Vladimir L. Arlazarov
HoughToRadon Transform: New Neural Network Layer for Features Improvement in Projection Space
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce HoughToRadon Transform layer, a novel layer designed to improve the speed of neural networks incorporated with Hough Transform to solve semantic image segmentation problems. By placing it after a Hough Transform layer, "inner" convolutions receive modified feature maps with new beneficial properties, such as a smaller area of processed images and parameter space linearity by angle and shift. These properties were not presented in Hough Transform alone. Furthermore, HoughToRadon Transform layer allows us to adjust the size of intermediate feature maps using two new parameters, thus allowing us to balance the speed and quality of the resulting neural network. Our experiments on the open MIDV-500 dataset show that this new approach leads to time savings in document segmentation tasks and achieves state-of-the-art 97.7% accuracy, outperforming HoughEncoder with larger computational complexity.
Recognition of Images of Korean Characters Using Embedded Networks
Dec 03, 2019


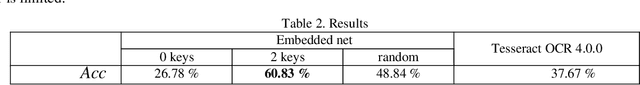
Abstract:Despite the significant success in the field of text recognition, complex and unsolved problems still exist in this field. In recent years, the recognition accuracy of the English language has greatly increased, while the problem of recognition of hieroglyphs has received much less attention. Hieroglyph recognition or image recognition with Korean, Japanese or Chinese characters have differences from the traditional text recognition task. This article discusses the main differences between hieroglyph languages and the Latin alphabet in the context of image recognition. A light-weight method for recognizing images of the hieroglyphs is proposed and tested on a public dataset of Korean hieroglyph images. Despite the existing solutions, the proposed method is suitable for mobile devices. Its recognition accuracy is better than the accuracy of the open-source OCR framework. The presented method of training embedded net bases on the similarities in the recognition data.
Methods of Weighted Combination for Text Field Recognition in a Video Stream
Nov 27, 2019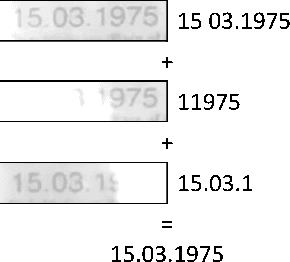
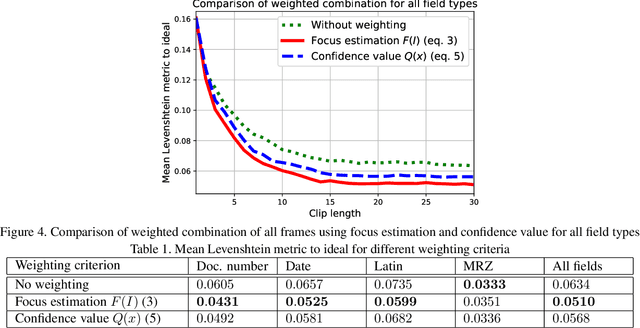
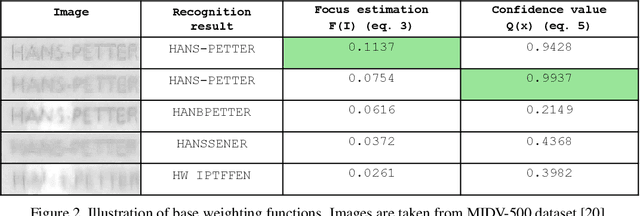
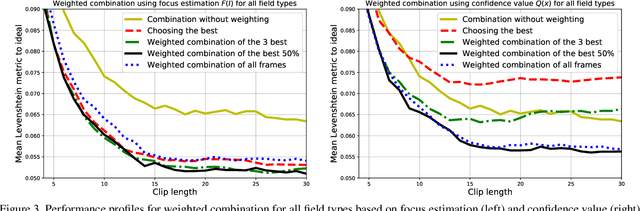
Abstract:Due to a noticeable expansion of document recognition applicability, there is a high demand for recognition on mobile devices. A mobile camera, unlike a scanner, cannot always ensure the absence of various image distortions, therefore the task of improving the recognition precision is relevant. The advantage of mobile devices over scanners is the ability to use video stream input, which allows to get multiple images of a recognized document. Despite this, not enough attention is currently paid to the issue of combining recognition results obtained from different frames when using video stream input. In this paper we propose a weighted text string recognition results combination method and weighting criteria, and provide experimental data for verifying their validity and effectiveness. Based on the obtained results, it is concluded that the use of such weighted combination is appropriate for improving the quality of the video stream recognition result.
A Dataset for Identity Documents Analysis and Recognition on Mobile Devices in Video Stream
Oct 26, 2018
Abstract:A lot of research has been devoted to identity documents analysis and recognition on mobile devices. However, no publicly available datasets designed for this particular problem currently exist. There are a few datasets which are useful for associated subtasks but in order to facilitate a more comprehensive scientific and technical approach to identity documents recognition more specialized datasets are required. In this paper we present a Mobile Identity Document Video dataset (MIDV-500) consisting of 500 video clips for 50 different identity document types with ground truth which allows to perform research in a wide scope of document analysis problems. Since an important feature of identity documents is their sensitiveness as they contain personal data, all source document images used in MIDV-500 are either in public domain or distributed under public copyright licenses. The dataset is available for download at ftp://smartengines.com/midv-500/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge