Leander Girrbach
SUB: Benchmarking CBM Generalization via Synthetic Attribute Substitutions
Jul 31, 2025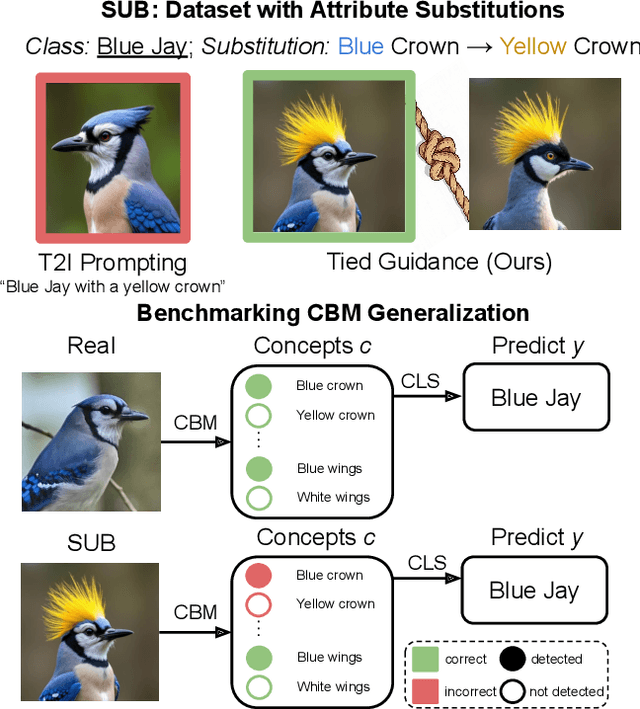
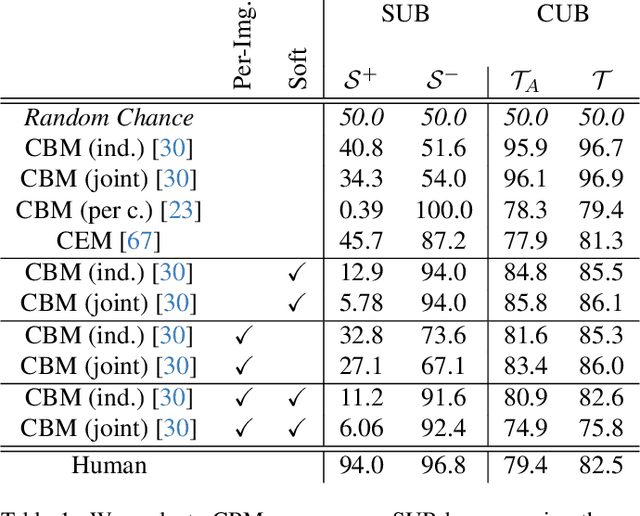
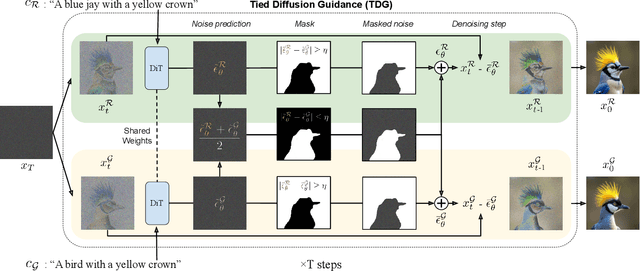

Abstract:Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) and other concept-based interpretable models show great promise for making AI applications more transparent, which is essential in fields like medicine. Despite their success, we demonstrate that CBMs struggle to reliably identify the correct concepts under distribution shifts. To assess the robustness of CBMs to concept variations, we introduce SUB: a fine-grained image and concept benchmark containing 38,400 synthetic images based on the CUB dataset. To create SUB, we select a CUB subset of 33 bird classes and 45 concepts to generate images which substitute a specific concept, such as wing color or belly pattern. We introduce a novel Tied Diffusion Guidance (TDG) method to precisely control generated images, where noise sharing for two parallel denoising processes ensures that both the correct bird class and the correct attribute are generated. This novel benchmark enables rigorous evaluation of CBMs and similar interpretable models, contributing to the development of more robust methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/sub and the dataset at http://huggingface.co/datasets/Jessica-bader/SUB.
Align-then-Unlearn: Embedding Alignment for LLM Unlearning
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are trained on massive datasets, they have raised significant privacy and ethical concerns due to their potential to inadvertently retain sensitive information. Unlearning seeks to selectively remove specific data from trained models, such as personal information or copyrighted content. Current approaches targeting specific output sequences at the token level often fail to achieve complete forgetting and remain susceptible to prompt rephrasing. We propose Align-then-Unlearn, a novel framework that performs unlearning in the semantic embedding space rather than directly on output tokens. Align-then-Unlearn first augments the LLM with an embedding prediction module trained to anticipate future context representations. Unlearning is then achieved by fine-tuning the model to minimize the similarity between these predicted embeddings and a target embedding that represents the concept to be removed. Initial results show that Align-then-Unlearn effectively removes targeted knowledge with minimal degradation in overall model utility. These findings suggest that embedding-based unlearning offers a promising and robust approach to removing conceptual knowledge. Our code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/align-then-unlearn.
A Large Scale Analysis of Gender Biases in Text-to-Image Generative Models
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:With the increasing use of image generation technology, understanding its social biases, including gender bias, is essential. This paper presents the first large-scale study on gender bias in text-to-image (T2I) models, focusing on everyday situations. While previous research has examined biases in occupations, we extend this analysis to gender associations in daily activities, objects, and contexts. We create a dataset of 3,217 gender-neutral prompts and generate 200 images per prompt from five leading T2I models. We automatically detect the perceived gender of people in the generated images and filter out images with no person or multiple people of different genders, leaving 2,293,295 images. To enable a broad analysis of gender bias in T2I models, we group prompts into semantically similar concepts and calculate the proportion of male- and female-gendered images for each prompt. Our analysis shows that T2I models reinforce traditional gender roles, reflect common gender stereotypes in household roles, and underrepresent women in financial related activities. Women are predominantly portrayed in care- and human-centered scenarios, and men in technical or physical labor scenarios.
Revealing and Reducing Gender Biases in Vision and Language Assistants (VLAs)
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:Pre-trained large language models (LLMs) have been reliably integrated with visual input for multimodal tasks. The widespread adoption of instruction-tuned image-to-text vision-language assistants (VLAs) like LLaVA and InternVL necessitates evaluating gender biases. We study gender bias in 22 popular open-source VLAs with respect to personality traits, skills, and occupations. Our results show that VLAs replicate human biases likely present in the data, such as real-world occupational imbalances. Similarly, they tend to attribute more skills and positive personality traits to women than to men, and we see a consistent tendency to associate negative personality traits with men. To eliminate the gender bias in these models, we find that finetuning-based debiasing methods achieve the best tradeoff between debiasing and retaining performance on downstream tasks. We argue for pre-deploying gender bias assessment in VLAs and motivate further development of debiasing strategies to ensure equitable societal outcomes.
Addressing caveats of neural persistence with deep graph persistence
Jul 20, 2023
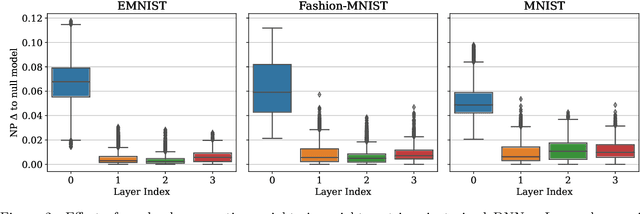
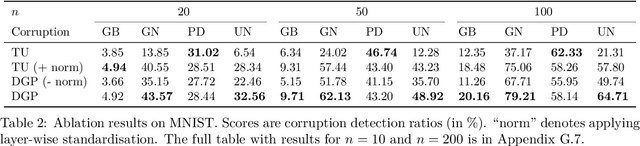
Abstract:Neural Persistence is a prominent measure for quantifying neural network complexity, proposed in the emerging field of topological data analysis in deep learning. In this work, however, we find both theoretically and empirically that the variance of network weights and spatial concentration of large weights are the main factors that impact neural persistence. Whilst this captures useful information for linear classifiers, we find that no relevant spatial structure is present in later layers of deep neural networks, making neural persistence roughly equivalent to the variance of weights. Additionally, the proposed averaging procedure across layers for deep neural networks does not consider interaction between layers. Based on our analysis, we propose an extension of the filtration underlying neural persistence to the whole neural network instead of single layers, which is equivalent to calculating neural persistence on one particular matrix. This yields our deep graph persistence measure, which implicitly incorporates persistent paths through the network and alleviates variance-related issues through standardisation. Code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/Deep-Graph-Persistence .
Word Segmentation and Morphological Parsing for Sanskrit
Jan 30, 2022



Abstract:We describe our participation in the Word Segmentation and Morphological Parsing (WSMP) for Sanskrit hackathon. We approach the word segmentation task as a sequence labelling task by predicting edit operations from which segmentations are derived. We approach the morphological analysis task by predicting morphological tags and rules that transform inflected words into their corresponding stems. Also, we propose an end-to-end trainable pipeline model for joint segmentation and morphological analysis. Our model performed best in the joint segmentation and analysis subtask (80.018 F1 score) and performed second best in the individual subtasks (segmentation: 96.189 F1 score / analysis: 69.180 F1 score). Finally, we analyse errors made by our models and suggest future work and possible improvements regarding data and evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge