Kevin Kelly
Machine Learning Meets Advanced Robotic Manipulation
Sep 22, 2023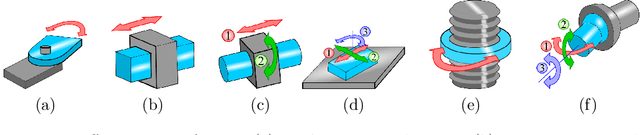
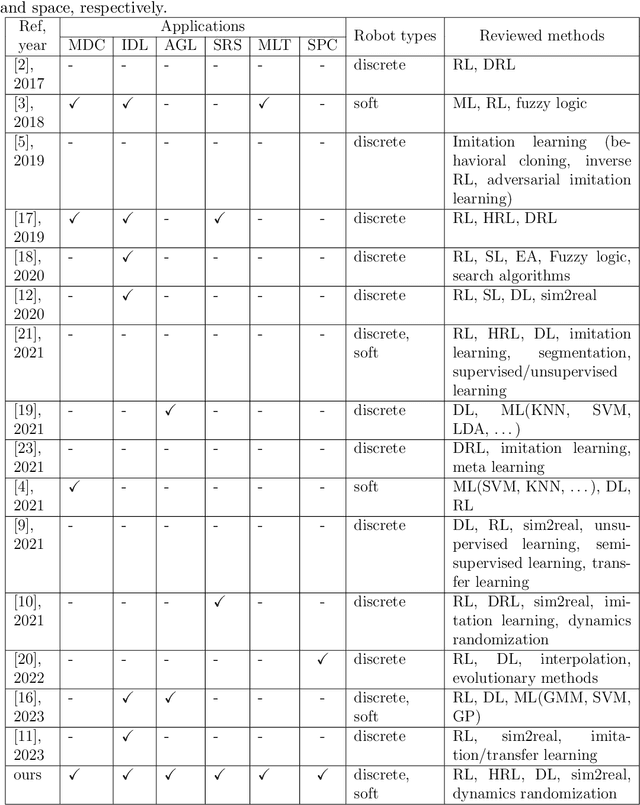
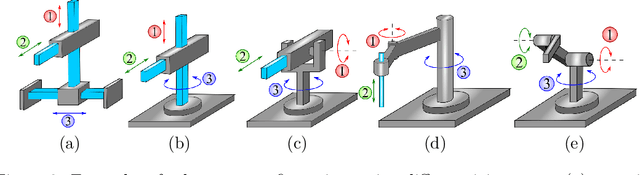
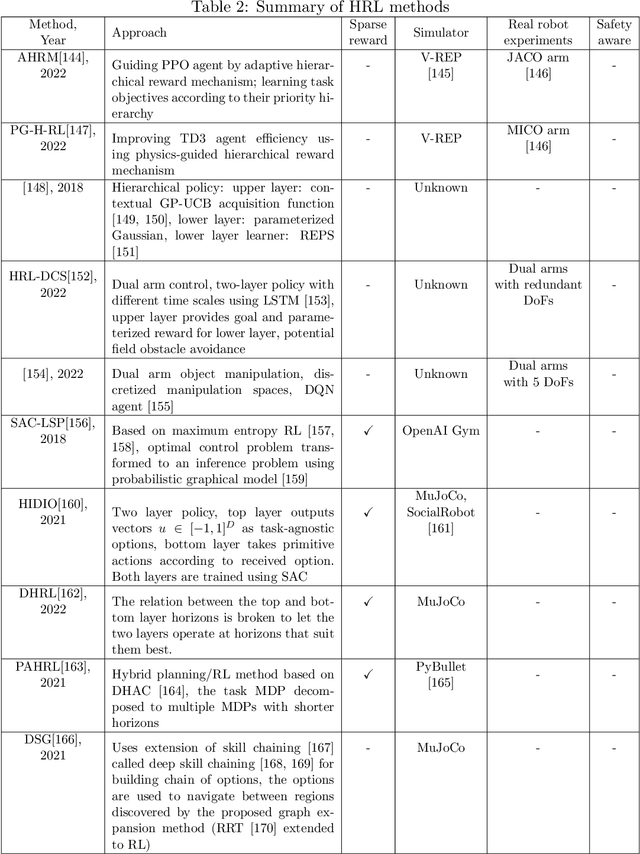
Abstract:Automated industries lead to high quality production, lower manufacturing cost and better utilization of human resources. Robotic manipulator arms have major role in the automation process. However, for complex manipulation tasks, hard coding efficient and safe trajectories is challenging and time consuming. Machine learning methods have the potential to learn such controllers based on expert demonstrations. Despite promising advances, better approaches must be developed to improve safety, reliability, and efficiency of ML methods in both training and deployment phases. This survey aims to review cutting edge technologies and recent trends on ML methods applied to real-world manipulation tasks. After reviewing the related background on ML, the rest of the paper is devoted to ML applications in different domains such as industry, healthcare, agriculture, space, military, and search and rescue. The paper is closed with important research directions for future works.
Video Compressive Sensing for Spatial Multiplexing Cameras using Motion-Flow Models
Aug 05, 2015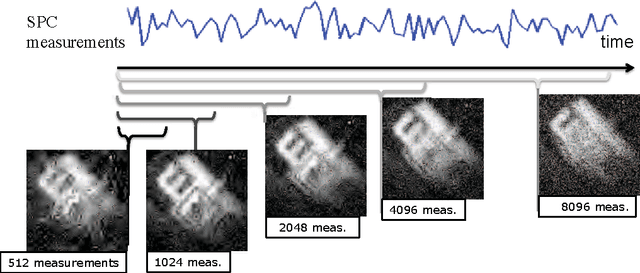

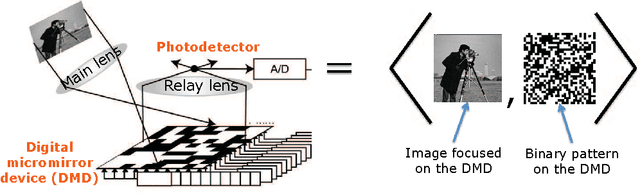

Abstract:Spatial multiplexing cameras (SMCs) acquire a (typically static) scene through a series of coded projections using a spatial light modulator (e.g., a digital micro-mirror device) and a few optical sensors. This approach finds use in imaging applications where full-frame sensors are either too expensive (e.g., for short-wave infrared wavelengths) or unavailable. Existing SMC systems reconstruct static scenes using techniques from compressive sensing (CS). For videos, however, existing acquisition and recovery methods deliver poor quality. In this paper, we propose the CS multi-scale video (CS-MUVI) sensing and recovery framework for high-quality video acquisition and recovery using SMCs. Our framework features novel sensing matrices that enable the efficient computation of a low-resolution video preview, while enabling high-resolution video recovery using convex optimization. To further improve the quality of the reconstructed videos, we extract optical-flow estimates from the low-resolution previews and impose them as constraints in the recovery procedure. We demonstrate the efficacy of our CS-MUVI framework for a host of synthetic and real measured SMC video data, and we show that high-quality videos can be recovered at roughly $60\times$ compression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge