Danijel Korzinek
Impact of ultrasound image reconstruction method on breast lesion classification with neural transfer learning
Apr 06, 2018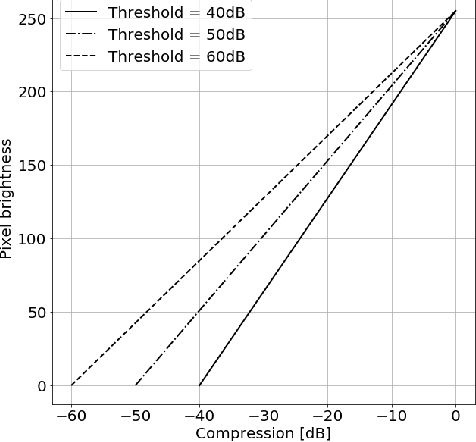

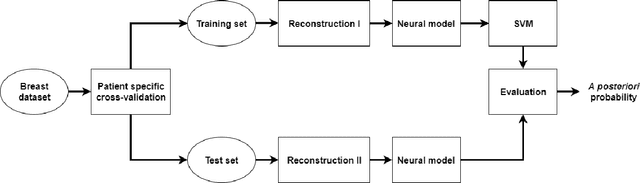
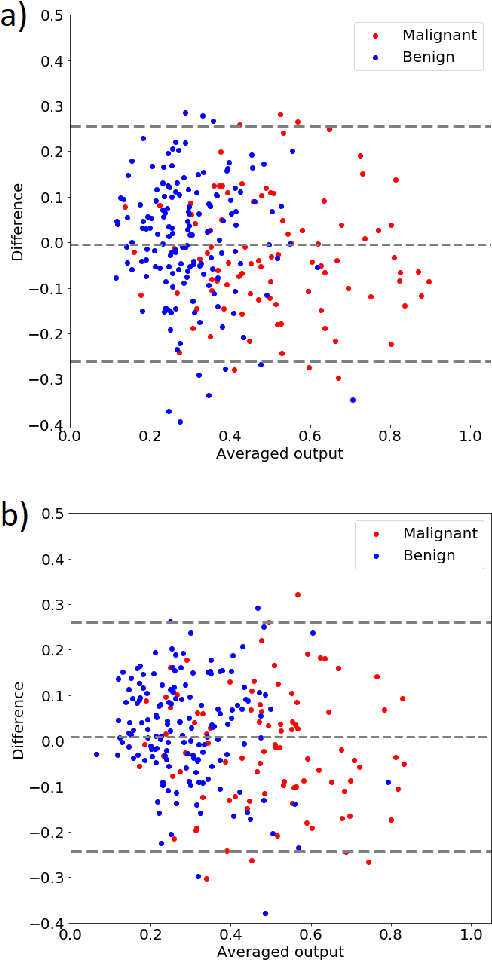
Abstract:Deep learning algorithms, especially convolutional neural networks, have become a methodology of choice in medical image analysis. However, recent studies in computer vision show that even a small modification of input image intensities may cause a deep learning model to classify the image differently. In medical imaging, the distribution of image intensities is related to applied image reconstruction algorithm. In this paper we investigate the impact of ultrasound image reconstruction method on breast lesion classification with neural transfer learning. Due to high dynamic range raw ultrasonic signals are commonly compressed in order to reconstruct B-mode images. Based on raw data acquired from breast lesions, we reconstruct B-mode images using different compression levels. Next, transfer learning is applied for classification. Differently reconstructed images are employed for training and evaluation. We show that the modification of the reconstruction algorithm leads to decrease of classification performance. As a remedy, we propose a method of data augmentation. We show that the augmentation of the training set with differently reconstructed B-mode images leads to a more robust and efficient classification. Our study suggests that it is important to take into account image reconstruction algorithms implemented in medical scanners during development of computer aided diagnosis systems.
Spoken Language Translation for Polish
Nov 24, 2015Abstract:Spoken language translation (SLT) is becoming more important in the increasingly globalized world, both from a social and economic point of view. It is one of the major challenges for automatic speech recognition (ASR) and machine translation (MT), driving intense research activities in these areas. While past research in SLT, due to technology limitations, dealt mostly with speech recorded under controlled conditions, today's major challenge is the translation of spoken language as it can be found in real life. Considered application scenarios range from portable translators for tourists, lectures and presentations translation, to broadcast news and shows with live captioning. We would like to present PJIIT's experiences in the SLT gained from the Eu-Bridge 7th framework project and the U-Star consortium activities for the Polish/English language pair. Presented research concentrates on ASR adaptation for Polish (state-of-the-art acoustic models: DBN-BLSTM training, Kaldi: LDA+MLLT+SAT+MMI), language modeling for ASR & MT (text normalization, RNN-based LMs, n-gram model domain interpolation) and statistical translation techniques (hierarchical models, factored translation models, automatic casing and punctuation, comparable and bilingual corpora preparation). While results for the well-defined domains (phrases for travelers, parliament speeches, medical documentation, movie subtitling) are very encouraging, less defined domains (presentation, lectures) still form a challenge. Our progress in the IWSLT TED task (MT only) will be presented, as well as current progress in the Polish ASR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge