Kiho Kwak
METAVerse: Meta-Learning Traversability Cost Map for Off-Road Navigation
Jul 26, 2023Abstract:Autonomous navigation in off-road conditions requires an accurate estimation of terrain traversability. However, traversability estimation in unstructured environments is subject to high uncertainty due to the variability of numerous factors that influence vehicle-terrain interaction. Consequently, it is challenging to obtain a generalizable model that can accurately predict traversability in a variety of environments. This paper presents METAVerse, a meta-learning framework for learning a global model that accurately and reliably predicts terrain traversability across diverse environments. We train the traversability prediction network to generate a dense and continuous-valued cost map from a sparse LiDAR point cloud, leveraging vehicle-terrain interaction feedback in a self-supervised manner. Meta-learning is utilized to train a global model with driving data collected from multiple environments, effectively minimizing estimation uncertainty. During deployment, online adaptation is performed to rapidly adapt the network to the local environment by exploiting recent interaction experiences. To conduct a comprehensive evaluation, we collect driving data from various terrains and demonstrate that our method can obtain a global model that minimizes uncertainty. Moreover, by integrating our model with a model predictive controller, we demonstrate that the reduced uncertainty results in safe and stable navigation in unstructured and unknown terrains.
Uncertainty Reduction for 3D Point Cloud Self-Supervised Traversability Estimation
Nov 21, 2022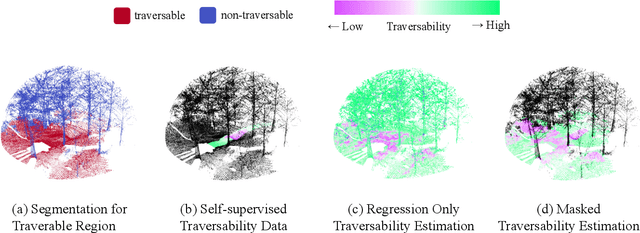
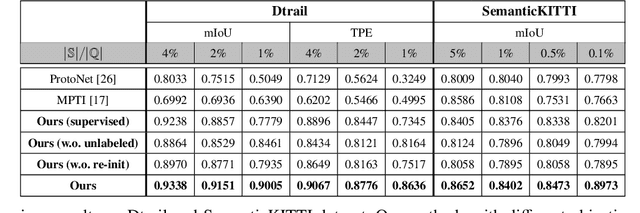
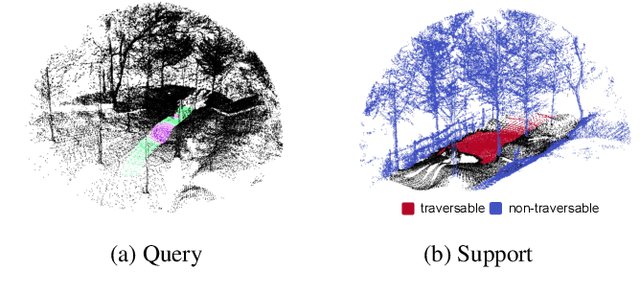
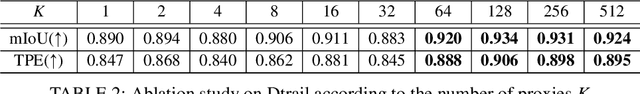
Abstract:Traversability estimation in off-road environments requires a robust perception system. Recently, approaches to learning a traversability estimation from past vehicle experiences in a self-supervised manner are arising as they can greatly reduce human labeling costs and labeling errors. Nonetheless, the learning setting from self-supervised traversability estimation suffers from congenital uncertainties that appear according to the scarcity of negative information. Negative data are rarely harvested as the system can be severely damaged while logging the data. To mitigate the uncertainty, we introduce a method to incorporate unlabeled data in order to leverage the uncertainty. First, we design a learning architecture that inputs query and support data. Second, unlabeled data are assigned based on the proximity in the metric space. Third, a new metric for uncertainty measures is introduced. We evaluated our approach on our own dataset, `Dtrail', which is composed of a wide variety of negative data.
ScaTE: A Scalable Framework for Self-Supervised Traversability Estimation in Unstructured Environments
Sep 14, 2022



Abstract:For the safe and successful navigation of autonomous vehicles in unstructured environments, the traversability of terrain should vary based on the driving capabilities of the vehicles. Actual driving experience can be utilized in a self-supervised fashion to learn vehicle-specific traversability. However, existing methods for learning self-supervised traversability are not highly scalable for learning the traversability of various vehicles. In this work, we introduce a scalable framework for learning self-supervised traversability, which can learn the traversability directly from vehicle-terrain interaction without any human supervision. We train a neural network that predicts the proprioceptive experience that a vehicle would undergo from 3D point clouds. Using a novel PU learning method, the network simultaneously identifies non-traversable regions where estimations can be overconfident. With driving data of various vehicles gathered from simulation and the real world, we show that our framework is capable of learning the self-supervised traversability of various vehicles. By integrating our framework with a model predictive controller, we demonstrate that estimated traversability results in effective navigation that enables distinct maneuvers based on the driving characteristics of the vehicles. In addition, experimental results validate the ability of our method to identify and avoid non-traversable regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge