Liguo Huang
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning on Software Engineering Tasks
Dec 25, 2023Abstract:Pre-trained models (PTMs) have achieved great success in various Software Engineering (SE) downstream tasks following the ``pre-train then fine-tune'' paradigm. As fully fine-tuning all parameters of PTMs can be computationally expensive, a widely used solution is parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), which freezes PTMs while introducing extra parameters. Though work has been done to test PEFT methods in the SE field, a comprehensive evaluation is still lacking. This paper aims to fill in this gap by evaluating the effectiveness of five PEFT methods on eight PTMs and four SE downstream tasks. For different tasks and PEFT methods, we seek answers to the following research questions: 1) Is it more effective to use PTMs trained specifically on source code, or is it sufficient to use PTMs trained on natural language text? 2) What is the impact of varying model sizes? 3) How does the model architecture affect the performance? Besides effectiveness, we also discuss the efficiency of PEFT methods, concerning the costs of required training time and GPU resource consumption. We hope that our findings can provide a deeper understanding of PEFT methods on various PTMs and SE downstream tasks. All the codes and data are available at \url{https://github.com/zwtnju/PEFT.git}.
Synergy between Machine/Deep Learning and Software Engineering: How Far Are We?
Aug 12, 2020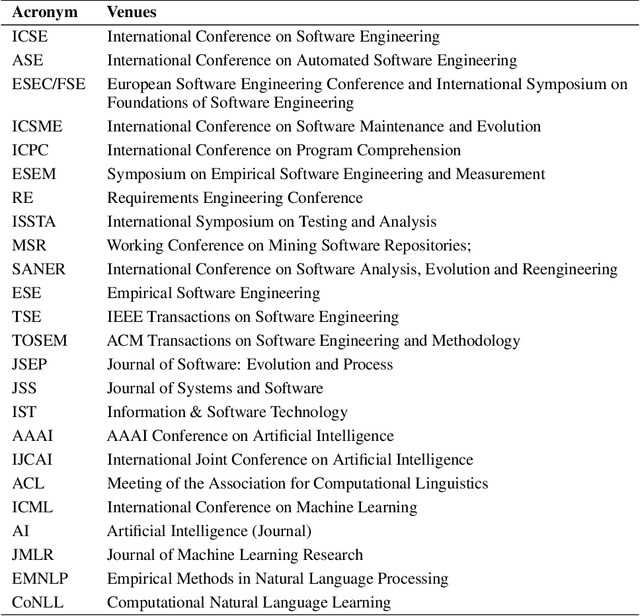

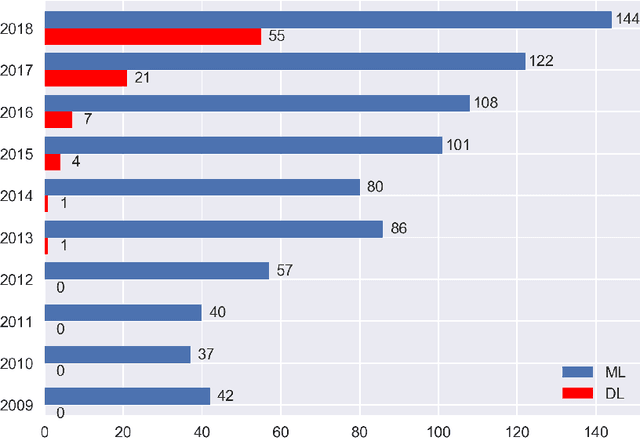
Abstract:Since 2009, the deep learning revolution, which was triggered by the introduction of ImageNet, has stimulated the synergy between Machine Learning (ML)/Deep Learning (DL) and Software Engineering (SE). Meanwhile, critical reviews have emerged that suggest that ML/DL should be used cautiously. To improve the quality (especially the applicability and generalizability) of ML/DL-related SE studies, and to stimulate and enhance future collaborations between SE/AI researchers and industry practitioners, we conducted a 10-year Systematic Literature Review (SLR) on 906 ML/DL-related SE papers published between 2009 and 2018. Our trend analysis demonstrated the mutual impacts that ML/DL and SE have had on each other. At the same time, however, we also observed a paucity of replicable and reproducible ML/DL-related SE studies and identified five factors that influence their replicability and reproducibility. To improve the applicability and generalizability of research results, we analyzed what ingredients in a study would facilitate an understanding of why a ML/DL technique was selected for a specific SE problem. In addition, we identified the unique trends of impacts of DL models on SE tasks, as well as five unique challenges that needed to be met in order to better leverage DL to improve the productivity of SE tasks. Finally, we outlined a road-map that we believe can facilitate the transfer of ML/DL-based SE research results into real-world industry practices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge