Keyan Guo
AI-Cybersecurity Education Through Designing AI-based Cyberharassment Detection Lab
May 16, 2024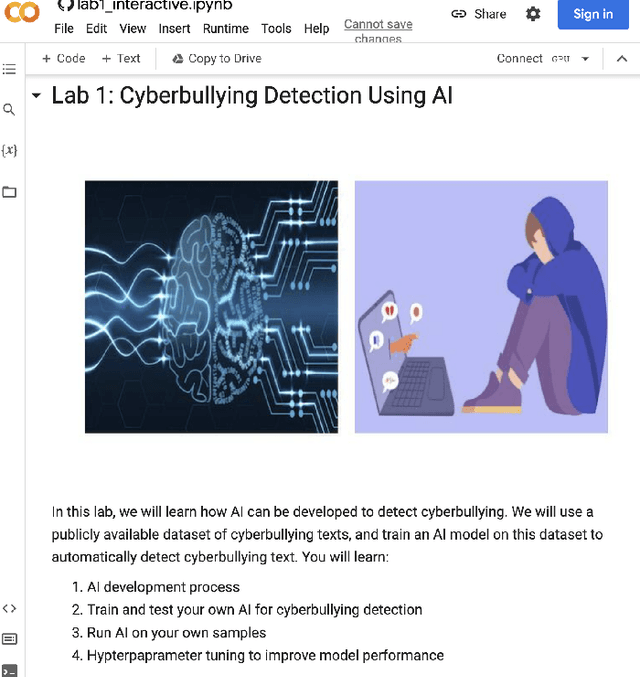


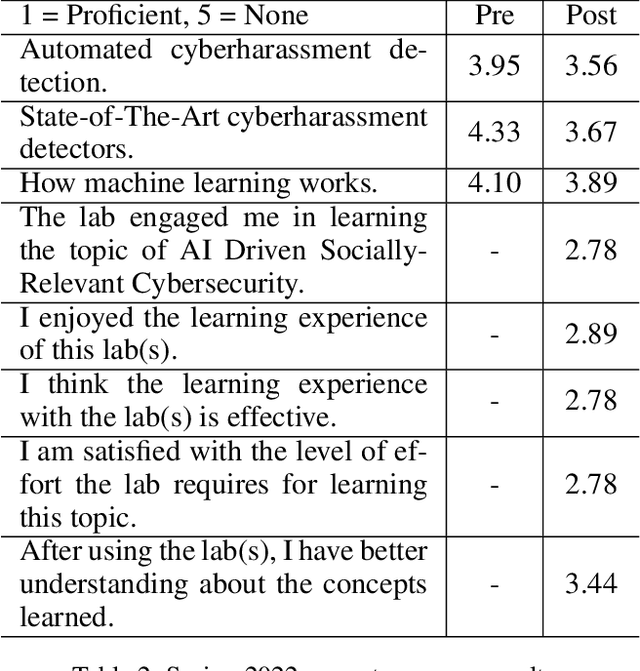
Abstract:Cyberharassment is a critical, socially relevant cybersecurity problem because of the adverse effects it can have on targeted groups or individuals. While progress has been made in understanding cyber-harassment, its detection, attacks on artificial intelligence (AI) based cyberharassment systems, and the social problems in cyberharassment detectors, little has been done in designing experiential learning educational materials that engage students in this emerging social cybersecurity in the era of AI. Experiential learning opportunities are usually provided through capstone projects and engineering design courses in STEM programs such as computer science. While capstone projects are an excellent example of experiential learning, given the interdisciplinary nature of this emerging social cybersecurity problem, it can be challenging to use them to engage non-computing students without prior knowledge of AI. Because of this, we were motivated to develop a hands-on lab platform that provided experiential learning experiences to non-computing students with little or no background knowledge in AI and discussed the lessons learned in developing this lab. In this lab used by social science students at North Carolina A&T State University across two semesters (spring and fall) in 2022, students are given a detailed lab manual and are to complete a set of well-detailed tasks. Through this process, students learn AI concepts and the application of AI for cyberharassment detection. Using pre- and post-surveys, we asked students to rate their knowledge or skills in AI and their understanding of the concepts learned. The results revealed that the students moderately understood the concepts of AI and cyberharassment.
Moderating Illicit Online Image Promotion for Unsafe User-Generated Content Games Using Large Vision-Language Models
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:Online user-generated content games (UGCGs) are increasingly popular among children and adolescents for social interaction and more creative online entertainment. However, they pose a heightened risk of exposure to explicit content, raising growing concerns for the online safety of children and adolescents. Despite these concerns, few studies have addressed the issue of illicit image-based promotions of unsafe UGCGs on social media, which can inadvertently attract young users. This challenge arises from the difficulty of obtaining comprehensive training data for UGCG images and the unique nature of these images, which differ from traditional unsafe content. In this work, we take the first step towards studying the threat of illicit promotions of unsafe UGCGs. We collect a real-world dataset comprising 2,924 images that display diverse sexually explicit and violent content used to promote UGCGs by their game creators. Our in-depth studies reveal a new understanding of this problem and the urgent need for automatically flagging illicit UGCG promotions. We additionally create a cutting-edge system, UGCG-Guard, designed to aid social media platforms in effectively identifying images used for illicit UGCG promotions. This system leverages recently introduced large vision-language models (VLMs) and employs a novel conditional prompting strategy for zero-shot domain adaptation, along with chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning for contextual identification. UGCG-Guard achieves outstanding results, with an accuracy rate of 94% in detecting these images used for the illicit promotion of such games in real-world scenarios.
An Investigation of Large Language Models for Real-World Hate Speech Detection
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:Hate speech has emerged as a major problem plaguing our social spaces today. While there have been significant efforts to address this problem, existing methods are still significantly limited in effectively detecting hate speech online. A major limitation of existing methods is that hate speech detection is a highly contextual problem, and these methods cannot fully capture the context of hate speech to make accurate predictions. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in several natural language tasks. LLMs have undergone extensive training using vast amounts of natural language data, enabling them to grasp intricate contextual details. Hence, they could be used as knowledge bases for context-aware hate speech detection. However, a fundamental problem with using LLMs to detect hate speech is that there are no studies on effectively prompting LLMs for context-aware hate speech detection. In this study, we conduct a large-scale study of hate speech detection, employing five established hate speech datasets. We discover that LLMs not only match but often surpass the performance of current benchmark machine learning models in identifying hate speech. By proposing four diverse prompting strategies that optimize the use of LLMs in detecting hate speech. Our study reveals that a meticulously crafted reasoning prompt can effectively capture the context of hate speech by fully utilizing the knowledge base in LLMs, significantly outperforming existing techniques. Furthermore, although LLMs can provide a rich knowledge base for the contextual detection of hate speech, suitable prompting strategies play a crucial role in effectively leveraging this knowledge base for efficient detection.
Moderating New Waves of Online Hate with Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2023Abstract:Online hate is an escalating problem that negatively impacts the lives of Internet users, and is also subject to rapid changes due to evolving events, resulting in new waves of online hate that pose a critical threat. Detecting and mitigating these new waves present two key challenges: it demands reasoning-based complex decision-making to determine the presence of hateful content, and the limited availability of training samples hinders updating the detection model. To address this critical issue, we present a novel framework called HATEGUARD for effectively moderating new waves of online hate. HATEGUARD employs a reasoning-based approach that leverages the recently introduced chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting technique, harnessing the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). HATEGUARD further achieves prompt-based zero-shot detection by automatically generating and updating detection prompts with new derogatory terms and targets in new wave samples to effectively address new waves of online hate. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we compile a new dataset consisting of tweets related to three recently witnessed new waves: the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the 2021 insurrection of the US Capitol, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Our studies reveal crucial longitudinal patterns in these new waves concerning the evolution of events and the pressing need for techniques to rapidly update existing moderation tools to counteract them. Comparative evaluations against state-of-the-art tools illustrate the superiority of our framework, showcasing a substantial 22.22% to 83.33% improvement in detecting the three new waves of online hate. Our work highlights the severe threat posed by the emergence of new waves of online hate and represents a paradigm shift in addressing this threat practically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge