Laure Ciernik
Beyond the final layer: Attentive multilayer fusion for vision transformers
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:With the rise of large-scale foundation models, efficiently adapting them to downstream tasks remains a central challenge. Linear probing, which freezes the backbone and trains a lightweight head, is computationally efficient but often restricted to last-layer representations. We show that task-relevant information is distributed across the network hierarchy rather than solely encoded in any of the last layers. To leverage this distribution of information, we apply an attentive probing mechanism that dynamically fuses representations from all layers of a Vision Transformer. This mechanism learns to identify the most relevant layers for a target task and combines low-level structural cues with high-level semantic abstractions. Across 20 diverse datasets and multiple pretrained foundation models, our method achieves consistent, substantial gains over standard linear probes. Attention heatmaps further reveal that tasks different from the pre-training domain benefit most from intermediate representations. Overall, our findings underscore the value of intermediate layer information and demonstrate a principled, task aware approach for unlocking their potential in probing-based adaptation.
Training objective drives the consistency of representational similarity across datasets
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:The Platonic Representation Hypothesis claims that recent foundation models are converging to a shared representation space as a function of their downstream task performance, irrespective of the objectives and data modalities used to train these models. Representational similarity is generally measured for individual datasets and is not necessarily consistent across datasets. Thus, one may wonder whether this convergence of model representations is confounded by the datasets commonly used in machine learning. Here, we propose a systematic way to measure how representational similarity between models varies with the set of stimuli used to construct the representations. We find that the objective function is the most crucial factor in determining the consistency of representational similarities across datasets. Specifically, self-supervised vision models learn representations whose relative pairwise similarities generalize better from one dataset to another compared to those of image classification or image-text models. Moreover, the correspondence between representational similarities and the models' task behavior is dataset-dependent, being most strongly pronounced for single-domain datasets. Our work provides a framework for systematically measuring similarities of model representations across datasets and linking those similarities to differences in task behavior.
xMIL: Insightful Explanations for Multiple Instance Learning in Histopathology
Jun 06, 2024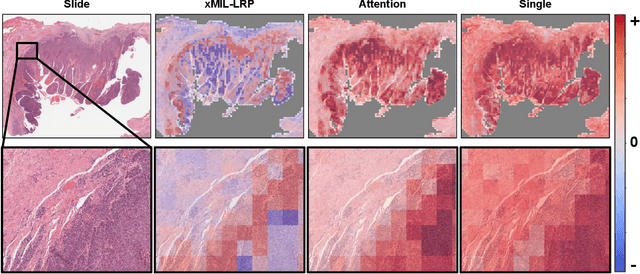
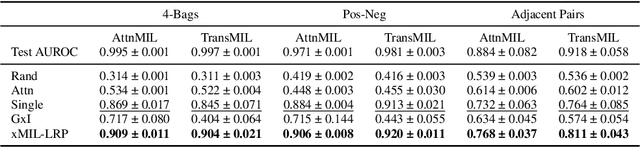
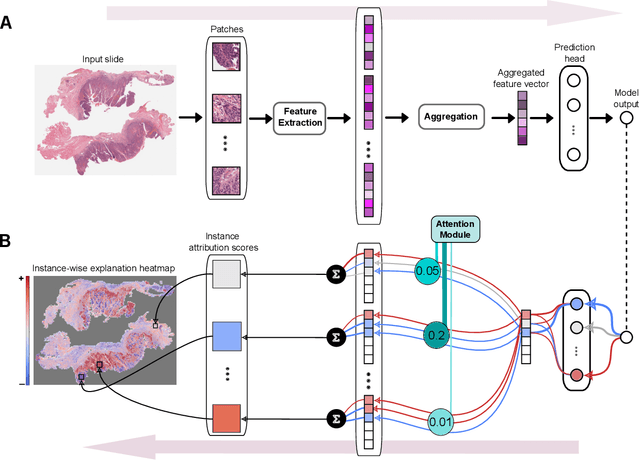
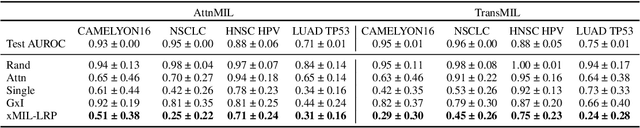
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is an effective and widely used approach for weakly supervised machine learning. In histopathology, MIL models have achieved remarkable success in tasks like tumor detection, biomarker prediction, and outcome prognostication. However, MIL explanation methods are still lagging behind, as they are limited to small bag sizes or disregard instance interactions. We revisit MIL through the lens of explainable AI (XAI) and introduce xMIL, a refined framework with more general assumptions. We demonstrate how to obtain improved MIL explanations using layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) and conduct extensive evaluation experiments on three toy settings and four real-world histopathology datasets. Our approach consistently outperforms previous explanation attempts with particularly improved faithfulness scores on challenging biomarker prediction tasks. Finally, we showcase how xMIL explanations enable pathologists to extract insights from MIL models, representing a significant advance for knowledge discovery and model debugging in digital histopathology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge