Kunpeng Han
Effective Generation of Feasible Solutions for Integer Programming via Guided Diffusion
Jun 18, 2024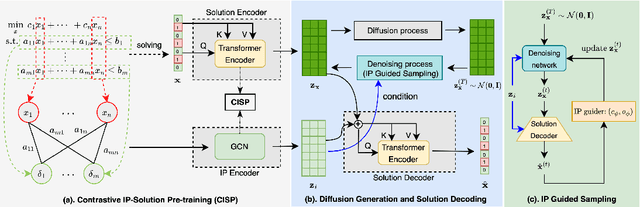
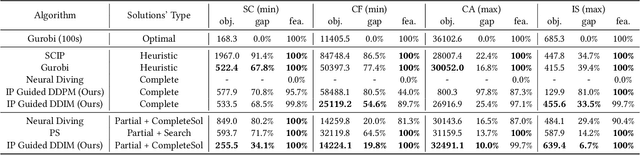
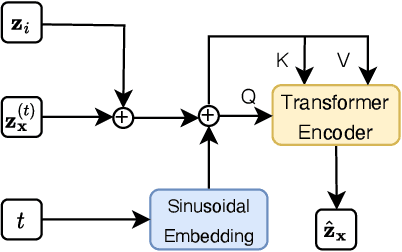

Abstract:Feasible solutions are crucial for Integer Programming (IP) since they can substantially speed up the solving process. In many applications, similar IP instances often exhibit similar structures and shared solution distributions, which can be potentially modeled by deep learning methods. Unfortunately, existing deep-learning-based algorithms, such as Neural Diving and Predict-and-search framework, are limited to generating only partial feasible solutions, and they must rely on solvers like SCIP and Gurobi to complete the solutions for a given IP problem. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that generates complete feasible solutions end-to-end. Our framework leverages contrastive learning to characterize the relationship between IP instances and solutions, and learns latent embeddings for both IP instances and their solutions. Further, the framework employs diffusion models to learn the distribution of solution embeddings conditioned on IP representations, with a dedicated guided sampling strategy that accounts for both constraints and objectives. We empirically evaluate our framework on four typical datasets of IP problems, and show that it effectively generates complete feasible solutions with a high probability (> 89.7 \%) without the reliance of Solvers and the quality of solutions is comparable to the best heuristic solutions from Gurobi. Furthermore, by integrating our method's sampled partial solutions with the CompleteSol heuristic from SCIP, the resulting feasible solutions outperform those from state-of-the-art methods across all datasets, exhibiting a 3.7 to 33.7\% improvement in the gap to optimal values, and maintaining a feasible ratio of over 99.7\% for all datasets.
A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for Constrained Online Logistics Route Assignment
Sep 08, 2021



Abstract:As online shopping prevails and e-commerce platforms emerge, there is a tremendous number of parcels being transported every day. Thus, it is crucial for the logistics industry on how to assign a candidate logistics route for each shipping parcel properly as it leaves a significant impact on the total logistics cost optimization and business constraints satisfaction such as transit hub capacity and delivery proportion of delivery providers. This online route-assignment problem can be viewed as a constrained online decision-making problem. Notably, the large amount (beyond ${10^5}$) of daily parcels, the variability and non-Markovian characteristics of parcel information impose difficulties on attaining (near-) optimal solution without violating constraints excessively. In this paper, we develop a model-free DRL approach named PPO-RA, in which Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is improved with dedicated techniques to address the challenges for route assignment (RA). The actor and critic networks use attention mechanism and parameter sharing to accommodate each incoming parcel with varying numbers and identities of candidate routes, without modeling non-Markovian parcel arriving dynamics since we make assumption of i.i.d. parcel arrival. We use recorded delivery parcel data to evaluate the performance of PPO-RA by comparing it with widely-used baselines via simulation. The results show the capability of the proposed approach to achieve considerable cost savings while satisfying most constraints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge