Lei Lan
ElastoGen: 4D Generative Elastodynamics
May 23, 2024Abstract:We present ElastoGen, a knowledge-driven model that generates physically accurate and coherent 4D elastodynamics. Instead of relying on petabyte-scale data-driven learning, ElastoGen leverages the principles of physics-in-the-loop and learns from established physical knowledge, such as partial differential equations and their numerical solutions. The core idea of ElastoGen is converting the global differential operator, corresponding to the nonlinear elastodynamic equations, into iterative local convolution-like operations, which naturally fit modern neural networks. Each network module is specifically designed to support this goal rather than functioning as a black box. As a result, ElastoGen is exceptionally lightweight in terms of both training requirements and network scale. Additionally, due to its alignment with physical procedures, ElastoGen efficiently generates accurate dynamics for a wide range of hyperelastic materials and can be easily integrated with upstream and downstream deep modules to enable end-to-end 4D generation.
High-order Differentiable Autoencoder for Nonlinear Model Reduction
Feb 19, 2021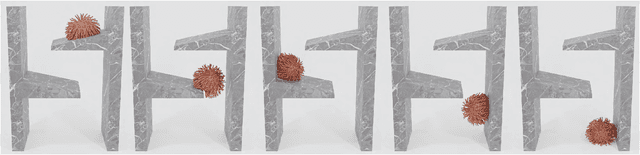


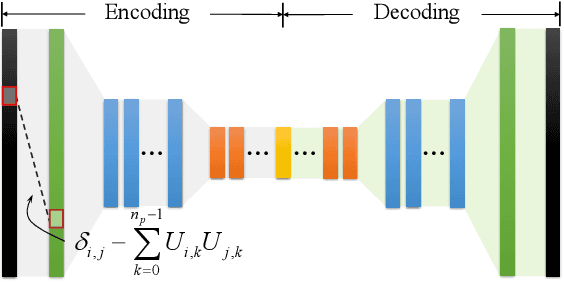
Abstract:This paper provides a new avenue for exploiting deep neural networks to improve physics-based simulation. Specifically, we integrate the classic Lagrangian mechanics with a deep autoencoder to accelerate elastic simulation of deformable solids. Due to the inertia effect, the dynamic equilibrium cannot be established without evaluating the second-order derivatives of the deep autoencoder network. This is beyond the capability of off-the-shelf automatic differentiation packages and algorithms, which mainly focus on the gradient evaluation. Solving the nonlinear force equilibrium is even more challenging if the standard Newton's method is to be used. This is because we need to compute a third-order derivative of the network to obtain the variational Hessian. We attack those difficulties by exploiting complex-step finite difference, coupled with reverse automatic differentiation. This strategy allows us to enjoy the convenience and accuracy of complex-step finite difference and in the meantime, to deploy complex-value perturbations as collectively as possible to save excessive network passes. With a GPU-based implementation, we are able to wield deep autoencoders (e.g., $10+$ layers) with a relatively high-dimension latent space in real-time. Along this pipeline, we also design a sampling network and a weighting network to enable \emph{weight-varying} Cubature integration in order to incorporate nonlinearity in the model reduction. We believe this work will inspire and benefit future research efforts in nonlinearly reduced physical simulation problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge