Kim
A State-of-the-art Survey on Full-duplex Network Design
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:Full-duplex (FD) technology is gaining popularity for integration into a wide range of wireless networks due to its demonstrated potential in recent studies. In contrast to half-duplex (HD) technology, the implementation of FD in networks necessitates considering inter-node interference (INI) from various network perspectives. When deploying FD technology in networks, several critical factors must be taken into account. These include self-interference (SI) and the requisite SI cancellation (SIC) processes, as well as the selection of multiple user equipment (UE) per time slot. Additionally, inter-node interference (INI), including cross-link interference (CLI) and inter-cell interference (ICI), become crucial issues during concurrent uplink (UL) and downlink (DL) transmission and reception, similar to SI. Since most INI is challenging to eliminate, a comprehensive investigation that covers radio resource control (RRC), medium access control (MAC), and the physical layer (PHY) is essential in the context of FD network design, rather than focusing on individual network layers and types. This paper covers state-of-the-art studies, including protocols and documents from 3GPP for FD, MAC protocol, user scheduling, and CLI handling. The methods are also compared through a network-level system simulation based on 3D ray-tracing.
AoA-based Position and Orientation Estimation Using Lens MIMO in Cooperative Vehicle-to-Vehicle Systems
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Positioning accuracy is a critical requirement for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) use cases. Therefore, this paper derives the theoretical limits of estimation for the position and orientation of vehicles in a cooperative vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) scenario, using a lens-based multiple-input multiple-output (lens-MIMO) system. Following this, we analyze the Cram$\acute{\text{e}}$r-Rao lower bounds (CRLBs) of the position and orientation estimation and explore a received signal model of a lens-MIMO for the particular angle of arrival (AoA) estimation with a V2V geometric model. Further, we propose a lower complexity AoA estimation technique exploiting the unique characteristics of the lens-MIMO for a single target vehicle; as a result, its estimation scheme is effectively extended by the successive interference cancellation (SIC) method for multiple target vehicles. Given these AoAs, we investigate the lens-MIMO estimation capability for the positions and orientations of vehicles. Subsequently, we prove that the lens-MIMO outperforms a conventional uniform linear array (ULA) in a certain configuration of a lens's structure. Finally, we confirm that the proposed localization algorithm is superior to ULA's CRLB as the resolution of the lens increases in spite of the lower complexity.
Toward Compact Data from Big Data
Dec 26, 2020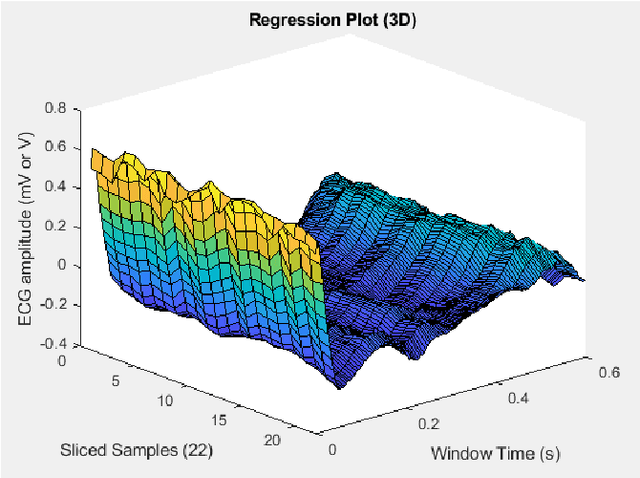
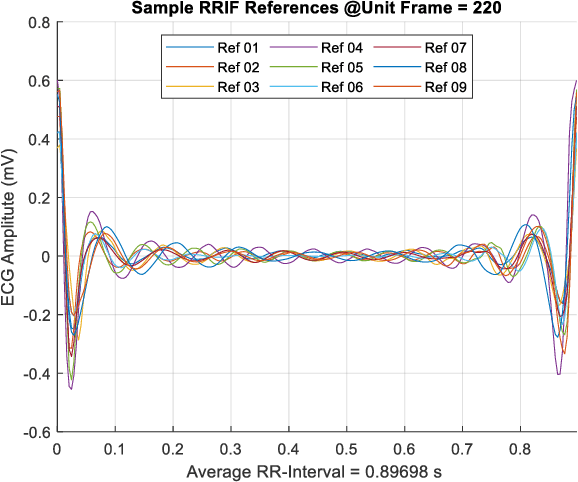
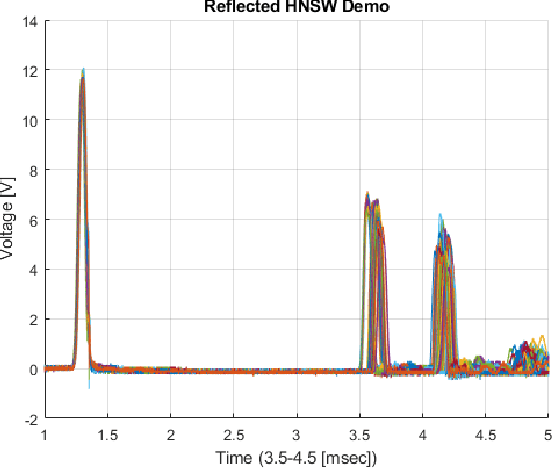
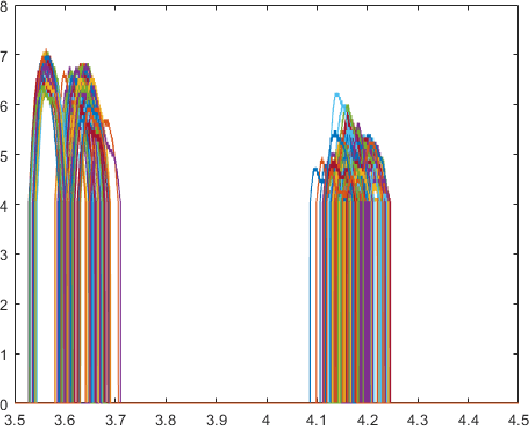
Abstract:Bigdata is a dataset of which size is beyond the ability of handling a valuable raw material that can be refined and distilled into valuable specific insights. Compact data is a method that optimizes the big dataset that gives best assets without handling complex bigdata. The compact dataset contains the maximum knowledge patterns at fine grained level for effective and personalized utilization of bigdata systems without bigdata. The compact data method is a tailor-made design which depends on problem situations. Various compact data techniques have been demonstrated into various data-driven research area in the paper.
An Enhanced Machine Learning-based Biometric Authentication System Using RR-Interval Framed Electrocardiograms
Aug 07, 2019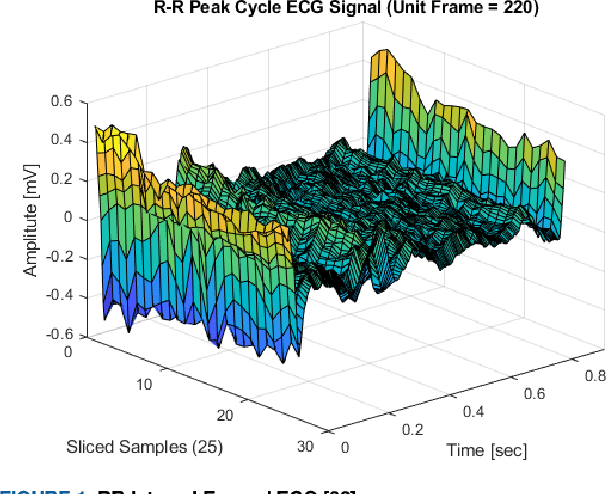
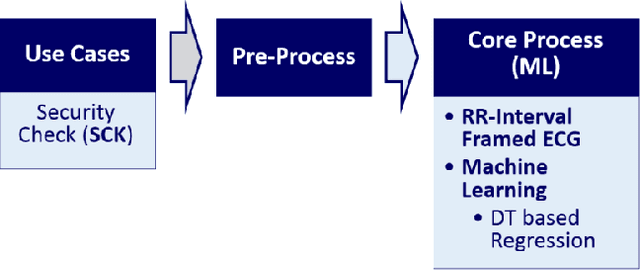
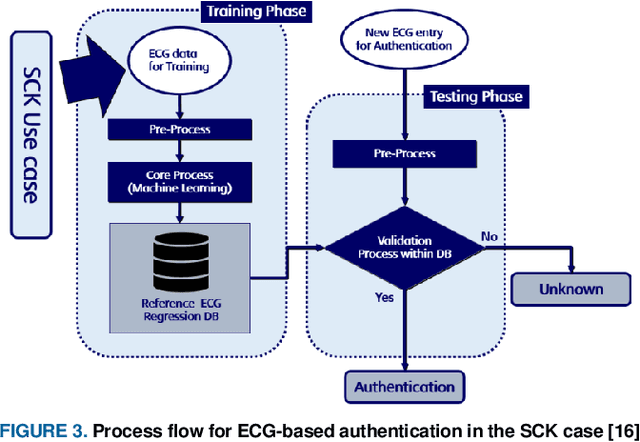
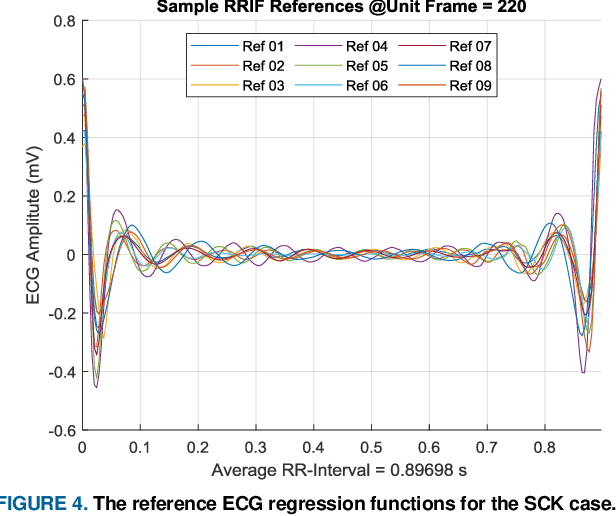
Abstract:This paper is targeted in the area of biometric data enabled security system based on the machine learning for the digital health. The disadvantages of traditional authentication systems include the risks of forgetfulness, loss, and theft. Biometric authentication is therefore rapidly replacing traditional authentication methods and is becoming an everyday part of life. The electrocardiogram (ECG) was recently introduced as a biometric authentication system suitable for security checks. The proposed authentication system helps investigators studying ECG-based biometric authentication techniques to reshape input data by slicing based on the RR-interval, and defines the Overall Performance (OP), which is the combined performance metric of multiple authentication measures. We evaluated the performance of the proposed system using a confusion matrix and achieved up to 95% accuracy by compact data analysis. We also used the Amang ECG (amgecg) toolbox in MATLAB to investigate the upper-range control limit (UCL) based on the mean square error, which directly affects three authentication performance metrics: the accuracy, the number of accepted samples, and the OP. Using this approach, we found that the OP can be optimized by using a UCL of 0.0028, which indicates 61 accepted samples out of 70 and ensures that the proposed authentication system achieves an accuracy of 95%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge