Kwok-Leung Tsui
Optimistic Reinforcement Learning with Quantile Objectives
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has achieved tremendous success in recent years. However, the classical foundations of RL do not account for the risk sensitivity of the objective function, which is critical in various fields, including healthcare and finance. A popular approach to incorporate risk sensitivity is to optimize a specific quantile of the cumulative reward distribution. In this paper, we develop UCB-QRL, an optimistic learning algorithm for the $τ$-quantile objective in finite-horizon Markov decision processes (MDPs). UCB-QRL is an iterative algorithm in which, at each iteration, we first estimate the underlying transition probability and then optimize the quantile value function over a confidence ball around this estimate. We show that UCB-QRL yields a high-probability regret bound $\mathcal O\left((2/κ)^{H+1}H\sqrt{SATH\log(2SATH/δ)}\right)$ in the episodic setting with $S$ states, $A$ actions, $T$ episodes, and $H$ horizons. Here, $κ>0$ is a problem-dependent constant that captures the sensitivity of the underlying MDP's quantile value.
Effect Decomposition of Functional-Output Computer Experiments via Orthogonal Additive Gaussian Processes
Jun 15, 2025



Abstract:Functional ANOVA (FANOVA) is a widely used variance-based sensitivity analysis tool. However, studies on functional-output FANOVA remain relatively scarce, especially for black-box computer experiments, which often involve complex and nonlinear functional-output relationships with unknown data distribution. Conventional approaches often rely on predefined basis functions or parametric structures that lack the flexibility to capture complex nonlinear relationships. Additionally, strong assumptions about the underlying data distributions further limit their ability to achieve a data-driven orthogonal effect decomposition. To address these challenges, this study proposes a functional-output orthogonal additive Gaussian process (FOAGP) to efficiently perform the data-driven orthogonal effect decomposition. By enforcing a conditional orthogonality constraint on the separable prior process, the proposed functional-output orthogonal additive kernel enables data-driven orthogonality without requiring prior distributional assumptions. The FOAGP framework also provides analytical formulations for local Sobol' indices and expected conditional variance sensitivity indices, enabling comprehensive sensitivity analysis by capturing both global and local effect significance. Validation through two simulation studies and a real case study on fuselage shape control confirms the model's effectiveness in orthogonal effect decomposition and variance decomposition, demonstrating its practical value in engineering applications.
Data-Driven Portfolio Management for Motion Pictures Industry: A New Data-Driven Optimization Methodology Using a Large Language Model as the Expert
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Portfolio management is one of the unresponded problems of the Motion Pictures Industry (MPI). To design an optimal portfolio for an MPI distributor, it is essential to predict the box office of each project. Moreover, for an accurate box office prediction, it is critical to consider the effect of the celebrities involved in each MPI project, which was impossible with any precedent expert-based method. Additionally, the asymmetric characteristic of MPI data decreases the performance of any predictive algorithm. In this paper, firstly, the fame score of the celebrities is determined using a large language model. Then, to tackle the asymmetric character of MPI's data, projects are classified. Furthermore, the box office prediction takes place for each class of projects. Finally, using a hybrid multi-attribute decision-making technique, the preferability of each project for the distributor is calculated, and benefiting from a bi-objective optimization model, the optimal portfolio is designed.
PSTN: Periodic Spatial-temporal Deep Neural Network for Traffic Condition Prediction
Aug 05, 2021



Abstract:Accurate forecasting of traffic conditions is critical for improving safety, stability, and efficiency of a city transportation system. In reality, it is challenging to produce accurate traffic forecasts due to the complex and dynamic spatiotemporal correlations. Most existing works only consider partial characteristics and features of traffic data, and result in unsatisfactory performances on modeling and forecasting. In this paper, we propose a periodic spatial-temporal deep neural network (PSTN) with three pivotal modules to improve the forecasting performance of traffic conditions through a novel integration of three types of information. First, the historical traffic information is folded and fed into a module consisting of a graph convolutional network and a temporal convolutional network. Second, the recent traffic information together with the historical output passes through the second module consisting of a graph convolutional network and a gated recurrent unit framework. Finally, a multi-layer perceptron is applied to process the auxiliary road attributes and output the final predictions. Experimental results on two publicly accessible real-world urban traffic data sets show that the proposed PSTN outperforms the state-of-the-art benchmarks by significant margins for short-term traffic conditions forecasting
Automatic Detection of Rail Components via A Deep Convolutional Transformer Network
Aug 05, 2021



Abstract:Automatic detection of rail track and its fasteners via using continuously collected railway images is important to maintenance as it can significantly improve maintenance efficiency and better ensure system safety. Dominant computer vision-based detection models typically rely on convolutional neural networks that utilize local image features and cumbersome prior settings to generate candidate boxes. In this paper, we propose a deep convolutional transformer network based method to detect multi-class rail components including the rail, clip, and bolt. We effectively synergize advantages of the convolutional structure on extracting latent features from raw images as well as advantages of transformers on selectively determining valuable latent features to achieve an efficient and accurate performance on rail component detections. Our proposed method simplifies the detection pipeline by eliminating the need of prior settings, such as anchor box, aspect ratio, default coordinates, and post-processing, such as the threshold for non-maximum suppression; as well as allows users to trade off the quality and complexity of the detector with limited training data. Results of a comprehensive computational study show that our proposed method outperforms a set of existing state-of-art approaches with large margins
Intelligent Railway Foreign Object Detection: A Semi-supervised Convolutional Autoencoder Based Method
Aug 05, 2021



Abstract:Automated inspection and detection of foreign objects on railways is important for rail transportation safety as it helps prevent potential accidents and trains derailment. Most existing vision-based approaches focus on the detection of frontal intrusion objects with prior labels, such as categories and locations of the objects. In reality, foreign objects with unknown categories can appear anytime on railway tracks. In this paper, we develop a semi-supervised convolutional autoencoder based framework that only requires railway track images without prior knowledge on the foreign objects in the training process. It consists of three different modules, a bottleneck feature generator as encoder, a photographic image generator as decoder, and a reconstruction discriminator developed via adversarial learning. In the proposed framework, the problem of detecting the presence, location, and shape of foreign objects is addressed by comparing the input and reconstructed images as well as setting thresholds based on reconstruction errors. The proposed method is evaluated through comprehensive studies under different performance criteria. The results show that the proposed method outperforms some well-known benchmarking methods. The proposed framework is useful for data analytics via the train Internet-of-Things (IoT) systems
Viewpoint-Invariant Exercise Repetition Counting
Jul 29, 2021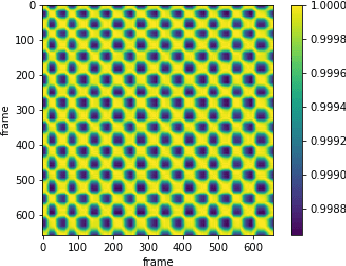
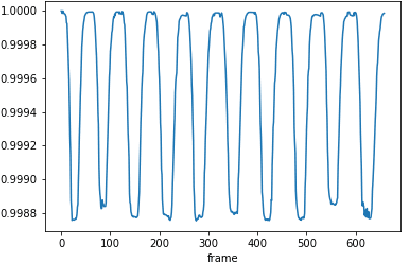
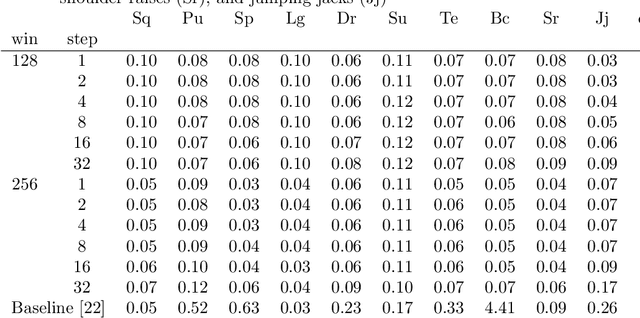
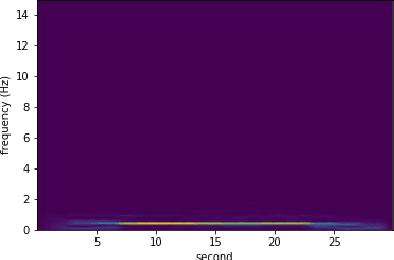
Abstract:Counting the repetition of human exercise and physical rehabilitation is a common task in rehabilitation and exercise training. The existing vision-based repetition counting methods less emphasize the concurrent motions in the same video. This work presents a vision-based human motion repetition counting applicable to counting concurrent motions through the skeleton location extracted from various pose estimation methods. The presented method was validated on the University of Idaho Physical Rehabilitation Movements Data Set (UI-PRMD), and MM-fit dataset. The overall mean absolute error (MAE) for mm-fit was 0.06 with off-by-one Accuracy (OBOA) 0.94. Overall MAE for UI-PRMD dataset was 0.06 with OBOA 0.95. We have also tested the performance in a variety of camera locations and concurrent motions with conveniently collected video with overall MAE 0.06 and OBOA 0.88. The proposed method provides a view-angle and motion agnostic concurrent motion counting. This method can potentially use in large-scale remote rehabilitation and exercise training with only one camera.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge