Kaiquan Cai
Knots: A Large-Scale Multi-Agent Enhanced Expert-Annotated Dataset and LLM Prompt Optimization for NOTAM Semantic Parsing
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Notice to Air Missions (NOTAMs) serve as a critical channel for disseminating key flight safety information, yet their complex linguistic structures and implicit reasoning pose significant challenges for automated parsing. Existing research mainly focuses on surface-level tasks such as classification and named entity recognition, lacking deep semantic understanding. To address this gap, we propose NOTAM semantic parsing, a task emphasizing semantic inference and the integration of aviation domain knowledge to produce structured, inference-rich outputs. To support this task, we construct Knots (Knowledge and NOTAM Semantics), a high-quality dataset of 12,347 expert-annotated NOTAMs covering 194 Flight Information Regions, enhanced through a multi-agent collaborative framework for comprehensive field discovery. We systematically evaluate a wide range of prompt-engineering strategies and model-adaptation techniques, achieving substantial improvements in aviation text understanding and processing. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach and offer valuable insights for automated NOTAM analysis systems. Our code is available at: https://github.com/Estrellajer/Knots.
NOTAM-Evolve: A Knowledge-Guided Self-Evolving Optimization Framework with LLMs for NOTAM Interpretation
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Accurate interpretation of Notices to Airmen (NOTAMs) is critical for aviation safety, yet their condensed and cryptic language poses significant challenges to both manual and automated processing. Existing automated systems are typically limited to shallow parsing, failing to extract the actionable intelligence needed for operational decisions. We formalize the complete interpretation task as deep parsing, a dual-reasoning challenge requiring both dynamic knowledge grounding (linking the NOTAM to evolving real-world aeronautical data) and schema-based inference (applying static domain rules to deduce operational status). To tackle this challenge, we propose NOTAM-Evolve, a self-evolving framework that enables a large language model (LLM) to autonomously master complex NOTAM interpretation. Leveraging a knowledge graph-enhanced retrieval module for data grounding, the framework introduces a closed-loop learning process where the LLM progressively improves from its own outputs, minimizing the need for extensive human-annotated reasoning traces. In conjunction with this framework, we introduce a new benchmark dataset of 10,000 expert-annotated NOTAMs. Our experiments demonstrate that NOTAM-Evolve achieves a 30.4% absolute accuracy improvement over the base LLM, establishing a new state of the art on the task of structured NOTAM interpretation.
Pinching-Antenna Systems-Enabled Multi-User Communications: Transmission Structures and Beamforming Optimization
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Pinching-antenna systems (PASS) represent an innovative advancement in flexible-antenna technologies, aimed at significantly improving wireless communications by ensuring reliable line-of-sight connections and dynamic antenna array reconfigurations. To employ multi-waveguide PASS in multi-user communications, three practical transmission structures are proposed, namely waveguide multiplexing (WM), waveguide division (WD), and waveguide switching (WS). Based on the proposed structures, the joint baseband signal processing and pinching beamforming design is studied for a general multi-group multicast communication system, with the unicast communication encompassed as a special case. A max-min fairness problem is formulated for each proposed transmission structure, subject to the maximum transmit power constraint. For WM, to solve the highly-coupled and non-convex MMF problem with complex exponential and fractional expressions, a penalty dual decomposition (PDD)-based algorithm is invoked for obtaining locally optimal solutions. Specifically, the augmented Lagrangian relaxation is first applied to alleviate the stringent coupling constraints, which is followed by the block decomposition over the resulting augmented Lagrangian function. Then, the proposed PDD-based algorithm is extended to solve the MMF problem for both WD and WS. Furthermore, a low-complexity algorithm is proposed for the unicast case employing the WS structure, by simultaneously aligning the signal phases and minimizing the large-scale path loss at each user. Finally, numerical results reveal that: 1) the MMF performance is significantly improved by employing the PASS compared to conventional fixed-position antenna systems; 2) WS and WM are suitable for unicast and multicast communications, respectively; 3) the performance gap between WD and WM can be significantly alleviated when the users are geographically isolated.
RIS-Assisted Beamfocusing in Near-Field IoT Communication Systems: A Transformer-Based Approach
Apr 17, 2025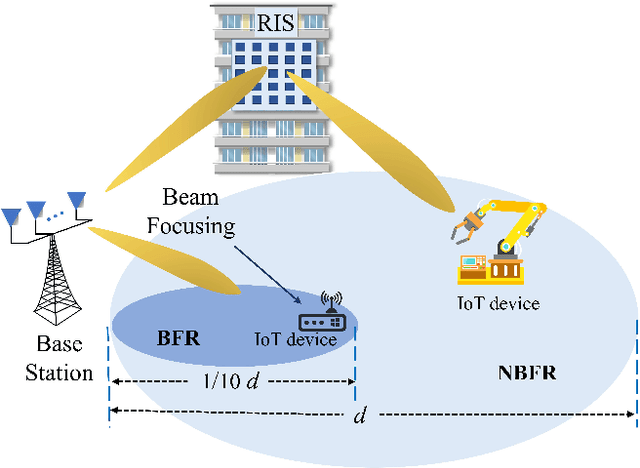
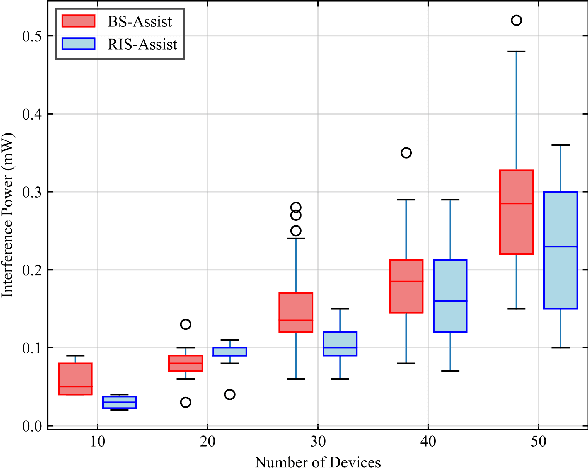
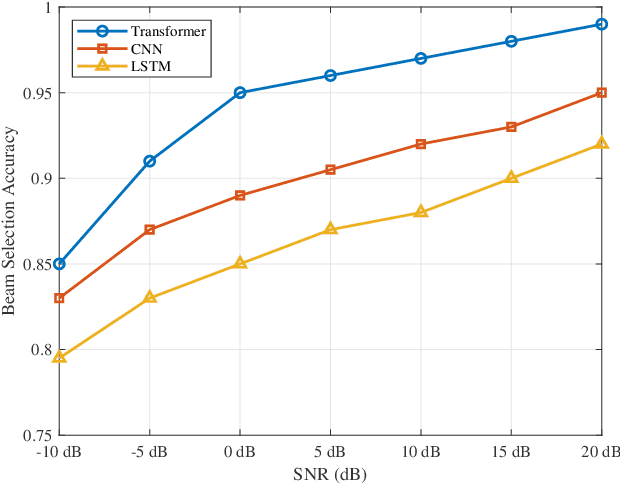
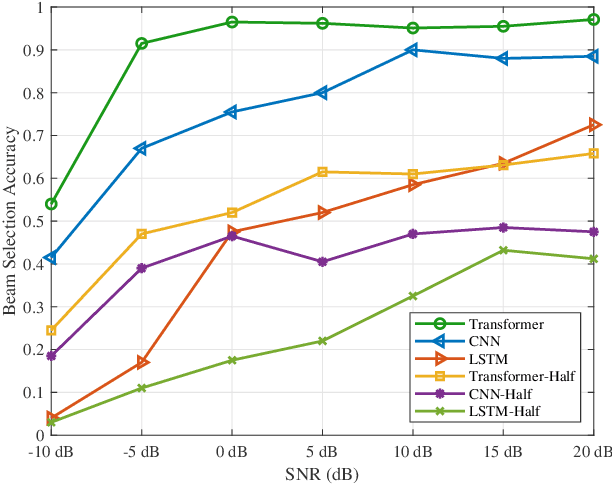
Abstract:The massive number of antennas in extremely large aperture array (ELAA) systems shifts the propagation regime of signals in internet of things (IoT) communication systems towards near-field spherical wave propagation. We propose a reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS)-assisted beamfocusing mechanism, where the design of the two-dimensional beam codebook that contains both the angular and distance domains is challenging. To address this issue, we introduce a novel Transformer-based two-stage beam training algorithm, which includes the coarse and fine search phases. The proposed mechanism provides a fine-grained codebook with enhanced spatial resolution, enabling precise beamfocusing. Specifically, in the first stage, the beam training is performed to estimate the approximate location of the device by using a simple codebook, determining whether it is within the beamfocusing range (BFR) or the none-beamfocusing range (NBFR). In the second stage, by using a more precise codebook, a fine-grained beam search strategy is conducted. Experimental results unveil that the precision of the RIS-assisted beamfocusing is greatly improved. The proposed method achieves beam selection accuracy up to 97% at signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 20 dB, and improves 10% to 50% over the baseline method at different SNRs.
Continuous Aperture Array (CAPA)-Based Secure Wireless Communications
Apr 15, 2025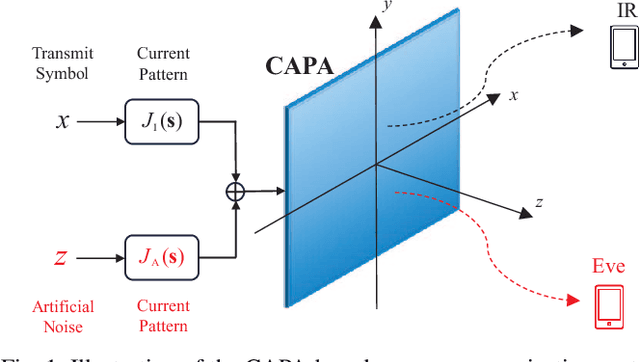
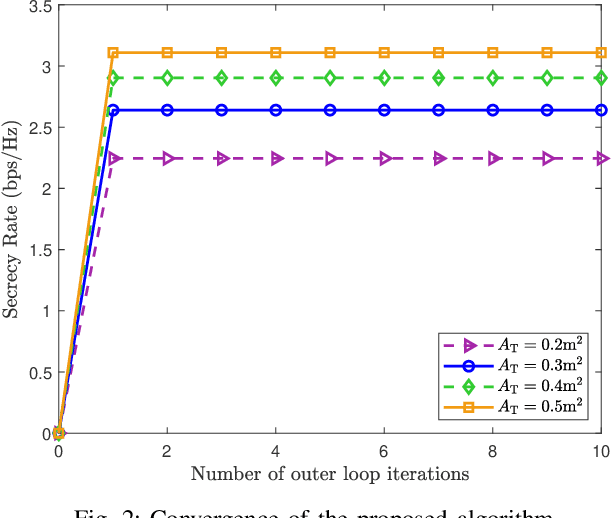
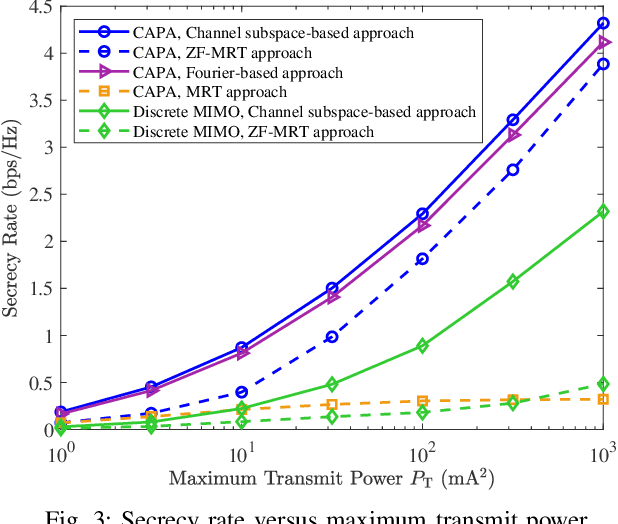
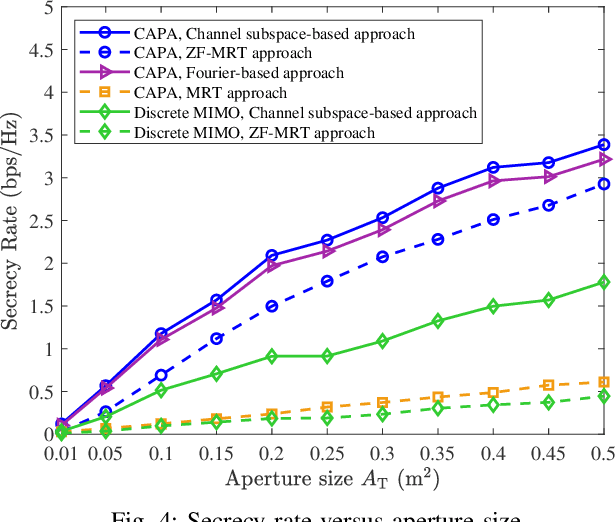
Abstract:A continuous aperture array (CAPA)-based secure communication system is investigated, where a base station equipped with a CAPA transmits signals to a legitimate user under the existence of an eavesdropper. For improving the secrecy performance, the artificial noise (AN) is employed at the BS for the jamming purpose. We aim at maximizing the secrecy rate by jointly optimizing the information-bearing and AN source current patterns, subject to the maximum transmit power constraint. To solve the resultant non-convex integral-based functional programming problem, a channel subspace-based approach is first proposed via exploiting the result that the optimal current patterns always lie within the subspace spanned by all users' channel responses. Then, the intractable CAPA continuous source current pattern design problem with an infinite number of optimization variables is equivalently transformed into the channel-subspace weighting factor optimization problem with a finite number of optimization variables. A penalty-based successive convex approximation method is developed for iteratively optimizing the finite-size weighting vectors. To further reduce the computational complexity, we propose a two-stage source current patterns design scheme. Specifically, the information-bearing and AN patterns are first designed using the maximal ration transmission and zero-forcing transmission, respectively. Then, the remaining power allocation is addressed via the one-dimensional search method. Numerical results unveil that 1) the CAPA brings in significant secrecy rate gain compared to the conventional discrete multiple-input multiple-output; 2) the proposed channel subspace-based algorithm outperforms the conventional Fourier-based approach, while sustaining much lower computational complexity; and 3) the two-stage ZF-MRT approach has negligible performance loss for the large transmit power regime.
Movable-Element RIS-Aided Wireless Communications: An Element-Wise Position Optimization Approach
Mar 19, 2025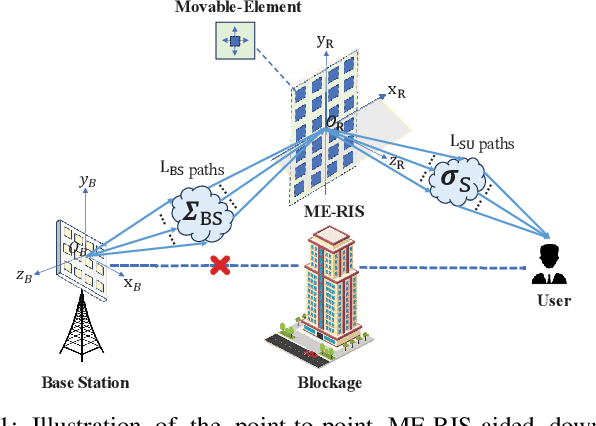
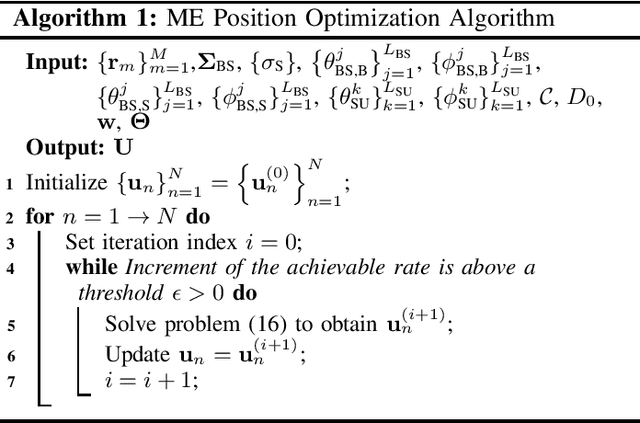
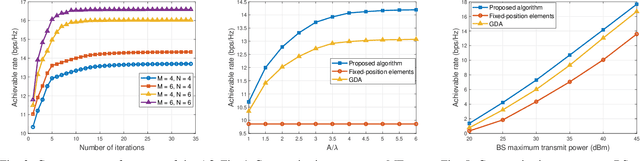
Abstract:A point-to-point movable element (ME) enabled reconfigurable intelligent surface (ME-RIS) communication system is investigated, where each element position can be flexibly adjusted to create favorable channel conditions. For maximizing the communication rate, an efficient ME position optimization approach is proposed. Specifically, by characterizing the cascaded channel power gain in an element-wise manner, the position of each ME is iteratively updated by invoking the successive convex approximation method. Numerical results unveil that 1) the proposed element-wise ME position optimization algorithm outperforms the gradient descent algorithm; and 2) the ME-RIS significantly improves the communication rate compared to the conventional RIS with fixed-position elements.
Waveguide Division Multiple Access for Pinching-Antenna Systems (PASS)
Feb 25, 2025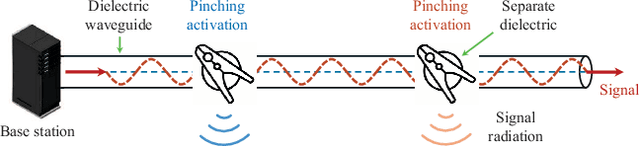
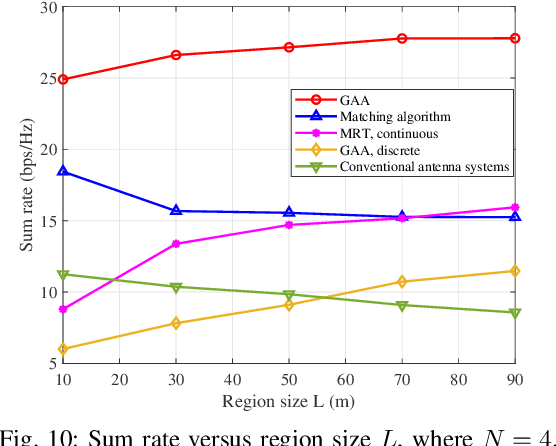
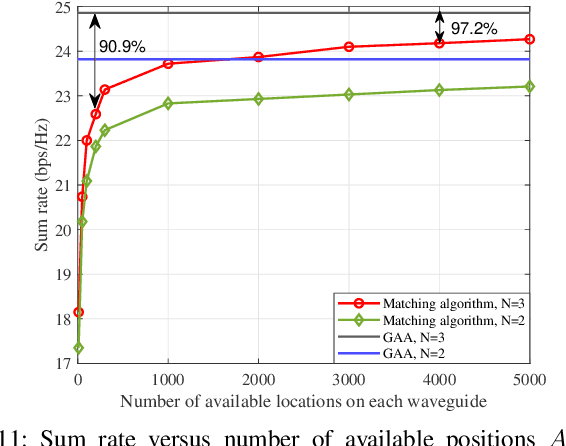
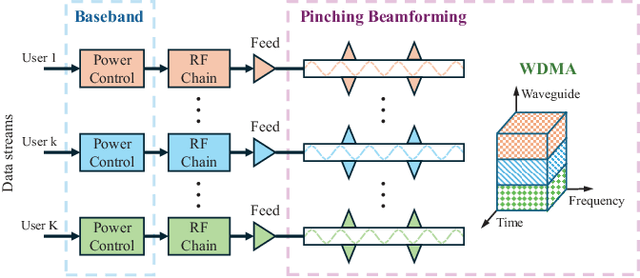
Abstract:A novel concept of waveguide division multiple access (WDMA) is proposed for multi-user pinching-antenna systems (PASS). The key principle of WDMA is to allocate each user with a dedicated waveguide, which is regarded as a new type of radio resources, so as to facilitate multi-user communications. By adjusting the activation positions of pinching antennas (PAs) over each waveguide, the pinching beamforming can be exploited for intended user signal enhancement and inter-user interference mitigation. Considering both ideal continuous and practical discrete PA position activation schemes, a joint power allocation and pinching beamforming optimization problem is formulated for the maximization of the sum rate. An alternating optimization-based algorithm is developed to address the formulated nonconvex problem. For solving the power allocation subproblem, the successive convex approximation method is invoked. For the pinching beamforming design subproblem, a penalty-based gradient ascent algorithm is first developed for the continuous PA activation case. Then, for the discrete PA activation case, a matching theory-based algorithm is proposed to achieve the near-optimal performance but with a low complexity. Numerical results unveil that: 1) For both continuous and discrete activation cases, PASS can achieve a significant performance gain over conventional fixed-position antenna systems; 2) the proposed WDMA can effectively underpin multi-user communications with the near orthogonality in free space achieved by the pinching beamforming; and 3) the performance gap between the discrete and continuous activation cases can be significantly alleviated with practically feasible numbers of PA candidate positions.
Exploiting Movable-Element STARS for Wireless Communications
Dec 28, 2024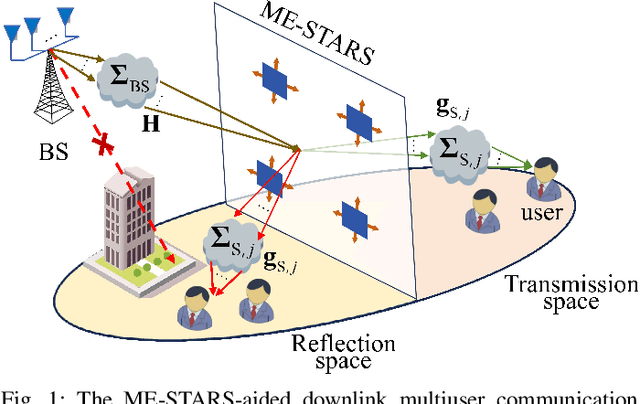
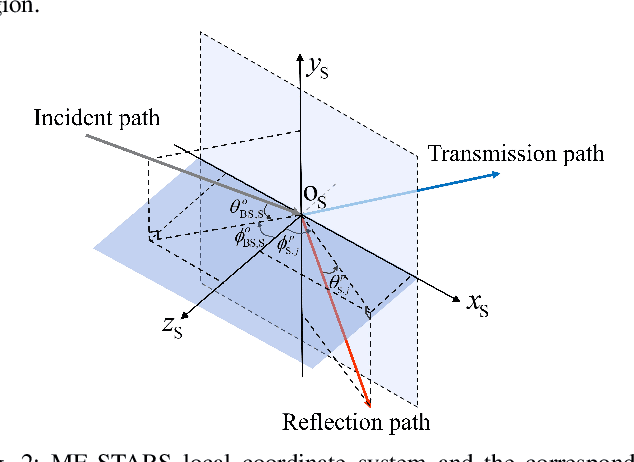
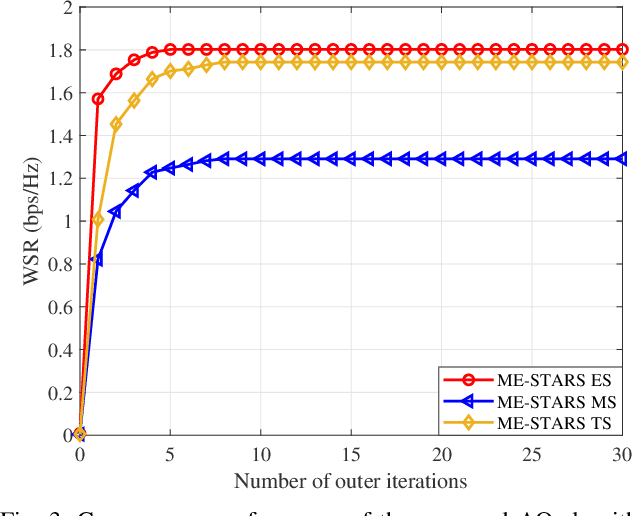
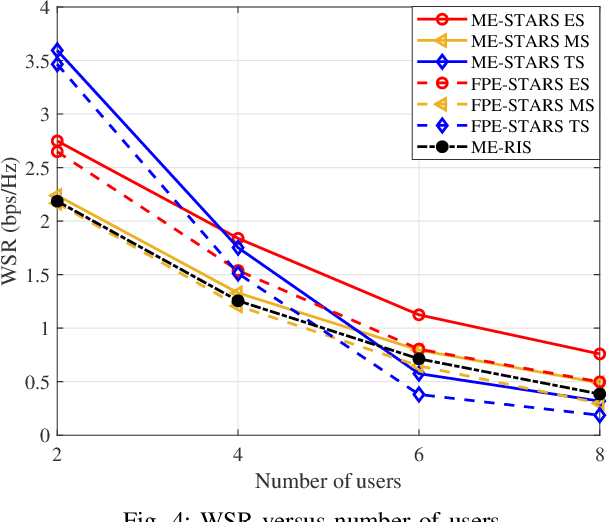
Abstract:A novel movable-element enabled simultaneously transmitting and reflecting surface (ME-STARS) communication system is proposed, where ME-STARS elements positions can be adjusted to enhance the degress-of-freedom for transmission and reflection. For each ME-STARS operating protocols, namely energy-splitting (ES), mode switching (MS), and time switching (TS), a weighted sum rate (WSR) maximization problem is formulated to jointly optimize the active beamforming at the base station (BS) as well as the elements positions and passive beamforming at the ME-STARS. An alternative optimization (AO)-based iterative algorithm is developed to decompose the original non-convex problem into three subproblems. Specifically, the gradient descent algorithm is employed for solving the ME-STARS element position optimization subproblem, and the weighted minimum mean square error and the successive convex approximation methods are invoked for solving the active and passive beamforming subproblems, respectively. It is further demonstrated that the proposed AO algorithm for ES can be extended to solve the problems for MS and TS. Numerical results unveil that: 1) the ME-STARS can significantly improve the WSR compared to the STARS with fixed position elements and the conventional reconfigurable intelligent surface with movable elements, thanks to the extra spatial-domain diversity and the higher flexibility in beamforming; and 2) the performance gain of ME-STARS is significant in the scenarios with larger number of users or more scatterers.
Interference-Robust Broadband Rapidly-Varying MIMO Communications: A Knowledge-Data Dual Driven Framework
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:A novel time-efficient framework is proposed for improving the robustness of a broadband multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system against unknown interference under rapidly-varying channels. A mean-squared error (MSE) minimization problem is formulated by optimizing the beamformers employed. Since the unknown interference statistics are the premise for solving the formulated problem, an interference statistics tracking (IST) module is first designed. The IST module exploits both the time- and spatial-domain correlations of the interference-plus-noise (IPN) covariance for the future predictions with data training. Compared to the conventional signal-free space sampling approach, the IST module can realize zero-pilot and low-latency estimation. Subsequently, an interference-resistant hybrid beamforming (IR-HBF) module is presented, which incorporates both the prior knowledge of the theoretical optimization method as well as the data-fed training. Taking advantage of the interpretable network structure, the IR-HBF module enables the simplified mapping from the interference statistics to the beamforming weights. The simulations are executed in high-mobility scenarios, where the numerical results unveil that: 1) the proposed IST module attains promising prediction accuracy compared to the conventional counterparts under different snapshot sampling errors; and 2) the proposed IR-HBF module achieves lower MSE with significantly reduced computational complexity.
Multiple-Antenna Aided Aeronautical Communications in Air-Ground Integrated Networks: Channel Estimation, Reliable Transmission, and Multiple Access
Jan 15, 2023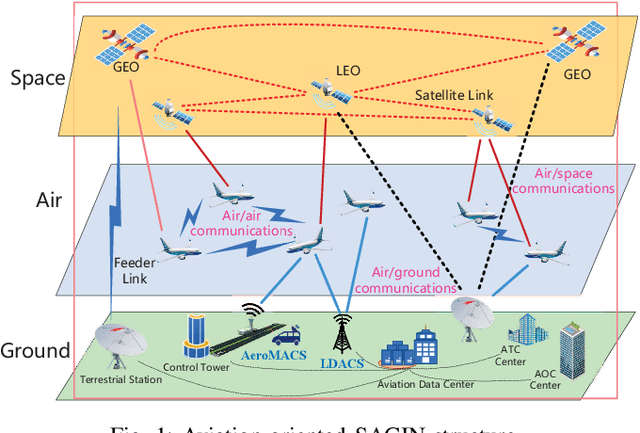
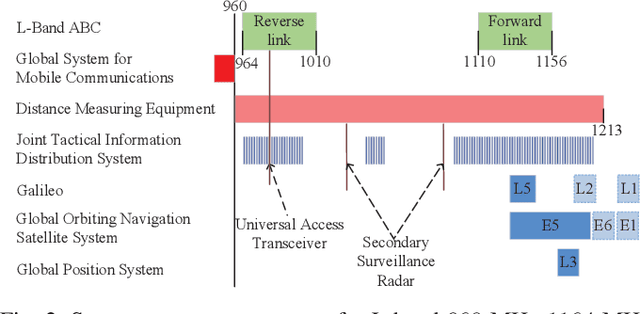
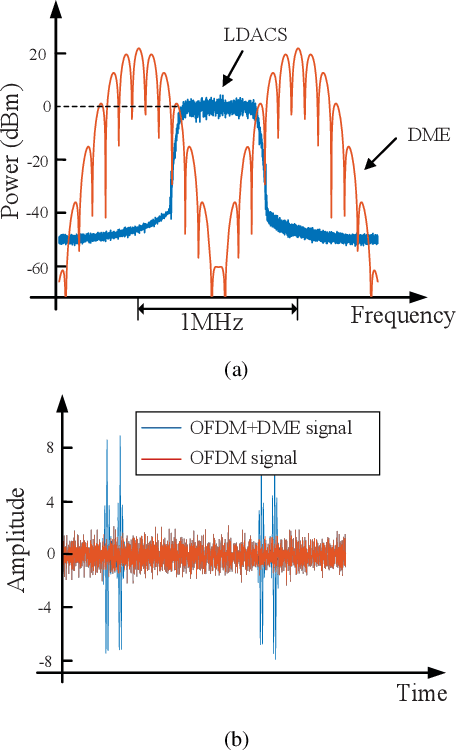
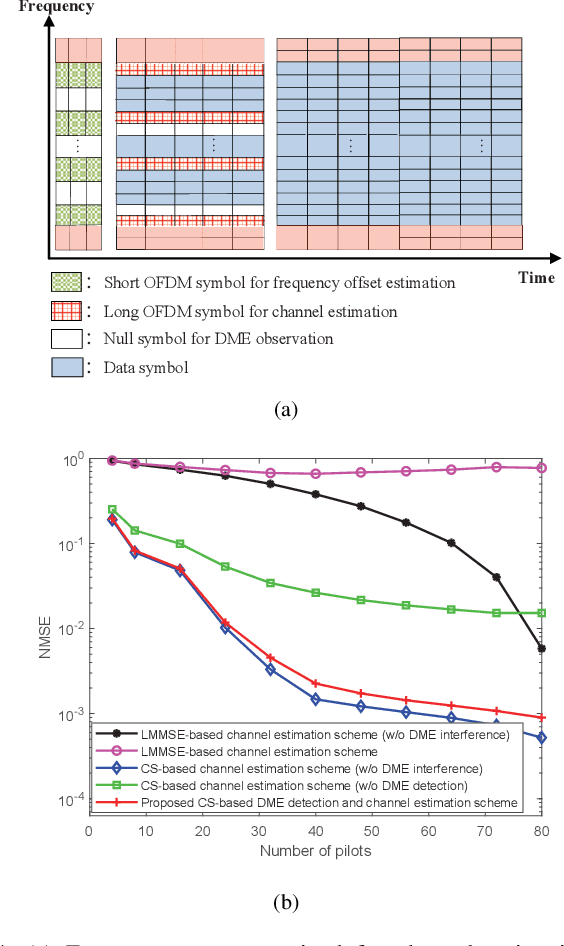
Abstract:To provide seamless coverage during all flight phases, aeronautical communications systems (ACS) have to integrate space-based, air-based, as well as ground-based platforms to formulate aviation-oriented space-air-ground integrated networks (SAGINs). In continental areas, L-band aeronautical broadband communications (ABC) are gaining popularity for supporting air traffic management (ATM) modernization. However, L-band ABC faces the challenges of spectrum congestion and severe interference due to the legacy systems. To circumvent these, we propose a novel multiple-antenna aided L-band ABC paradigm to tackle the key issues of reliable and high-rate air-to-ground (A2G) transmissions. Specifically, we first introduce the development roadmap of the ABC. Furthermore, we discuss the peculiarities of the L-band ABC propagation environment and the distinctive challenges of the associated multiple-antenna techniques. To overcome these challenges, we propose an advanced multiple-antenna assisted L-band ABC paradigm from the perspective of channel estimation, reliable transmission, and multiple access. Finally, we shed light on the compelling research directions of the aviation component of SAGINs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge