Kushaan Gowda
A Comprehensive Review on Hashtag Recommendation: From Traditional to Deep Learning and Beyond
Mar 25, 2025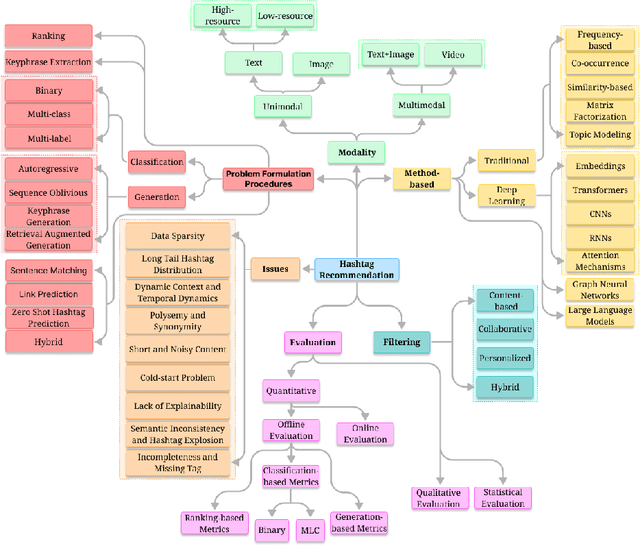
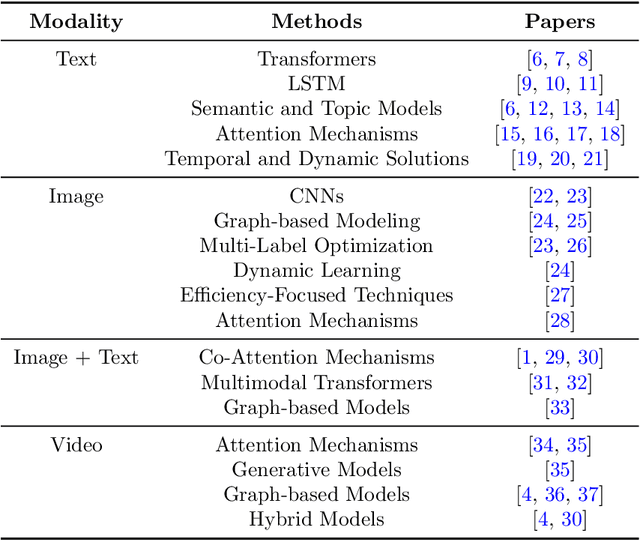
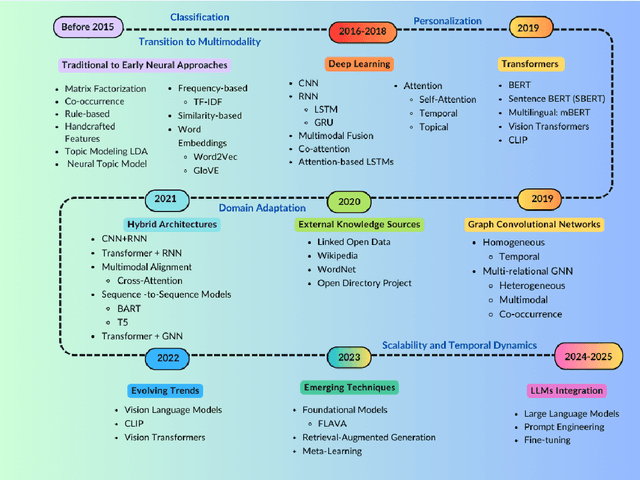

Abstract:The exponential growth of user-generated content on social media platforms has precipitated significant challenges in information management, particularly in content organization, retrieval, and discovery. Hashtags, as a fundamental categorization mechanism, play a pivotal role in enhancing content visibility and user engagement. However, the development of accurate and robust hashtag recommendation systems remains a complex and evolving research challenge. Existing surveys in this domain are limited in scope and recency, focusing narrowly on specific platforms, methodologies, or timeframes. To address this gap, this review article conducts a systematic analysis of hashtag recommendation systems, comprehensively examining recent advancements across several dimensions. We investigate unimodal versus multimodal methodologies, diverse problem formulations, filtering strategies, methodological evolution from traditional frequency-based models to advanced deep learning architectures. Furthermore, we critically evaluate performance assessment paradigms, including quantitative metrics, qualitative analyses, and hybrid evaluation frameworks. Our analysis underscores a paradigm shift toward transformer-based deep learning models, which harness contextual and semantic features to achieve superior recommendation accuracy. Key challenges such as data sparsity, cold-start scenarios, polysemy, and model explainability are rigorously discussed, alongside practical applications in tweet classification, sentiment analysis, and content popularity prediction. By synthesizing insights from diverse methodological and platform-specific perspectives, this survey provides a structured taxonomy of current research, identifies unresolved gaps, and proposes future directions for developing adaptive, user-centric recommendation systems.
AMuSeD: An Attentive Deep Neural Network for Multimodal Sarcasm Detection Incorporating Bi-modal Data Augmentation
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Detecting sarcasm effectively requires a nuanced understanding of context, including vocal tones and facial expressions. The progression towards multimodal computational methods in sarcasm detection, however, faces challenges due to the scarcity of data. To address this, we present AMuSeD (Attentive deep neural network for MUltimodal Sarcasm dEtection incorporating bi-modal Data augmentation). This approach utilizes the Multimodal Sarcasm Detection Dataset (MUStARD) and introduces a two-phase bimodal data augmentation strategy. The first phase involves generating varied text samples through Back Translation from several secondary languages. The second phase involves the refinement of a FastSpeech 2-based speech synthesis system, tailored specifically for sarcasm to retain sarcastic intonations. Alongside a cloud-based Text-to-Speech (TTS) service, this Fine-tuned FastSpeech 2 system produces corresponding audio for the text augmentations. We also investigate various attention mechanisms for effectively merging text and audio data, finding self-attention to be the most efficient for bimodal integration. Our experiments reveal that this combined augmentation and attention approach achieves a significant F1-score of 81.0% in text-audio modalities, surpassing even models that use three modalities from the MUStARD dataset.
A Hybrid Filtering for Micro-video Hashtag Recommendation using Graph-based Deep Neural Network
Oct 14, 2024


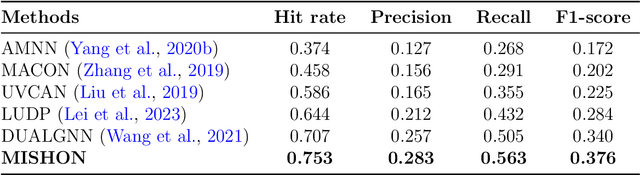
Abstract:Due to the growing volume of user generated content, hashtags are employed as topic indicators to manage content efficiently on social media platforms. However, finding these vital topics is challenging in microvideos since they contain substantial information in a short duration. Existing methods that recommend hashtags for microvideos primarily focus on content and personalization while disregarding relatedness among users. Moreover, the cold start user issue prevails in hashtag recommendation systems. Considering the above, we propose a hybrid filtering based MIcro-video haSHtag recommendatiON MISHON technique to recommend hashtags for micro-videos. Besides content based filtering, we employ user-based collaborative filtering to enhance recommendations. Since hashtags reflect users topical interests, we find similar users based on historical tagging behavior to model user relatedness. We employ a graph-based deep neural network to model user to user, modality to modality, and user to modality interactions. We then use refined modality specific and user representations to recommend pertinent hashtags for microvideos. The empirical results on three real world datasets demonstrate that MISHON attains a comparative enhancement of 3.6, 2.8, and 6.5 reported in percentage concerning the F1 score, respectively. Since cold start users exist whose historical tagging information is unavailable, we also propose a content and social influence based technique to model the relatedness of cold start users with influential users. The proposed solution shows a relative improvement of 15.8 percent in the F1 score over its content only counterpart. These results show that the proposed framework mitigates the cold start user problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge