Kezi Yu
Online Meta-Learning on Non-convex Setting
Oct 22, 2019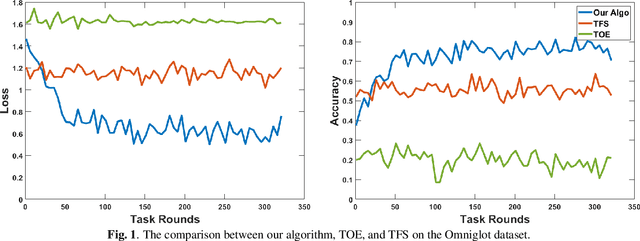
Abstract:The online meta-learning framework is designed for the continual lifelong learning setting. It bridges two fields: meta-learning which tries to extract prior knowledge from existing tasks for fast learning of future tasks, and online-learning which focuses on the sequential setting in which problems are revealed one by one. In this paper, we generalize the original framework from convex to non-convex setting, and introduce the local regret as the alternative performance measure. We then apply this framework to stochastic settings, and show theoretically that it enjoys a logarithmic local regret, and is robust to any hyperparameter initialization. The empirical test on a real-world task demonstrates its superiority compared with traditional methods.
Rare Disease Detection by Sequence Modeling with Generative Adversarial Networks
Jul 01, 2019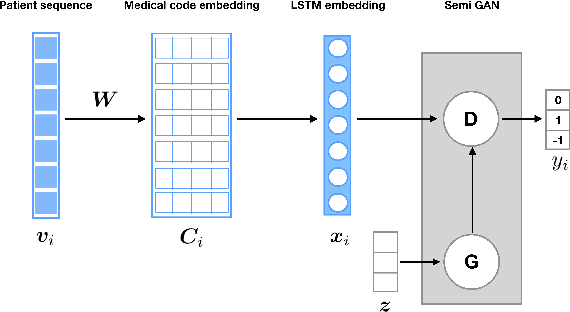
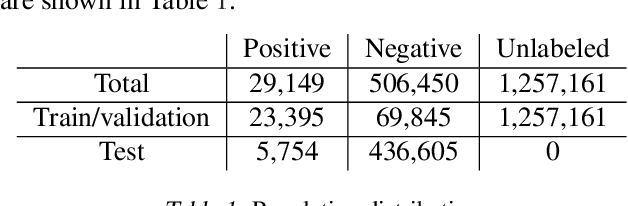
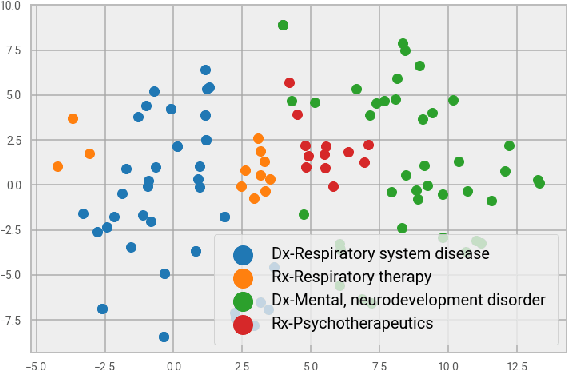
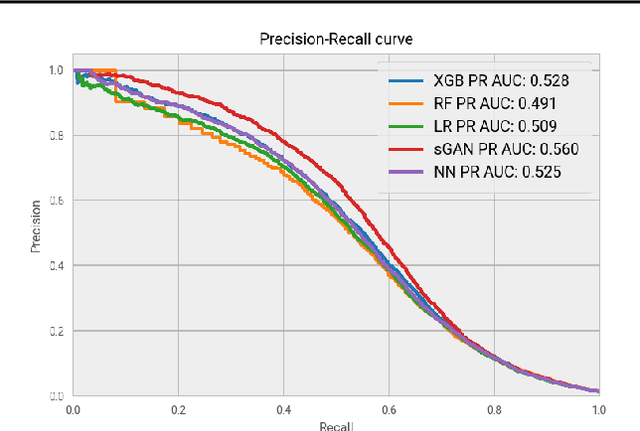
Abstract:Rare diseases affecting 350 million individuals are commonly associated with delay in diagnosis or misdiagnosis. To improve those patients' outcome, rare disease detection is an important task for identifying patients with rare conditions based on longitudinal medical claims. In this paper, we present a deep learning method for detecting patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) (a rare disease). The contribution includes 1) a large longitudinal study using 7 years medical claims from 1.8 million patients including 29,149 EPI patients, 2) a new deep learning model using generative adversarial networks (GANs) to boost rare disease class, and also leveraging recurrent neural networks to model patient sequence data, 3) an accurate prediction with 0.56 PR-AUC which outperformed benchmark models in terms of precision and recall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge