Laura Kopf
Capturing Polysemanticity with PRISM: A Multi-Concept Feature Description Framework
Jun 18, 2025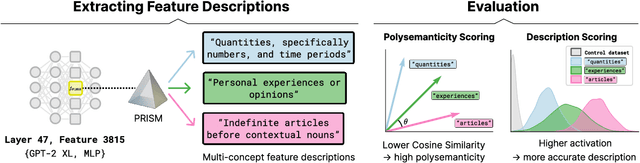
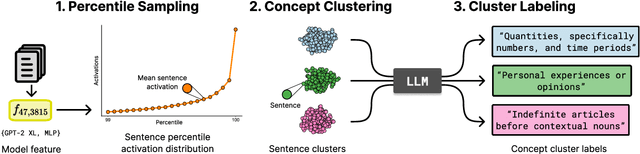

Abstract:Automated interpretability research aims to identify concepts encoded in neural network features to enhance human understanding of model behavior. Current feature description methods face two critical challenges: limited robustness and the flawed assumption that each neuron encodes only a single concept (monosemanticity), despite growing evidence that neurons are often polysemantic. This assumption restricts the expressiveness of feature descriptions and limits their ability to capture the full range of behaviors encoded in model internals. To address this, we introduce Polysemantic FeatuRe Identification and Scoring Method (PRISM), a novel framework that captures the inherent complexity of neural network features. Unlike prior approaches that assign a single description per feature, PRISM provides more nuanced descriptions for both polysemantic and monosemantic features. We apply PRISM to language models and, through extensive benchmarking against existing methods, demonstrate that our approach produces more accurate and faithful feature descriptions, improving both overall description quality (via a description score) and the ability to capture distinct concepts when polysemanticity is present (via a polysemanticity score).
CoSy: Evaluating Textual Explanations of Neurons
May 30, 2024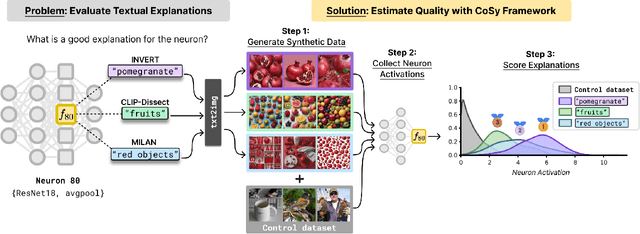
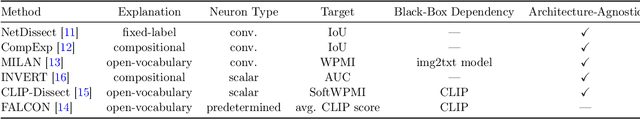
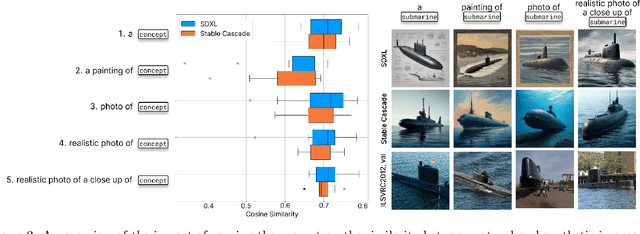
Abstract:A crucial aspect of understanding the complex nature of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) is the ability to explain learned concepts within their latent representations. While various methods exist to connect neurons to textual descriptions of human-understandable concepts, evaluating the quality of these explanation methods presents a major challenge in the field due to a lack of unified, general-purpose quantitative evaluation. In this work, we introduce CoSy (Concept Synthesis) -- a novel, architecture-agnostic framework to evaluate the quality of textual explanations for latent neurons. Given textual explanations, our proposed framework leverages a generative model conditioned on textual input to create data points representing the textual explanation. Then, the neuron's response to these explanation data points is compared with the response to control data points, providing a quality estimate of the given explanation. We ensure the reliability of our proposed framework in a series of meta-evaluation experiments and demonstrate practical value through insights from benchmarking various concept-based textual explanation methods for Computer Vision tasks, showing that tested explanation methods significantly differ in quality.
Labeling Neural Representations with Inverse Recognition
Nov 22, 2023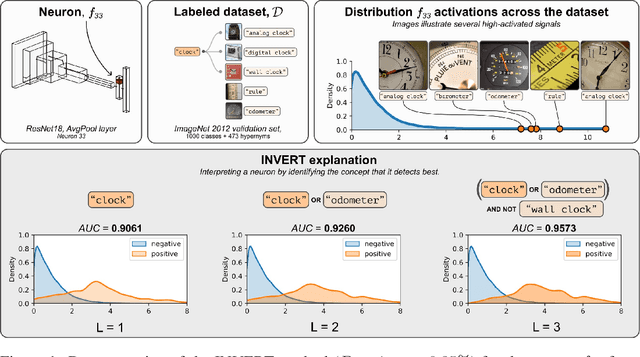
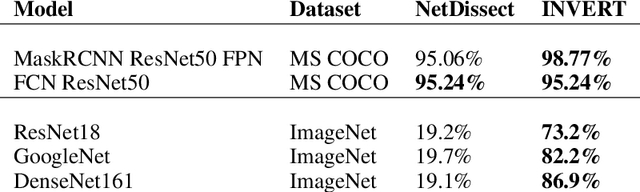
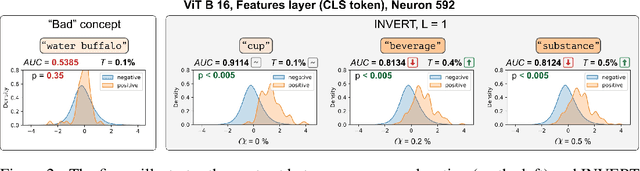
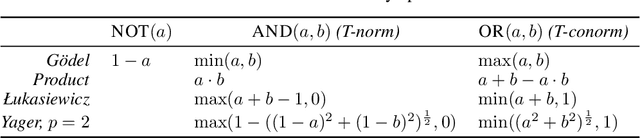
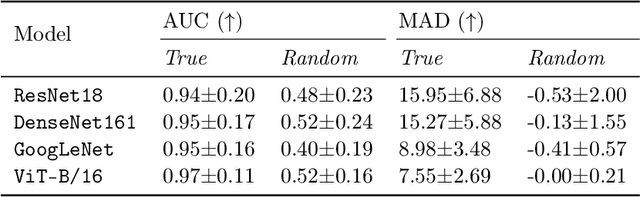
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) demonstrated remarkable capabilities in learning complex hierarchical data representations, but the nature of these representations remains largely unknown. Existing global explainability methods, such as Network Dissection, face limitations such as reliance on segmentation masks, lack of statistical significance testing, and high computational demands. We propose Inverse Recognition (INVERT), a scalable approach for connecting learned representations with human-understandable concepts by leveraging their capacity to discriminate between these concepts. In contrast to prior work, INVERT is capable of handling diverse types of neurons, exhibits less computational complexity, and does not rely on the availability of segmentation masks. Moreover, INVERT provides an interpretable metric assessing the alignment between the representation and its corresponding explanation and delivering a measure of statistical significance, emphasizing its utility and credibility. We demonstrate the applicability of INVERT in various scenarios, including the identification of representations affected by spurious correlations, and the interpretation of the hierarchical structure of decision-making within the models.
* 24 pages, 16 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge