Kosuke Nishida
Can LLMs Detect Their Own Hallucinations?
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can generate fluent responses, but sometimes hallucinate facts. In this paper, we investigate whether LLMs can detect their own hallucinations. We formulate hallucination detection as a classification task of a sentence. We propose a framework for estimating LLMs' capability of hallucination detection and a classification method using Chain-of-Thought (CoT) to extract knowledge from their parameters. The experimental results indicated that GPT-$3.5$ Turbo with CoT detected $58.2\%$ of its own hallucinations. We concluded that LLMs with CoT can detect hallucinations if sufficient knowledge is contained in their parameters.
Rationale-Enhanced Decoding for Multi-modal Chain-of-Thought
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities by integrating pre-trained vision encoders with large language models (LLMs). Similar to single-modal LLMs, chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting has been adapted for LVLMs to enhance multi-modal reasoning by generating intermediate rationales based on visual and textual inputs. While CoT is assumed to improve grounding and accuracy in LVLMs, our experiments reveal a key challenge: existing LVLMs often ignore the contents of generated rationales in CoT reasoning. To address this, we re-formulate multi-modal CoT reasoning as a KL-constrained reward maximization focused on rationale-conditional log-likelihood. As the optimal solution, we propose rationale-enhanced decoding (RED), a novel plug-and-play inference-time decoding strategy. RED harmonizes visual and rationale information by multiplying distinct image-conditional and rationale-conditional next token distributions. Extensive experiments show that RED consistently and significantly improves reasoning over standard CoT and other decoding methods across multiple benchmarks and LVLMs. Our work offers a practical and effective approach to improve both the faithfulness and accuracy of CoT reasoning in LVLMs, paving the way for more reliable rationale-grounded multi-modal systems.
Zero-shot Concept Bottleneck Models
Feb 13, 2025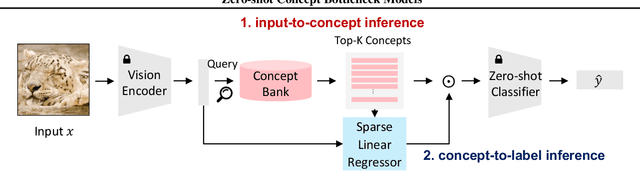

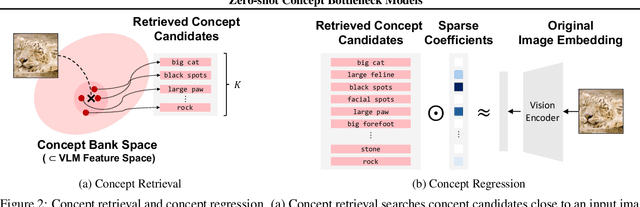

Abstract:Concept bottleneck models (CBMs) are inherently interpretable and intervenable neural network models, which explain their final label prediction by the intermediate prediction of high-level semantic concepts. However, they require target task training to learn input-to-concept and concept-to-label mappings, incurring target dataset collections and training resources. In this paper, we present \textit{zero-shot concept bottleneck models} (Z-CBMs), which predict concepts and labels in a fully zero-shot manner without training neural networks. Z-CBMs utilize a large-scale concept bank, which is composed of millions of vocabulary extracted from the web, to describe arbitrary input in various domains. For the input-to-concept mapping, we introduce concept retrieval, which dynamically finds input-related concepts by the cross-modal search on the concept bank. In the concept-to-label inference, we apply concept regression to select essential concepts from the retrieved concepts by sparse linear regression. Through extensive experiments, we confirm that our Z-CBMs provide interpretable and intervenable concepts without any additional training. Code will be available at https://github.com/yshinya6/zcbm.
Initialization of Large Language Models via Reparameterization to Mitigate Loss Spikes
Oct 07, 2024Abstract:Loss spikes, a phenomenon in which the loss value diverges suddenly, is a fundamental issue in the pre-training of large language models. This paper supposes that the non-uniformity of the norm of the parameters is one of the causes of loss spikes. Here, in training of neural networks, the scale of the gradients is required to be kept constant throughout the layers to avoid the vanishing and exploding gradients problem. However, to meet these requirements in the Transformer model, the norm of the model parameters must be non-uniform, and thus, parameters whose norm is smaller are more sensitive to the parameter update. To address this issue, we propose a novel technique, weight scaling as reparameterization (WeSaR). WeSaR introduces a gate parameter per parameter matrix and adjusts it to the value satisfying the requirements. Because of the gate parameter, WeSaR sets the norm of the original parameters uniformly, which results in stable training. Experimental results with the Transformer decoders consisting of 130 million, 1.3 billion, and 13 billion parameters showed that WeSaR stabilizes and accelerates training and that it outperformed compared methods including popular initialization methods.
Explanation Bottleneck Models
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Recent concept-based interpretable models have succeeded in providing meaningful explanations by pre-defined concept sets. However, the dependency on the pre-defined concepts restricts the application because of the limited number of concepts for explanations. This paper proposes a novel interpretable deep neural network called explanation bottleneck models (XBMs). XBMs generate a text explanation from the input without pre-defined concepts and then predict a final task prediction based on the generated explanation by leveraging pre-trained vision-language encoder-decoder models. To achieve both the target task performance and the explanation quality, we train XBMs through the target task loss with the regularization penalizing the explanation decoder via the distillation from the frozen pre-trained decoder. Our experiments, including a comparison to state-of-the-art concept bottleneck models, confirm that XBMs provide accurate and fluent natural language explanations without pre-defined concept sets. Code will be available at https://github.com/yshinya6/xbm/.
Robust Text-driven Image Editing Method that Adaptively Explores Directions in Latent Spaces of StyleGAN and CLIP
Apr 03, 2023Abstract:Automatic image editing has great demands because of its numerous applications, and the use of natural language instructions is essential to achieving flexible and intuitive editing as the user imagines. A pioneering work in text-driven image editing, StyleCLIP, finds an edit direction in the CLIP space and then edits the image by mapping the direction to the StyleGAN space. At the same time, it is difficult to tune appropriate inputs other than the original image and text instructions for image editing. In this study, we propose a method to construct the edit direction adaptively in the StyleGAN and CLIP spaces with SVM. Our model represents the edit direction as a normal vector in the CLIP space obtained by training a SVM to classify positive and negative images. The images are retrieved from a large-scale image corpus, originally used for pre-training StyleGAN, according to the CLIP similarity between the images and the text instruction. We confirmed that our model performed as well as the StyleCLIP baseline, whereas it allows simple inputs without increasing the computational time.
SlideVQA: A Dataset for Document Visual Question Answering on Multiple Images
Jan 12, 2023Abstract:Visual question answering on document images that contain textual, visual, and layout information, called document VQA, has received much attention recently. Although many datasets have been proposed for developing document VQA systems, most of the existing datasets focus on understanding the content relationships within a single image and not across multiple images. In this study, we propose a new multi-image document VQA dataset, SlideVQA, containing 2.6k+ slide decks composed of 52k+ slide images and 14.5k questions about a slide deck. SlideVQA requires complex reasoning, including single-hop, multi-hop, and numerical reasoning, and also provides annotated arithmetic expressions of numerical answers for enhancing the ability of numerical reasoning. Moreover, we developed a new end-to-end document VQA model that treats evidence selection and question answering in a unified sequence-to-sequence format. Experiments on SlideVQA show that our model outperformed existing state-of-the-art QA models, but that it still has a large gap behind human performance. We believe that our dataset will facilitate research on document VQA.
Self-Adaptive Named Entity Recognition by Retrieving Unstructured Knowledge
Oct 14, 2022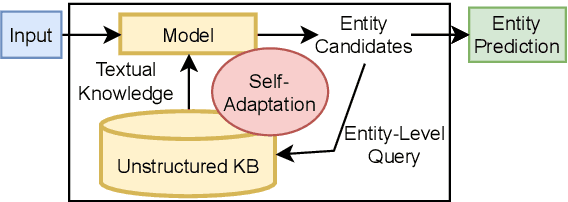
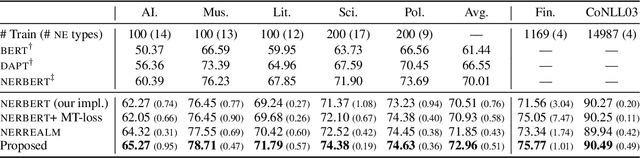
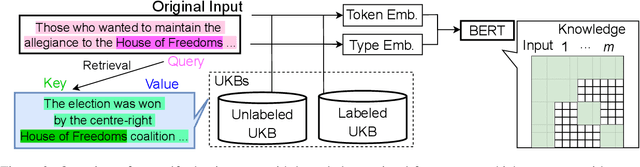
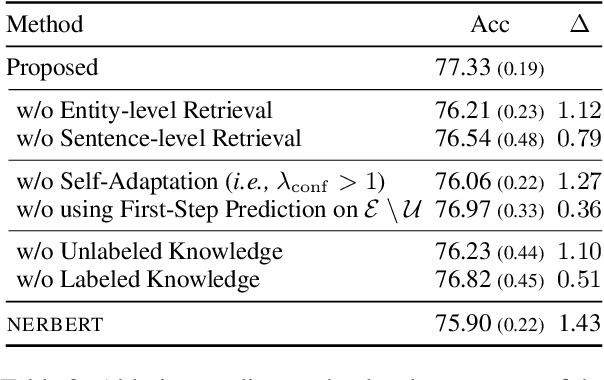
Abstract:Although named entity recognition (NER) helps us to extract various domain-specific entities from text (e.g., artists in the music domain), it is costly to create a large amount of training data or a structured knowledge base to perform accurate NER in the target domain. Here, we propose self-adaptive NER, where the model retrieves the external knowledge from unstructured text to learn the usage of entities that has not been learned well. To retrieve useful knowledge for NER, we design an effective two-stage model that retrieves unstructured knowledge using uncertain entities as queries. Our model first predicts the entities in the input and then finds the entities of which the prediction is not confident. Then, our model retrieves knowledge by using these uncertain entities as queries and concatenates the retrieved text to the original input to revise the prediction. Experiments on CrossNER datasets demonstrated that our model outperforms the strong NERBERT baseline by 2.45 points on average.
Improving Few-Shot Image Classification Using Machine- and User-Generated Natural Language Descriptions
Jul 07, 2022



Abstract:Humans can obtain the knowledge of novel visual concepts from language descriptions, and we thus use the few-shot image classification task to investigate whether a machine learning model can have this capability. Our proposed model, LIDE (Learning from Image and DEscription), has a text decoder to generate the descriptions and a text encoder to obtain the text representations of machine- or user-generated descriptions. We confirmed that LIDE with machine-generated descriptions outperformed baseline models. Moreover, the performance was improved further with high-quality user-generated descriptions. The generated descriptions can be viewed as the explanations of the model's predictions, and we observed that such explanations were consistent with prediction results. We also investigated why the language description improved the few-shot image classification performance by comparing the image representations and the text representations in the feature spaces.
Towards Interpretable and Reliable Reading Comprehension: A Pipeline Model with Unanswerability Prediction
Nov 18, 2021



Abstract:Multi-hop QA with annotated supporting facts, which is the task of reading comprehension (RC) considering the interpretability of the answer, has been extensively studied. In this study, we define an interpretable reading comprehension (IRC) model as a pipeline model with the capability of predicting unanswerable queries. The IRC model justifies the answer prediction by establishing consistency between the predicted supporting facts and the actual rationale for interpretability. The IRC model detects unanswerable questions, instead of outputting the answer forcibly based on the insufficient information, to ensure the reliability of the answer. We also propose an end-to-end training method for the pipeline RC model. To evaluate the interpretability and the reliability, we conducted the experiments considering unanswerability in a multi-hop question for a given passage. We show that our end-to-end trainable pipeline model outperformed a non-interpretable model on our modified HotpotQA dataset. Experimental results also show that the IRC model achieves comparable results to the previous non-interpretable models in spite of the trade-off between prediction performance and interpretability.
* IJCNN 2021 (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9534370)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge