Kamesh Namuduri
Collection: Datasets from AFAR Challenge
May 11, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a comprehensive real-world and Digital Twin (DT) dataset collected as part of the Find A Rover (AFAR) Challenge, organized by the NSF Aerial Experimentation and Research Platform for Advanced Wireless (AERPAW) testbed and hosted at the Lake Wheeler Field in Raleigh, North Carolina. The AFAR Challenge was a competition involving five finalist university teams, focused on promoting innovation in UAV-assisted radio frequency (RF) source localization. Participating teams were tasked with designing UAV flight trajectories and localization algorithms to detect the position of a hidden unmanned ground vehicle (UGV), also referred to as a rover, emitting wireless probe signals generated by GNU Radio. The competition was structured to evaluate solutions in a DT environment first, followed by deployment and testing in AERPAW's outdoor wireless testbed. For each team, the UGV was placed at three different positions, resulting in a total of 30 datasets, 15 collected in a DT simulation environment and 15 in a physical outdoor testbed. Each dataset contains time-synchronized measurements of received signal strength (RSS), received signal quality (RSQ), GPS coordinates, UAV velocity, and UAV orientation (roll, pitch, and yaw). Data is organized into structured folders by team, environment (DT and real-world), and UGV location. The dataset supports research in UAV-assisted RF source localization, air-to-ground (A2G) wireless propagation modeling, trajectory optimization, signal prediction, autonomous navigation, and DT validation. With approximately 300k time-synchronized samples collected from real-world experiments, the dataset provides a substantial foundation for training and evaluating deep learning (DL) models. Overall, the AFAR dataset serves as a valuable resource for advancing robust, real-world solutions in UAV-enabled wireless communications and sensing systems.
A UAV-assisted Wireless Localization Challenge on AERPAW
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:As wireless researchers are tasked to enable wireless communication as infrastructure in more dynamic aerial settings, there is a growing need for large-scale experimental platforms that provide realistic, reproducible, and reliable experimental validation. To bridge the research-to-implementation gap, the Aerial Experimentation and Research Platform for Advanced Wireless (AERPAW) offers open-source tools, reference experiments, and hardware to facilitate and evaluate the development of wireless research in controlled digital twin environments and live testbed flights. The inaugural AERPAW Challenge, "Find a Rover," was issued to spark collaborative efforts and test the platform's capabilities. The task involved localizing a narrowband wireless signal, with teams given ten minutes to find the "rover" within a twenty-acre area. By engaging in this exercise, researchers can validate the platform's value as a tool for innovation in wireless communications research within aerial robotics. This paper recounts the methods and experiences of the top three teams in automating and rapidly locating a wireless signal by automating and controlling an aerial drone in a realistic testbed scenario.
Wireless Connectivity and Localization for Advanced Air Mobility Services
Feb 21, 2022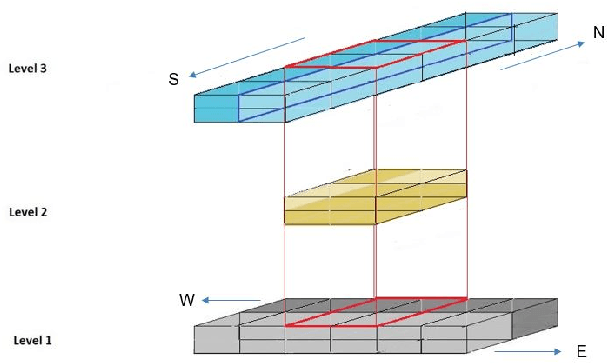
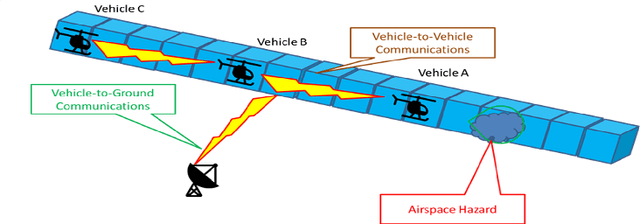
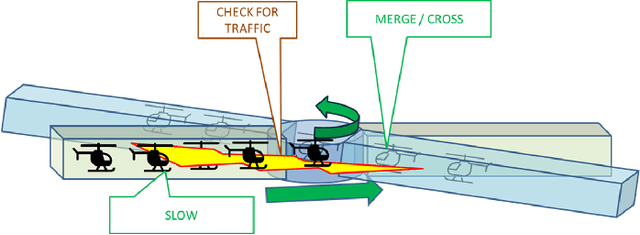
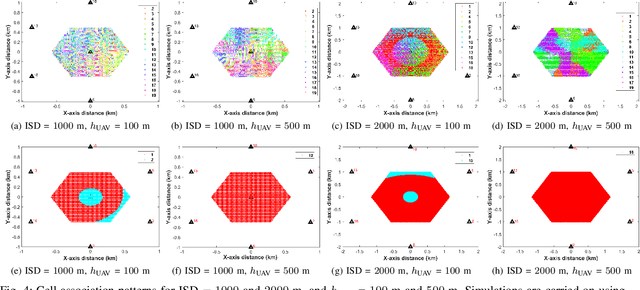
Abstract:By serving as an analog to traffic signal lights, communication signaling for drone to drone communications holds the key to the success of advanced air mobility (AAM) in both urban and rural settings. Deployment of AAM applications such as air taxis and air ambulances, especially at large-scale, requires a reliable channel for a point-to-point and broadcast communication between two or more aircraft. Achieving such high reliability, in a highly mobile environment, requires communication systems designed for agility and efficiency. This paper presents the foundations for establishing and maintaining a reliable communication channel among multiple aircraft in unique AAM settings. Subsequently, it presents concepts and results on wireless coverage and mobility for AAM services using cellular networks as a ground network infrastructure. Finally, we analyze the wireless localization performance at 3D AAM corridors when cellular networks are utilized, considering different corridor heights and base station densities. We highlight future research directions and open problems to improve wireless coverage and localization throughout the manuscript.
Dose Prediction with Deep Learning for Prostate Cancer Radiation Therapy: Model Adaptation to Different Treatment Planning Practices
Jun 30, 2020



Abstract:This work aims to study the generalizability of a pre-developed deep learning (DL) dose prediction model for volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for prostate cancer and to adapt the model to three different internal treatment planning styles and one external institution planning style. We built the source model with planning data from 108 patients previously treated with VMAT for prostate cancer. For the transfer learning, we selected patient cases planned with three different styles from the same institution and one style from a different institution to adapt the source model to four target models. We compared the dose distributions predicted by the source model and the target models with the clinical dose predictions and quantified the improvement in the prediction quality for the target models over the source model using the Dice similarity coefficients (DSC) of 10% to 100% isodose volumes and the dose-volume-histogram (DVH) parameters of the planning target volume and the organs-at-risk. The source model accurately predicts dose distributions for plans generated in the same source style but performs sub-optimally for the three internal and one external target styles, with the mean DSC ranging between 0.81-0.94 and 0.82-0.91 for the internal and the external styles, respectively. With transfer learning, the target model predictions improved the mean DSC to 0.88-0.95 and 0.92-0.96 for the internal and the external styles, respectively. Target model predictions significantly improved the accuracy of the DVH parameter predictions to within 1.6%. We demonstrated model generalizability for DL-based dose prediction and the feasibility of using transfer learning to solve this problem. With 14-29 cases per style, we successfully adapted the source model into several different practice styles. This indicates a realistic way to widespread clinical implementation of DL-based dose prediction.
Advances in Human Action Recognition: A Survey
Jan 23, 2015



Abstract:Human action recognition has been an important topic in computer vision due to its many applications such as video surveillance, human machine interaction and video retrieval. One core problem behind these applications is automatically recognizing low-level actions and high-level activities of interest. The former is usually the basis for the latter. This survey gives an overview of the most recent advances in human action recognition during the past several years, following a well-formed taxonomy proposed by a previous survey. From this state-of-the-art survey, researchers can view a panorama of progress in this area for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge