Konstantin Bulatov
MIDV-2020: A Comprehensive Benchmark Dataset for Identity Document Analysis
Jul 01, 2021

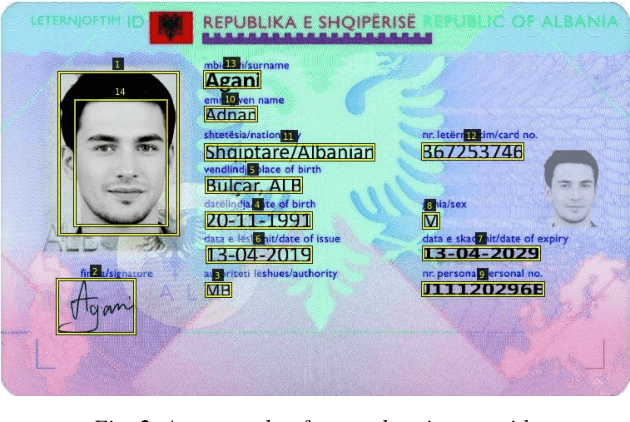
Abstract:Identity documents recognition is an important sub-field of document analysis, which deals with tasks of robust document detection, type identification, text fields recognition, as well as identity fraud prevention and document authenticity validation given photos, scans, or video frames of an identity document capture. Significant amount of research has been published on this topic in recent years, however a chief difficulty for such research is scarcity of datasets, due to the subject matter being protected by security requirements. A few datasets of identity documents which are available lack diversity of document types, capturing conditions, or variability of document field values. In addition, the published datasets were typically designed only for a subset of document recognition problems, not for a complex identity document analysis. In this paper, we present a dataset MIDV-2020 which consists of 1000 video clips, 2000 scanned images, and 1000 photos of 1000 unique mock identity documents, each with unique text field values and unique artificially generated faces, with rich annotation. For the presented benchmark dataset baselines are provided for such tasks as document location and identification, text fields recognition, and face detection. With 72409 annotated images in total, to the date of publication the proposed dataset is the largest publicly available identity documents dataset with variable artificially generated data, and we believe that it will prove invaluable for advancement of the field of document analysis and recognition. The dataset is available for download at ftp://smartengines.com/midv-2020 and http://l3i-share.univ-lr.fr .
Fast Approximate Modelling of the Next Combination Result for Stopping the Text Recognition in a Video
Aug 06, 2020
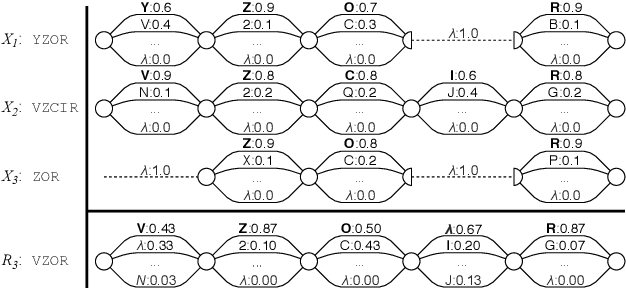
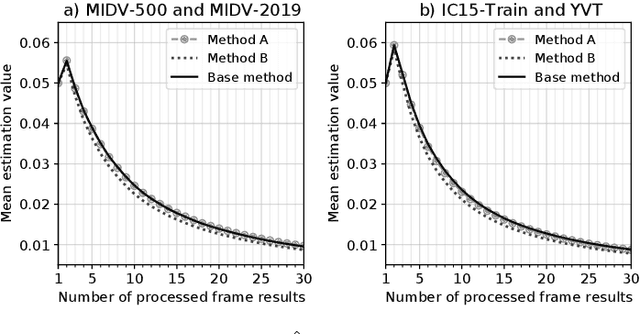
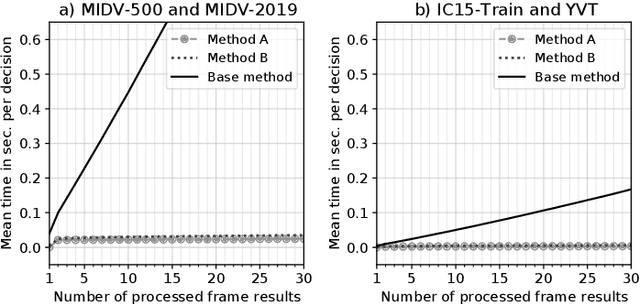
Abstract:In this paper, we consider a task of stopping the video stream recognition process of a text field, in which each frame is recognized independently and the individual results are combined together. The video stream recognition stopping problem is an under-researched topic with regards to computer vision, but its relevance for building high-performance video recognition systems is clear. Firstly, we describe an existing method of optimally stopping such a process based on a modelling of the next combined result. Then, we describe approximations and assumptions which allowed us to build an optimized computation scheme and thus obtain a method with reduced computational complexity. The methods were evaluated for the tasks of document text field recognition and arbitrary text recognition in a video. The experimental comparison shows that the introduced approximations do not diminish the quality of the stopping method in terms of the achieved combined result precision, while dramatically reducing the time required to make the stopping decision. The results were consistent for both text recognition tasks.
Methods of Weighted Combination for Text Field Recognition in a Video Stream
Nov 27, 2019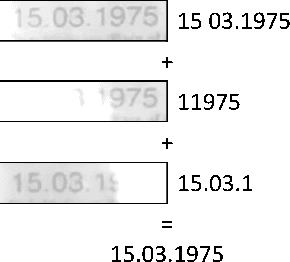
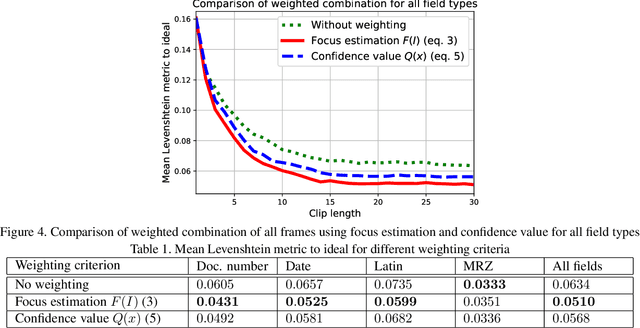
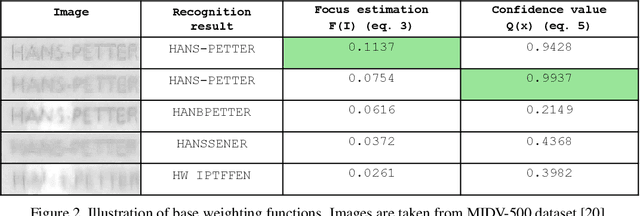
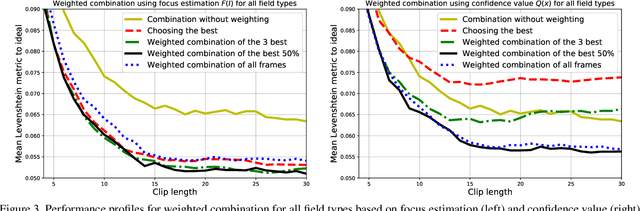
Abstract:Due to a noticeable expansion of document recognition applicability, there is a high demand for recognition on mobile devices. A mobile camera, unlike a scanner, cannot always ensure the absence of various image distortions, therefore the task of improving the recognition precision is relevant. The advantage of mobile devices over scanners is the ability to use video stream input, which allows to get multiple images of a recognized document. Despite this, not enough attention is currently paid to the issue of combining recognition results obtained from different frames when using video stream input. In this paper we propose a weighted text string recognition results combination method and weighting criteria, and provide experimental data for verifying their validity and effectiveness. Based on the obtained results, it is concluded that the use of such weighted combination is appropriate for improving the quality of the video stream recognition result.
Next integrated result modelling for stopping the text field recognition process in a video using a result model with per-character alternatives
Oct 09, 2019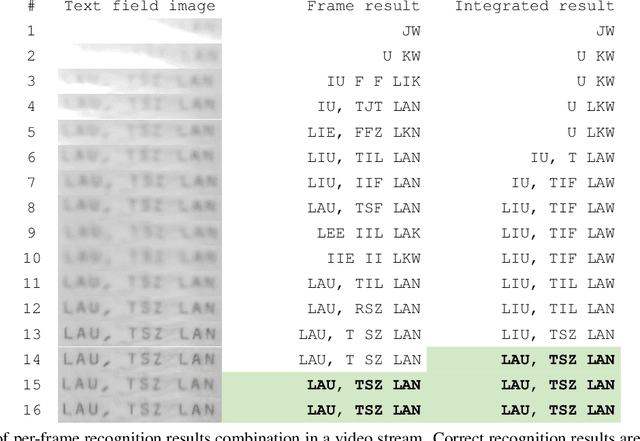
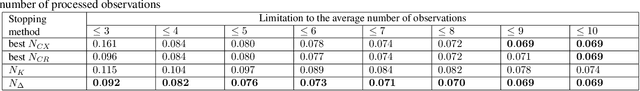
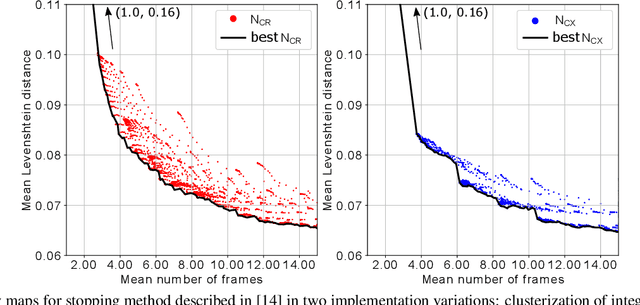
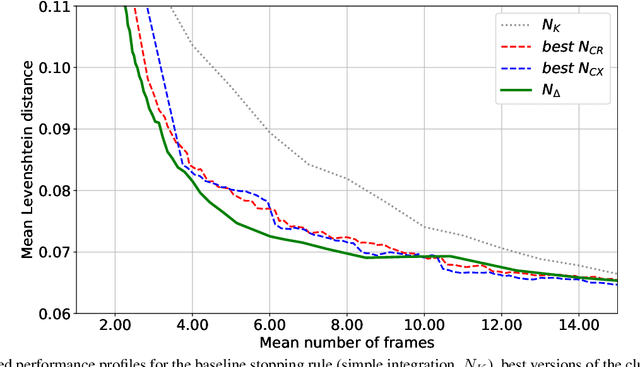
Abstract:In the field of document analysis and recognition using mobile devices for capturing, and the field of object recognition in a video stream, an important problem is determining the time when the capturing process should be stopped. Efficient stopping influences not only the total time spent for performing recognition and data entry, but the expected accuracy of the result as well. This paper is directed on extending the stopping method based on next integrated recognition result modelling, in order for it to be used within a string result recognition model with per-character alternatives. The stopping method and notes on its extension are described, and experimental evaluation is performed on an open dataset MIDV-500. The method was compares with previously published methods based on input observations clustering. The obtained results indicate that the stopping method based on the next integrated result modelling allows to achieve higher accuracy, even when compared with the best achievable configuration of the competing methods.
MIDV-2019: Challenges of the modern mobile-based document OCR
Oct 09, 2019



Abstract:Recognition of identity documents using mobile devices has become a topic of a wide range of computer vision research. The portfolio of methods and algorithms for solving such tasks as face detection, document detection and rectification, text field recognition, and other, is growing, and the scarcity of datasets has become an important issue. One of the openly accessible datasets for evaluating such methods is MIDV-500, containing video clips of 50 identity document types in various conditions. However, the variability of capturing conditions in MIDV-500 did not address some of the key issues, mainly significant projective distortions and different lighting conditions. In this paper we present a MIDV-2019 dataset, containing video clips shot with modern high-resolution mobile cameras, with strong projective distortions and with low lighting conditions. The description of the added data is presented, and experimental baselines for text field recognition in different conditions. The dataset is available for download at ftp://smartengines.com/midv-500/extra/midv-2019/.
A Dataset for Identity Documents Analysis and Recognition on Mobile Devices in Video Stream
Oct 26, 2018
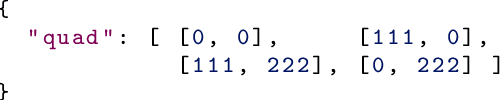
Abstract:A lot of research has been devoted to identity documents analysis and recognition on mobile devices. However, no publicly available datasets designed for this particular problem currently exist. There are a few datasets which are useful for associated subtasks but in order to facilitate a more comprehensive scientific and technical approach to identity documents recognition more specialized datasets are required. In this paper we present a Mobile Identity Document Video dataset (MIDV-500) consisting of 500 video clips for 50 different identity document types with ground truth which allows to perform research in a wide scope of document analysis problems. Since an important feature of identity documents is their sensitiveness as they contain personal data, all source document images used in MIDV-500 are either in public domain or distributed under public copyright licenses. The dataset is available for download at ftp://smartengines.com/midv-500/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge