Krzysztof Wołk
Automated speech-based screening of depression using deep convolutional neural networks
Dec 02, 2019


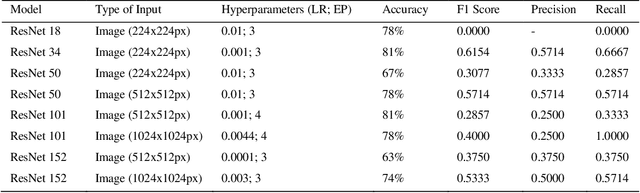
Abstract:Early detection and treatment of depression is essential in promoting remission, preventing relapse, and reducing the emotional burden of the disease. Current diagnoses are primarily subjective, inconsistent across professionals, and expensive for individuals who may be in urgent need of help. This paper proposes a novel approach to automated depression detection in speech using convolutional neural network (CNN) and multipart interactive training. The model was tested using 2568 voice samples obtained from 77 non-depressed and 30 depressed individuals. In experiment conducted, data were applied to residual CNNs in the form of spectrograms, images auto-generated from audio samples. The experimental results obtained using different ResNet architectures gave a promising baseline accuracy reaching 77%.
Deep learning and sub-word-unit approach in written art generation
Jan 22, 2019



Abstract:Automatic poetry generation is novel and interesting application of natural language processing research. It became more popular during the last few years due to the rapid development of technology and neural computing power. This line of research can be applied to the study of linguistics and literature, for social science experiments, or simply for entertainment. The most effective known method of artificial poem generation uses recurrent neural networks (RNN). We also used RNNs to generate poems in the style of Adam Mickiewicz. Our network was trained on the Sir Thaddeus poem. For data pre-processing, we used a specialized stemming tool, which is one of the major innovations and contributions of this work. Our experiment was conducted on the source text, divided into sub-word units (at a level of resolution close to syllables). This approach is novel and is not often employed in the published literature. The subwords units seem to be a natural choice for analysis of the Polish language, as the language is morphologically rich due to cases, gender forms and a large vocabulary. Moreover, Sir Thaddeus contains rhymes, so the analysis of syllables can be meaningful. We verified our model with different settings for the temperature parameter, which controls the randomness of the generated text. We also compared our results with similar models trained on the same text but divided into characters (which is the most common approach alongside the use of full word units). The differences were tremendous. Our solution generated much better poems that were able to follow the metre and vocabulary of the source data text.
Polish Read Speech Corpus for Speech Tools and Services
Jun 01, 2017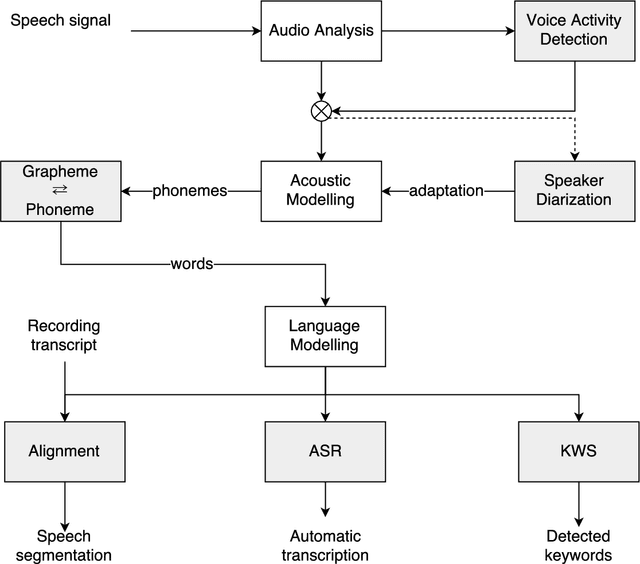
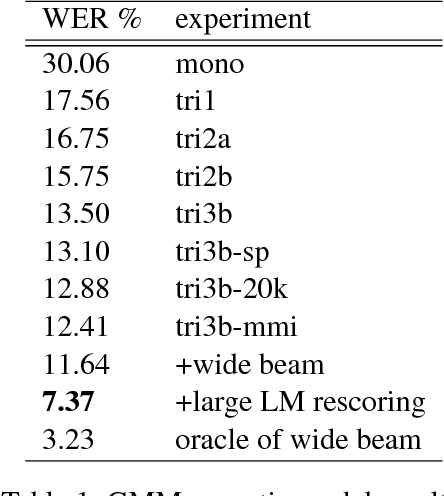
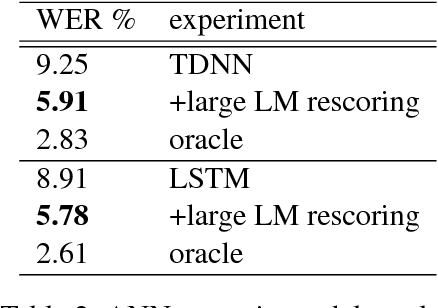
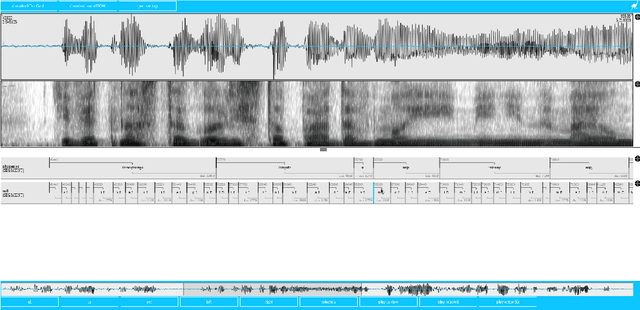
Abstract:This paper describes the speech processing activities conducted at the Polish consortium of the CLARIN project. The purpose of this segment of the project was to develop specific tools that would allow for automatic and semi-automatic processing of large quantities of acoustic speech data. The tools include the following: grapheme-to-phoneme conversion, speech-to-text alignment, voice activity detection, speaker diarization, keyword spotting and automatic speech transcription. Furthermore, in order to develop these tools, a large high-quality studio speech corpus was recorded and released under an open license, to encourage development in the area of Polish speech research. Another purpose of the corpus was to serve as a reference for studies in phonetics and pronunciation. All the tools and resources were released on the the Polish CLARIN website. This paper discusses the current status and future plans for the project.
Multi-domain machine translation enhancements by parallel data extraction from comparable corpora
Mar 22, 2016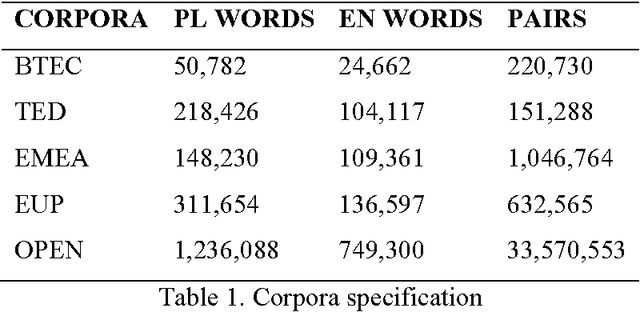

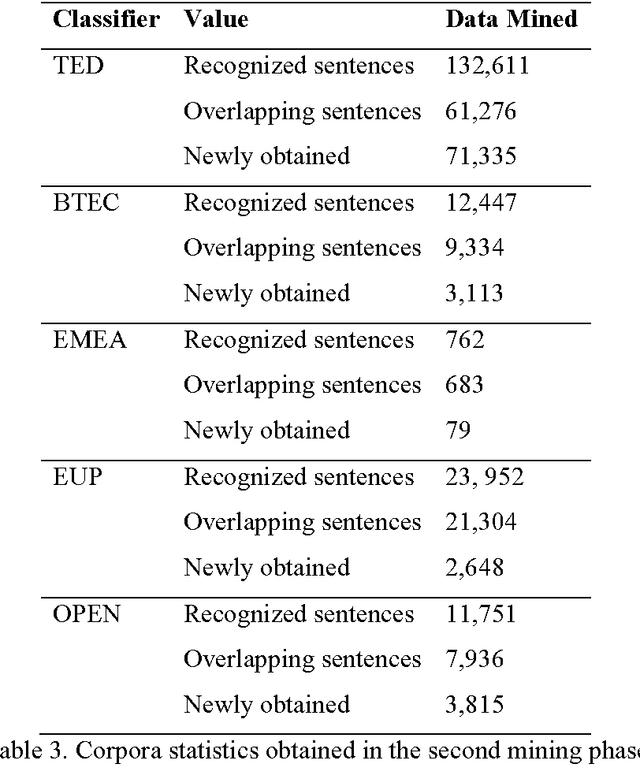
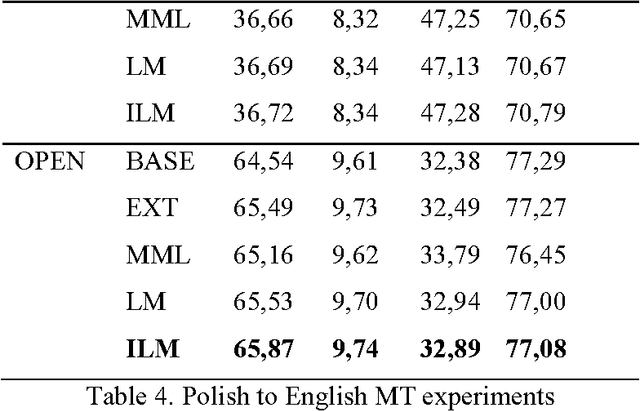
Abstract:Parallel texts are a relatively rare language resource, however, they constitute a very useful research material with a wide range of applications. This study presents and analyses new methodologies we developed for obtaining such data from previously built comparable corpora. The methodologies are automatic and unsupervised which makes them good for large scale research. The task is highly practical as non-parallel multilingual data occur much more frequently than parallel corpora and accessing them is easy, although parallel sentences are a considerably more useful resource. In this study, we propose a method of automatic web crawling in order to build topic-aligned comparable corpora, e.g. based on the Wikipedia or Euronews.com. We also developed new methods of obtaining parallel sentences from comparable data and proposed methods of filtration of corpora capable of selecting inconsistent or only partially equivalent translations. Our methods are easily scalable to other languages. Evaluation of the quality of the created corpora was performed by analysing the impact of their use on statistical machine translation systems. Experiments were presented on the basis of the Polish-English language pair for texts from different domains, i.e. lectures, phrasebooks, film dialogues, European Parliament proceedings and texts contained medicines leaflets. We also tested a second method of creating parallel corpora based on data from comparable corpora which allows for automatically expanding the existing corpus of sentences about a given domain on the basis of analogies found between them. It does not require, therefore, having past parallel resources in order to train a classifier.
Comparison and Adaptation of Automatic Evaluation Metrics for Quality Assessment of Re-Speaking
Jan 12, 2016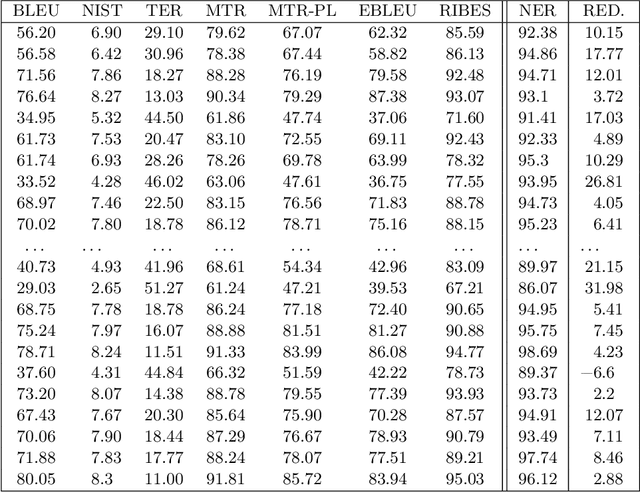
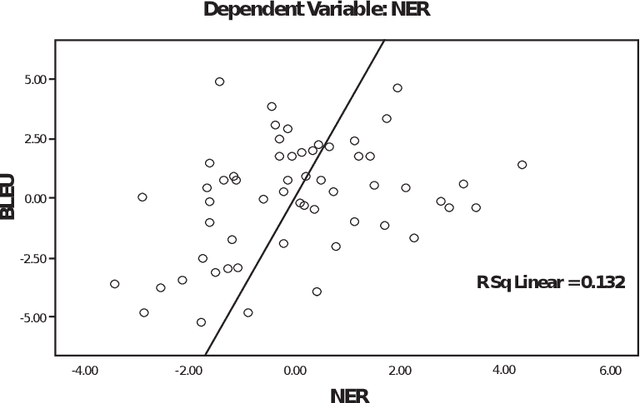
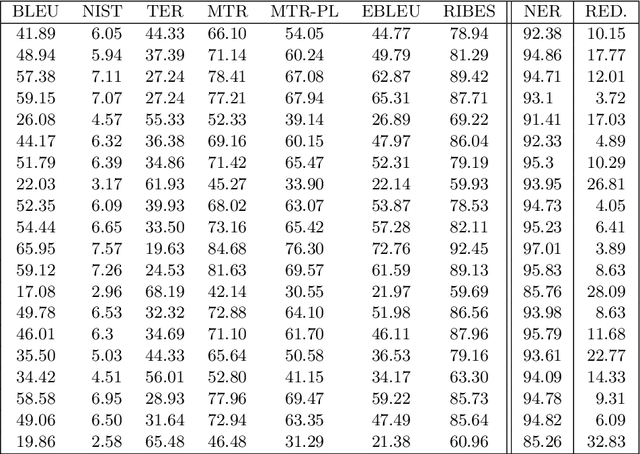
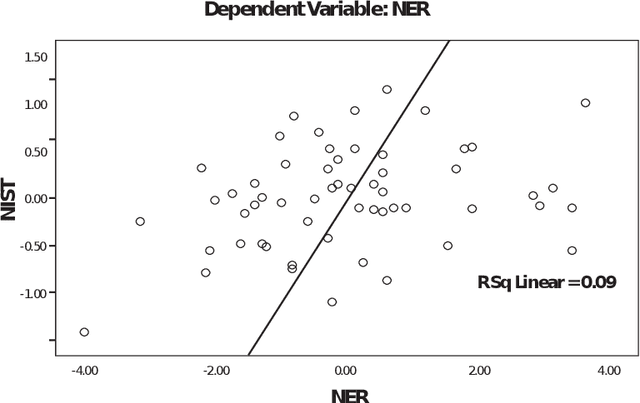
Abstract:Re-speaking is a mechanism for obtaining high quality subtitles for use in live broadcast and other public events. Because it relies on humans performing the actual re-speaking, the task of estimating the quality of the results is non-trivial. Most organisations rely on humans to perform the actual quality assessment, but purely automatic methods have been developed for other similar problems, like Machine Translation. This paper will try to compare several of these methods: BLEU, EBLEU, NIST, METEOR, METEOR-PL, TER and RIBES. These will then be matched to the human-derived NER metric, commonly used in re-speaking.
Unsupervised comparable corpora preparation and exploration for bi-lingual translation equivalents
Dec 05, 2015

Abstract:The multilingual nature of the world makes translation a crucial requirement today. Parallel dictionaries constructed by humans are a widely-available resource, but they are limited and do not provide enough coverage for good quality translation purposes, due to out-of-vocabulary words and neologisms. This motivates the use of statistical translation systems, which are unfortunately dependent on the quantity and quality of training data. Such systems have a very limited availability especially for some languages and very narrow text domains. In this research we present our improvements to current comparable corpora mining methodologies by re- implementation of the comparison algorithms (using Needleman-Wunch algorithm), introduction of a tuning script and computation time improvement by GPU acceleration. Experiments are carried out on bilingual data extracted from the Wikipedia, on various domains. For the Wikipedia itself, additional cross-lingual comparison heuristics were introduced. The modifications made a positive impact on the quality and quantity of mined data and on the translation quality.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1509.08639
PJAIT Systems for the IWSLT 2015 Evaluation Campaign Enhanced by Comparable Corpora
Dec 05, 2015
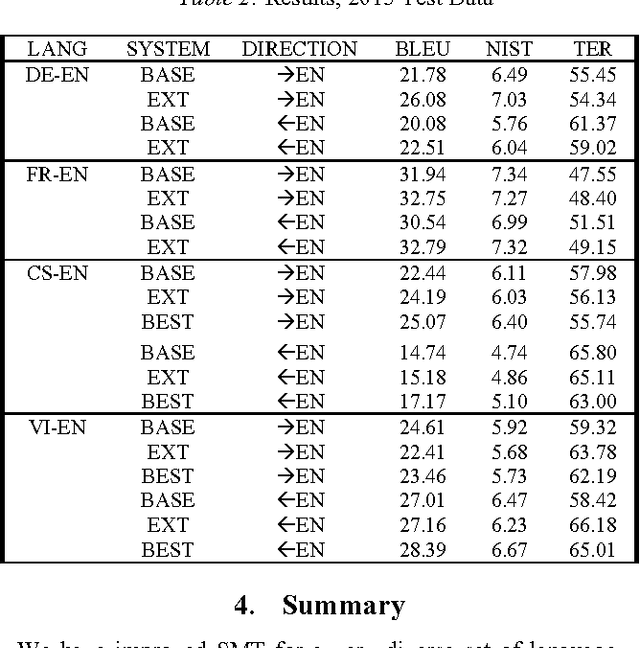

Abstract:In this paper, we attempt to improve Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) systems on a very diverse set of language pairs (in both directions): Czech - English, Vietnamese - English, French - English and German - English. To accomplish this, we performed translation model training, created adaptations of training settings for each language pair, and obtained comparable corpora for our SMT systems. Innovative tools and data adaptation techniques were employed. The TED parallel text corpora for the IWSLT 2015 evaluation campaign were used to train language models, and to develop, tune, and test the system. In addition, we prepared Wikipedia-based comparable corpora for use with our SMT system. This data was specified as permissible for the IWSLT 2015 evaluation. We explored the use of domain adaptation techniques, symmetrized word alignment models, the unsupervised transliteration models and the KenLM language modeling tool. To evaluate the effects of different preparations on translation results, we conducted experiments and used the BLEU, NIST and TER metrics. Our results indicate that our approach produced a positive impact on SMT quality.
Spoken Language Translation for Polish
Nov 24, 2015Abstract:Spoken language translation (SLT) is becoming more important in the increasingly globalized world, both from a social and economic point of view. It is one of the major challenges for automatic speech recognition (ASR) and machine translation (MT), driving intense research activities in these areas. While past research in SLT, due to technology limitations, dealt mostly with speech recorded under controlled conditions, today's major challenge is the translation of spoken language as it can be found in real life. Considered application scenarios range from portable translators for tourists, lectures and presentations translation, to broadcast news and shows with live captioning. We would like to present PJIIT's experiences in the SLT gained from the Eu-Bridge 7th framework project and the U-Star consortium activities for the Polish/English language pair. Presented research concentrates on ASR adaptation for Polish (state-of-the-art acoustic models: DBN-BLSTM training, Kaldi: LDA+MLLT+SAT+MMI), language modeling for ASR & MT (text normalization, RNN-based LMs, n-gram model domain interpolation) and statistical translation techniques (hierarchical models, factored translation models, automatic casing and punctuation, comparable and bilingual corpora preparation). While results for the well-defined domains (phrases for travelers, parliament speeches, medical documentation, movie subtitling) are very encouraging, less defined domains (presentation, lectures) still form a challenge. Our progress in the IWSLT TED task (MT only) will be presented, as well as current progress in the Polish ASR.
Enhancements in statistical spoken language translation by de-normalization of ASR results
Nov 18, 2015


Abstract:Spoken language translation (SLT) has become very important in an increasingly globalized world. Machine translation (MT) for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems is a major challenge of great interest. This research investigates that automatic sentence segmentation of speech that is important for enriching speech recognition output and for aiding downstream language processing. This article focuses on the automatic sentence segmentation of speech and improving MT results. We explore the problem of identifying sentence boundaries in the transcriptions produced by automatic speech recognition systems in the Polish language. We also experiment with reverse normalization of the recognized speech samples.
* International Academy Publishing. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1510.04500
Harvesting comparable corpora and mining them for equivalent bilingual sentences using statistical classification and analogy- based heuristics
Nov 18, 2015


Abstract:Parallel sentences are a relatively scarce but extremely useful resource for many applications including cross-lingual retrieval and statistical machine translation. This research explores our new methodologies for mining such data from previously obtained comparable corpora. The task is highly practical since non-parallel multilingual data exist in far greater quantities than parallel corpora, but parallel sentences are a much more useful resource. Here we propose a web crawling method for building subject-aligned comparable corpora from e.g. Wikipedia dumps and Euronews web page. The improvements in machine translation are shown on Polish-English language pair for various text domains. We also tested another method of building parallel corpora based on comparable corpora data. It lets automatically broad existing corpus of sentences from subject of corpora based on analogies between them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge