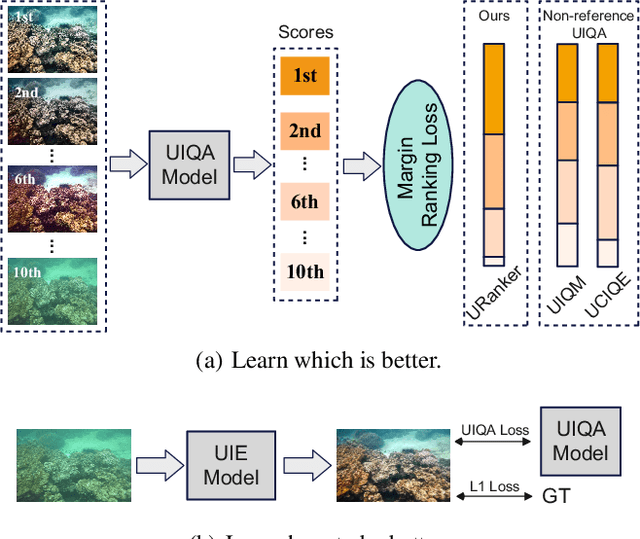
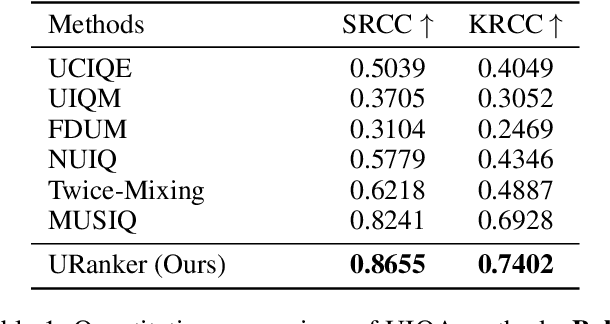

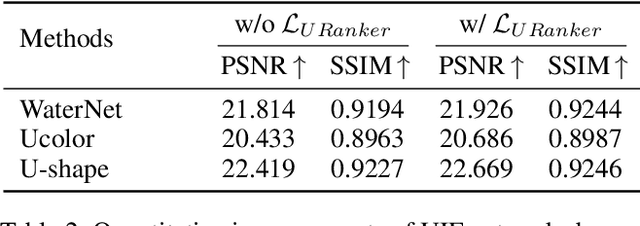
Abstract:In this paper, we present a ranking-based underwater image quality assessment (UIQA) method, abbreviated as URanker. The URanker is built on the efficient conv-attentional image Transformer. In terms of underwater images, we specially devise (1) the histogram prior that embeds the color distribution of an underwater image as histogram token to attend global degradation and (2) the dynamic cross-scale correspondence to model local degradation. The final prediction depends on the class tokens from different scales, which comprehensively considers multi-scale dependencies. With the margin ranking loss, our URanker can accurately rank the order of underwater images of the same scene enhanced by different underwater image enhancement (UIE) algorithms according to their visual quality. To achieve that, we also contribute a dataset, URankerSet, containing sufficient results enhanced by different UIE algorithms and the corresponding perceptual rankings, to train our URanker. Apart from the good performance of URanker, we found that a simple U-shape UIE network can obtain promising performance when it is coupled with our pre-trained URanker as additional supervision. In addition, we also propose a normalization tail that can significantly improve the performance of UIE networks. Extensive experiments demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our method. The key designs of our method are discussed. We will release our dataset and code.
Lighting the Darkness in the Deep Learning Era
Apr 21, 2021



Abstract:Low-light image enhancement (LLIE) aims at improving the perception or interpretability of an image captured in an environment with poor illumination. Recent advances in this area are dominated by deep learning-based solutions, where many learning strategies, network structures, loss functions, training data, etc. have been employed. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive survey to cover various aspects ranging from algorithm taxonomy to unsolved open issues. To examine the generalization of existing methods, we propose a large-scale low-light image and video dataset, in which the images and videos are taken by different mobile phones' cameras under diverse illumination conditions. Besides, for the first time, we provide a unified online platform that covers many popular LLIE methods, of which the results can be produced through a user-friendly web interface. In addition to qualitative and quantitative evaluation of existing methods on publicly available and our proposed datasets, we also validate their performance in face detection in the dark. This survey together with the proposed dataset and online platform could serve as a reference source for future study and promote the development of this research field. The proposed platform and the collected methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics are publicly available and will be regularly updated at https://github.com/Li-Chongyi/Lighting-the-Darkness-in-the-Deep-Learning-Era-Open. We will release our low-light image and video dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge