Kohitij Kar
Better, But Not Sufficient: Testing Video ANNs Against Macaque IT Dynamics
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Feedforward artificial neural networks (ANNs) trained on static images remain the dominant models of the the primate ventral visual stream, yet they are intrinsically limited to static computations. The primate world is dynamic, and the macaque ventral visual pathways, specifically the inferior temporal (IT) cortex not only supports object recognition but also encodes object motion velocity during naturalistic video viewing. Does IT's temporal responses reflect nothing more than time-unfolded feedforward transformations, framewise features with shallow temporal pooling, or do they embody richer dynamic computations? We tested this by comparing macaque IT responses during naturalistic videos against static, recurrent, and video-based ANN models. Video models provided modest improvements in neural predictivity, particularly at later response stages, raising the question of what kind of dynamics they capture. To probe this, we applied a stress test: decoders trained on naturalistic videos were evaluated on "appearance-free" variants that preserve motion but remove shape and texture. IT population activity generalized across this manipulation, but all ANN classes failed. Thus, current video models better capture appearance-bound dynamics rather than the appearance-invariant temporal computations expressed in IT, underscoring the need for new objectives that encode biological temporal statistics and invariances.
RTify: Aligning Deep Neural Networks with Human Behavioral Decisions
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:Current neural network models of primate vision focus on replicating overall levels of behavioral accuracy, often neglecting perceptual decisions' rich, dynamic nature. Here, we introduce a novel computational framework to model the dynamics of human behavioral choices by learning to align the temporal dynamics of a recurrent neural network (RNN) to human reaction times (RTs). We describe an approximation that allows us to constrain the number of time steps an RNN takes to solve a task with human RTs. The approach is extensively evaluated against various psychophysics experiments. We also show that the approximation can be used to optimize an "ideal-observer" RNN model to achieve an optimal tradeoff between speed and accuracy without human data. The resulting model is found to account well for human RT data. Finally, we use the approximation to train a deep learning implementation of the popular Wong-Wang decision-making model. The model is integrated with a convolutional neural network (CNN) model of visual processing and evaluated using both artificial and natural image stimuli. Overall, we present a novel framework that helps align current vision models with human behavior, bringing us closer to an integrated model of human vision.
Brain-Like Object Recognition with High-Performing Shallow Recurrent ANNs
Oct 28, 2019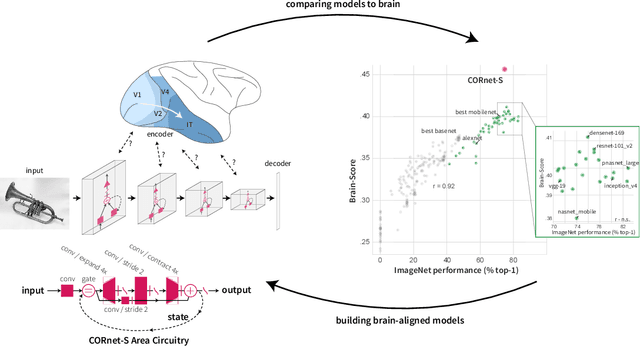
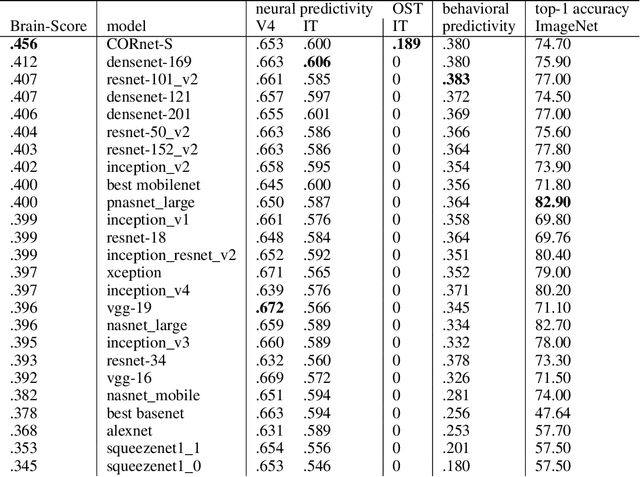
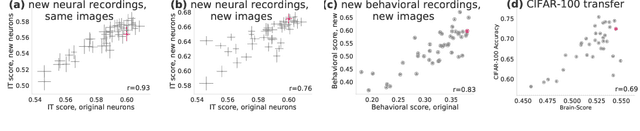

Abstract:Deep convolutional artificial neural networks (ANNs) are the leading class of candidate models of the mechanisms of visual processing in the primate ventral stream. While initially inspired by brain anatomy, over the past years, these ANNs have evolved from a simple eight-layer architecture in AlexNet to extremely deep and branching architectures, demonstrating increasingly better object categorization performance, yet bringing into question how brain-like they still are. In particular, typical deep models from the machine learning community are often hard to map onto the brain's anatomy due to their vast number of layers and missing biologically-important connections, such as recurrence. Here we demonstrate that better anatomical alignment to the brain and high performance on machine learning as well as neuroscience measures do not have to be in contradiction. We developed CORnet-S, a shallow ANN with four anatomically mapped areas and recurrent connectivity, guided by Brain-Score, a new large-scale composite of neural and behavioral benchmarks for quantifying the functional fidelity of models of the primate ventral visual stream. Despite being significantly shallower than most models, CORnet-S is the top model on Brain-Score and outperforms similarly compact models on ImageNet. Moreover, our extensive analyses of CORnet-S circuitry variants reveal that recurrence is the main predictive factor of both Brain-Score and ImageNet top-1 performance. Finally, we report that the temporal evolution of the CORnet-S "IT" neural population resembles the actual monkey IT population dynamics. Taken together, these results establish CORnet-S, a compact, recurrent ANN, as the current best model of the primate ventral visual stream.
Task-Driven Convolutional Recurrent Models of the Visual System
Oct 27, 2018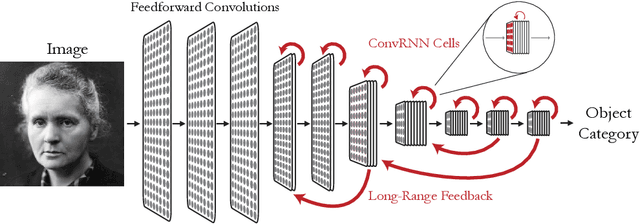
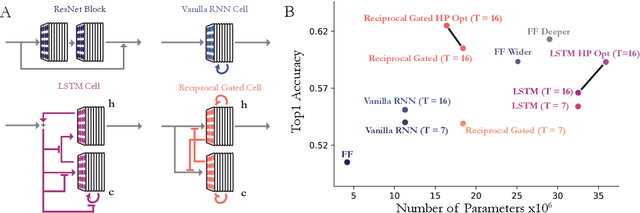
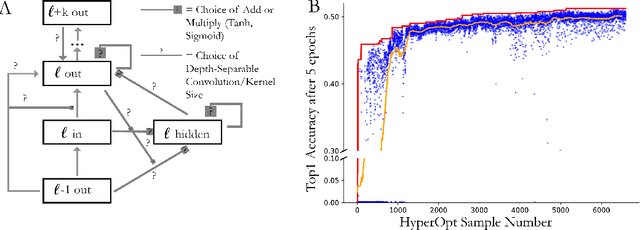
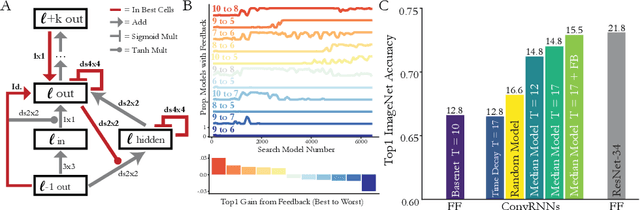
Abstract:Feed-forward convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are currently state-of-the-art for object classification tasks such as ImageNet. Further, they are quantitatively accurate models of temporally-averaged responses of neurons in the primate brain's visual system. However, biological visual systems have two ubiquitous architectural features not shared with typical CNNs: local recurrence within cortical areas, and long-range feedback from downstream areas to upstream areas. Here we explored the role of recurrence in improving classification performance. We found that standard forms of recurrence (vanilla RNNs and LSTMs) do not perform well within deep CNNs on the ImageNet task. In contrast, novel cells that incorporated two structural features, bypassing and gating, were able to boost task accuracy substantially. We extended these design principles in an automated search over thousands of model architectures, which identified novel local recurrent cells and long-range feedback connections useful for object recognition. Moreover, these task-optimized ConvRNNs matched the dynamics of neural activity in the primate visual system better than feedforward networks, suggesting a role for the brain's recurrent connections in performing difficult visual behaviors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge