Daniil Tropin
MIDV-2020: A Comprehensive Benchmark Dataset for Identity Document Analysis
Jul 01, 2021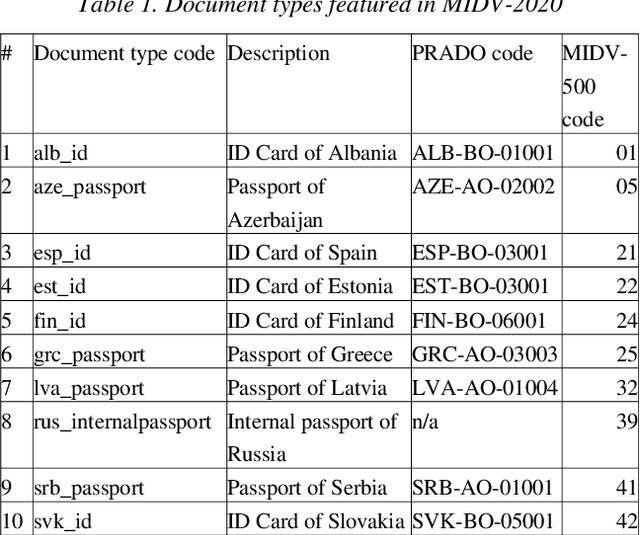

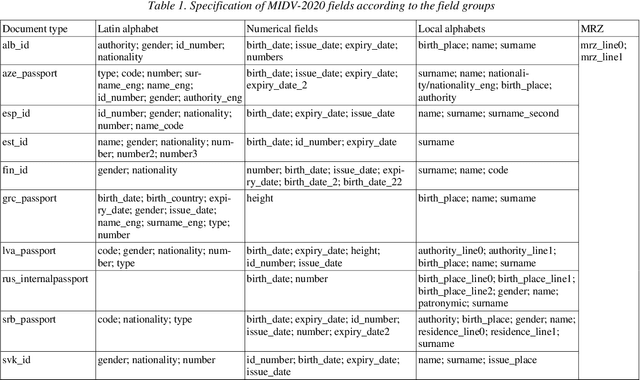
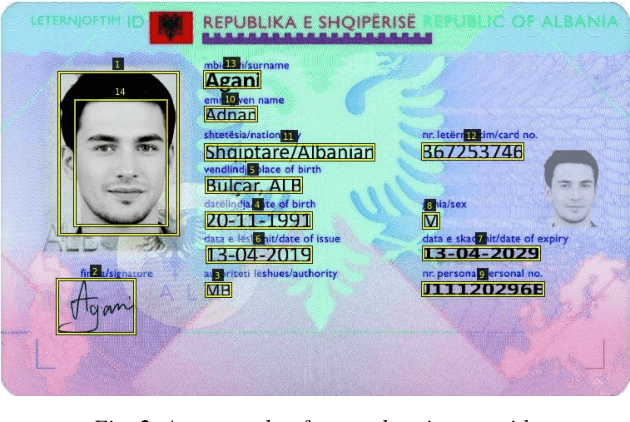
Abstract:Identity documents recognition is an important sub-field of document analysis, which deals with tasks of robust document detection, type identification, text fields recognition, as well as identity fraud prevention and document authenticity validation given photos, scans, or video frames of an identity document capture. Significant amount of research has been published on this topic in recent years, however a chief difficulty for such research is scarcity of datasets, due to the subject matter being protected by security requirements. A few datasets of identity documents which are available lack diversity of document types, capturing conditions, or variability of document field values. In addition, the published datasets were typically designed only for a subset of document recognition problems, not for a complex identity document analysis. In this paper, we present a dataset MIDV-2020 which consists of 1000 video clips, 2000 scanned images, and 1000 photos of 1000 unique mock identity documents, each with unique text field values and unique artificially generated faces, with rich annotation. For the presented benchmark dataset baselines are provided for such tasks as document location and identification, text fields recognition, and face detection. With 72409 annotated images in total, to the date of publication the proposed dataset is the largest publicly available identity documents dataset with variable artificially generated data, and we believe that it will prove invaluable for advancement of the field of document analysis and recognition. The dataset is available for download at ftp://smartengines.com/midv-2020 and http://l3i-share.univ-lr.fr .
Fast Projective Image Rectification for Planar Objects with Manhattan Structure
Dec 04, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents a method for metric rectification of planar objects that preserves angles and length ratios. An inner structure of an object is assumed to follow the laws of Manhattan World i.e. the majority of line segments are aligned with two orthogonal directions of the object. For that purpose we introduce the method that estimates the position of two vanishing points corresponding to the main object directions. It is based on an original optimization function of segments that estimates a vanishing point position. For calculation of the rectification homography with two vanishing points we propose a new method based on estimation of the camera rotation so that the camera axis is perpendicular to the object plane. The proposed method can be applied for rectification of various objects such as documents or building facades. Also since the camera rotation is estimated the method can be employed for estimation of object orientation (for example, during a surgery with radiograph of osteosynthesis implants). The method was evaluated on the MIDV-500 dataset containing projectively distorted images of documents with complex background. According to the experimental results an accuracy of the proposed method is better or equal to the-state-of-the-art if the background occupies no more than half of the image. Runtime of the method is around 3ms on core i7 3610qm CPU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge