Kim Hoang Tran
Enhanced Kalman with Adaptive Appearance Motion SORT for Grounded Generic Multiple Object Tracking
Oct 11, 2024
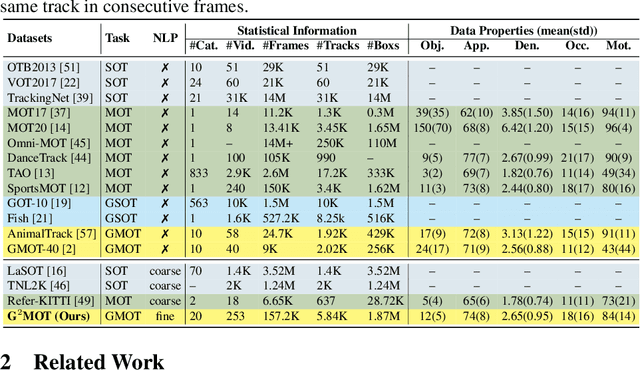
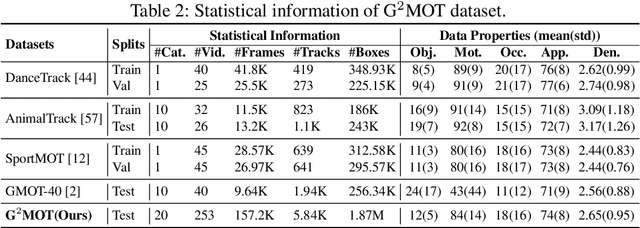

Abstract:Despite recent progress, Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) continues to face significant challenges, particularly its dependence on prior knowledge and predefined categories, complicating the tracking of unfamiliar objects. Generic Multiple Object Tracking (GMOT) emerges as a promising solution, requiring less prior information. Nevertheless, existing GMOT methods, primarily designed as OneShot-GMOT, rely heavily on initial bounding boxes and often struggle with variations in viewpoint, lighting, occlusion, and scale. To overcome the limitations inherent in both MOT and GMOT when it comes to tracking objects with specific generic attributes, we introduce Grounded-GMOT, an innovative tracking paradigm that enables users to track multiple generic objects in videos through natural language descriptors. Our contributions begin with the introduction of the G2MOT dataset, which includes a collection of videos featuring a wide variety of generic objects, each accompanied by detailed textual descriptions of their attributes. Following this, we propose a novel tracking method, KAM-SORT, which not only effectively integrates visual appearance with motion cues but also enhances the Kalman filter. KAM-SORT proves particularly advantageous when dealing with objects of high visual similarity from the same generic category in GMOT scenarios. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that Grounded-GMOT outperforms existing OneShot-GMOT approaches. Additionally, our extensive comparisons between various trackers highlight KAM-SORT's efficacy in GMOT, further establishing its significance in the field. Project page: https://UARK-AICV.github.io/G2MOT. The source code and dataset will be made publicly available.
TP-GMOT: Tracking Generic Multiple Object by Textual Prompt with Motion-Appearance Cost (MAC) SORT
Sep 04, 2024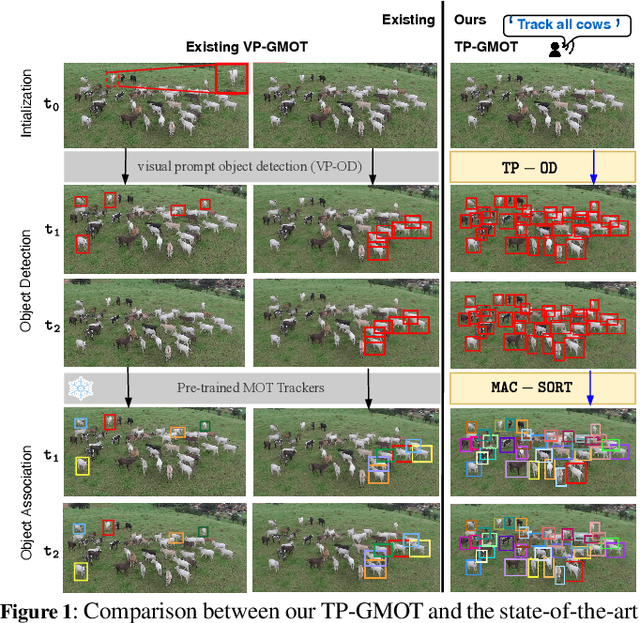
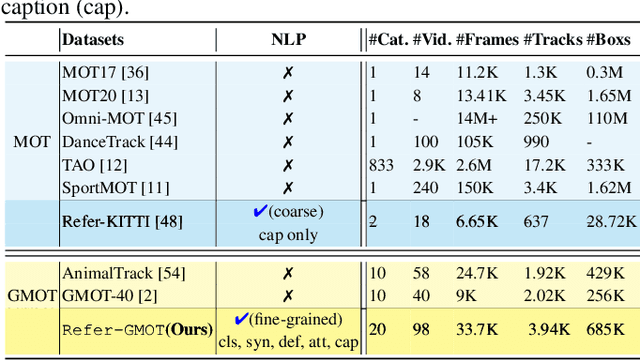

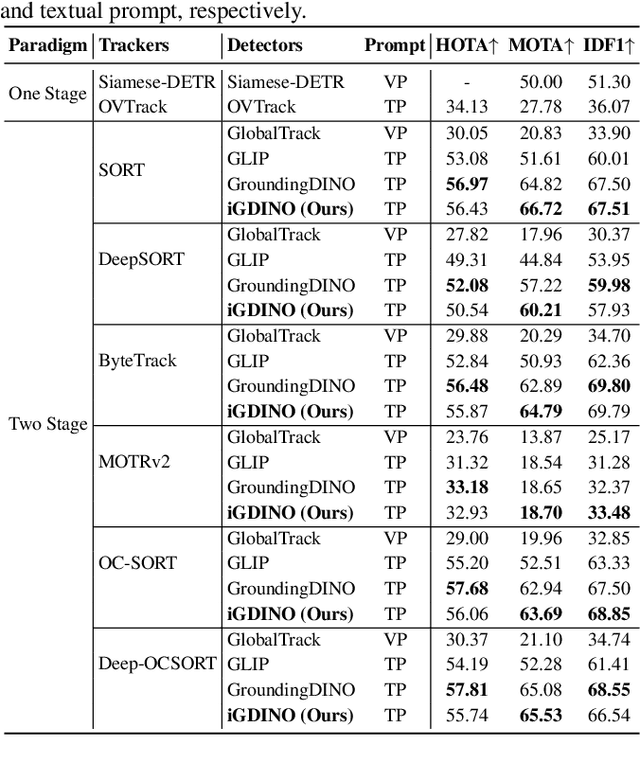
Abstract:While Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) has made substantial advancements, it is limited by heavy reliance on prior knowledge and limited to predefined categories. In contrast, Generic Multiple Object Tracking (GMOT), tracking multiple objects with similar appearance, requires less prior information about the targets but faces challenges with variants like viewpoint, lighting, occlusion, and resolution. Our contributions commence with the introduction of the \textbf{\text{Refer-GMOT dataset}} a collection of videos, each accompanied by fine-grained textual descriptions of their attributes. Subsequently, we introduce a novel text prompt-based open-vocabulary GMOT framework, called \textbf{\text{TP-GMOT}}, which can track never-seen object categories with zero training examples. Within \text{TP-GMOT} framework, we introduce two novel components: (i) {\textbf{\text{TP-OD}}, an object detection by a textual prompt}, for accurately detecting unseen objects with specific characteristics. (ii) Motion-Appearance Cost SORT \textbf{\text{MAC-SORT}}, a novel object association approach that adeptly integrates motion and appearance-based matching strategies to tackle the complex task of tracking multiple generic objects with high similarity. Our contributions are benchmarked on the \text{Refer-GMOT} dataset for GMOT task. Additionally, to assess the generalizability of the proposed \text{TP-GMOT} framework and the effectiveness of \text{MAC-SORT} tracker, we conduct ablation studies on the DanceTrack and MOT20 datasets for the MOT task. Our dataset, code, and models will be publicly available at: https://fsoft-aic.github.io/TP-GMOT
Unifying Global and Local Scene Entities Modelling for Precise Action Spotting
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Sports videos pose complex challenges, including cluttered backgrounds, camera angle changes, small action-representing objects, and imbalanced action class distribution. Existing methods for detecting actions in sports videos heavily rely on global features, utilizing a backbone network as a black box that encompasses the entire spatial frame. However, these approaches tend to overlook the nuances of the scene and struggle with detecting actions that occupy a small portion of the frame. In particular, they face difficulties when dealing with action classes involving small objects, such as balls or yellow/red cards in soccer, which only occupy a fraction of the screen space. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel approach that analyzes and models scene entities using an adaptive attention mechanism. Particularly, our model disentangles the scene content into the global environment feature and local relevant scene entities feature. To efficiently extract environmental features while considering temporal information with less computational cost, we propose the use of a 2D backbone network with a time-shift mechanism. To accurately capture relevant scene entities, we employ a Vision-Language model in conjunction with the adaptive attention mechanism. Our model has demonstrated outstanding performance, securing the 1st place in the SoccerNet-v2 Action Spotting, FineDiving, and FineGym challenge with a substantial performance improvement of 1.6, 2.0, and 1.3 points in avg-mAP compared to the runner-up methods. Furthermore, our approach offers interpretability capabilities in contrast to other deep learning models, which are often designed as black boxes. Our code and models are released at: https://github.com/Fsoft-AIC/unifying-global-local-feature.
Z-GMOT: Zero-shot Generic Multiple Object Tracking
May 28, 2023Abstract:Despite the significant progress made in recent years, Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) approaches still suffer from several limitations, including their reliance on prior knowledge of tracking targets, which necessitates the costly annotation of large labeled datasets. As a result, existing MOT methods are limited to a small set of predefined categories, and they struggle with unseen objects in the real world. To address these issues, Generic Multiple Object Tracking (GMOT) has been proposed, which requires less prior information about the targets. However, all existing GMOT approaches follow a one-shot paradigm, relying mainly on the initial bounding box and thus struggling to handle variants e.g., viewpoint, lighting, occlusion, scale, and etc. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to address the limitations of existing MOT and GMOT methods. Specifically, we propose a zero-shot GMOT (Z-GMOT) algorithm that can track never-seen object categories with zero training examples, without the need for predefined categories or an initial bounding box. To achieve this, we propose iGLIP, an improved version of Grounded language-image pretraining (GLIP), which can detect unseen objects while minimizing false positives. We evaluate our Z-GMOT thoroughly on the GMOT-40 dataset, AnimalTrack testset, DanceTrack testset. The results of these evaluations demonstrate a significant improvement over existing methods. For instance, on the GMOT-40 dataset, the Z-GMOT outperforms one-shot GMOT with OC-SORT by 27.79 points HOTA and 44.37 points MOTA. On the AnimalTrack dataset, it surpasses fully-supervised methods with DeepSORT by 12.55 points HOTA and 8.97 points MOTA. To facilitate further research, we will make our code and models publicly available upon acceptance of this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge