Kaike Zhang
RubricHub: A Comprehensive and Highly Discriminative Rubric Dataset via Automated Coarse-to-Fine Generation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has driven substantial progress in reasoning-intensive domains like mathematics. However, optimizing open-ended generation remains challenging due to the lack of ground truth. While rubric-based evaluation offers a structured proxy for verification, existing methods suffer from scalability bottlenecks and coarse criteria, resulting in a supervision ceiling effect. To address this, we propose an automated Coarse-to-Fine Rubric Generation framework. By synergizing principle-guided synthesis, multi-model aggregation, and difficulty evolution, our approach produces comprehensive and highly discriminative criteria capable of capturing the subtle nuances. Based on this framework, we introduce RubricHub, a large-scale ($\sim$110k) and multi-domain dataset. We validate its utility through a two-stage post-training pipeline comprising Rubric-based Rejection Sampling Fine-Tuning (RuFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RuRL). Experimental results demonstrate that RubricHub unlocks significant performance gains: our post-trained Qwen3-14B achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on HealthBench (69.3), surpassing proprietary frontier models such as GPT-5. The code and data will be released soon.
AsarRec: Adaptive Sequential Augmentation for Robust Self-supervised Sequential Recommendation
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Sequential recommender systems have demonstrated strong capabilities in modeling users' dynamic preferences and capturing item transition patterns. However, real-world user behaviors are often noisy due to factors such as human errors, uncertainty, and behavioral ambiguity, which can lead to degraded recommendation performance. To address this issue, recent approaches widely adopt self-supervised learning (SSL), particularly contrastive learning, by generating perturbed views of user interaction sequences and maximizing their mutual information to improve model robustness. However, these methods heavily rely on their pre-defined static augmentation strategies~(where the augmentation type remains fixed once chosen) to construct augmented views, leading to two critical challenges: (1) the optimal augmentation type can vary significantly across different scenarios; (2) inappropriate augmentations may even degrade recommendation performance, limiting the effectiveness of SSL. To overcome these limitations, we propose an adaptive augmentation framework. We first unify existing basic augmentation operations into a unified formulation via structured transformation matrices. Building on this, we introduce AsarRec (Adaptive Sequential Augmentation for Robust Sequential Recommendation), which learns to generate transformation matrices by encoding user sequences into probabilistic transition matrices and projecting them into hard semi-doubly stochastic matrices via a differentiable Semi-Sinkhorn algorithm. To ensure that the learned augmentations benefit downstream performance, we jointly optimize three objectives: diversity, semantic invariance, and informativeness. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets under varying noise levels validate the effectiveness of AsarRec, demonstrating its superior robustness and consistent improvements.
GoalRank: Group-Relative Optimization for a Large Ranking Model
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Mainstream ranking approaches typically follow a Generator-Evaluator two-stage paradigm, where a generator produces candidate lists and an evaluator selects the best one. Recent work has attempted to enhance performance by expanding the number of candidate lists, for example, through multi-generator settings. However, ranking involves selecting a recommendation list from a combinatorially large space. Simply enlarging the candidate set remains ineffective, and performance gains quickly saturate. At the same time, recent advances in large recommendation models have shown that end-to-end one-stage models can achieve promising performance with the expectation of scaling laws. Motivated by this, we revisit ranking from a generator-only one-stage perspective. We theoretically prove that, for any (finite Multi-)Generator-Evaluator model, there always exists a generator-only model that achieves strictly smaller approximation error to the optimal ranking policy, while also enjoying scaling laws as its size increases. Building on this result, we derive an evidence upper bound of the one-stage optimization objective, from which we find that one can leverage a reward model trained on real user feedback to construct a reference policy in a group-relative manner. This reference policy serves as a practical surrogate of the optimal policy, enabling effective training of a large generator-only ranker. Based on these insights, we propose GoalRank, a generator-only ranking framework. Extensive offline experiments on public benchmarks and large-scale online A/B tests demonstrate that GoalRank consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
LLM4MEA: Data-free Model Extraction Attacks on Sequential Recommenders via Large Language Models
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the vulnerability of sequential recommender systems to Model Extraction Attacks (MEAs). MEAs collect responses from recommender systems to replicate their functionality, enabling unauthorized deployments and posing critical privacy and security risks. Black-box attacks in prior MEAs are ineffective at exposing recommender system vulnerabilities due to random sampling in data selection, which leads to misaligned synthetic and real-world distributions. To overcome this limitation, we propose LLM4MEA, a novel model extraction method that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) as human-like rankers to generate data. It generates data through interactions between the LLM ranker and target recommender system. In each interaction, the LLM ranker analyzes historical interactions to understand user behavior, and selects items from recommendations with consistent preferences to extend the interaction history, which serves as training data for MEA. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LLM4MEA significantly outperforms existing approaches in data quality and attack performance, reducing the divergence between synthetic and real-world data by up to 64.98% and improving MEA performance by 44.82% on average. From a defensive perspective, we propose a simple yet effective defense strategy and identify key hyperparameters of recommender systems that can mitigate the risk of MEAs.
The 1st Workshop on Human-Centered Recommender Systems
Nov 22, 2024
Abstract:Recommender systems are quintessential applications of human-computer interaction. Widely utilized in daily life, they offer significant convenience but also present numerous challenges, such as the information cocoon effect, privacy concerns, fairness issues, and more. Consequently, this workshop aims to provide a platform for researchers to explore the development of Human-Centered Recommender Systems~(HCRS). HCRS refers to the creation of recommender systems that prioritize human needs, values, and capabilities at the core of their design and operation. In this workshop, topics will include, but are not limited to, robustness, privacy, transparency, fairness, diversity, accountability, ethical considerations, and user-friendly design. We hope to engage in discussions on how to implement and enhance these properties in recommender systems. Additionally, participants will explore diverse evaluation methods, including innovative metrics that capture user satisfaction and trust. This workshop seeks to foster a collaborative environment for researchers to share insights and advance the field toward more ethical, user-centric, and socially responsible recommender systems.
Improving the Shortest Plank: Vulnerability-Aware Adversarial Training for Robust Recommender System
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems play a pivotal role in mitigating information overload in various fields. Nonetheless, the inherent openness of these systems introduces vulnerabilities, allowing attackers to insert fake users into the system's training data to skew the exposure of certain items, known as poisoning attacks. Adversarial training has emerged as a notable defense mechanism against such poisoning attacks within recommender systems. Existing adversarial training methods apply perturbations of the same magnitude across all users to enhance system robustness against attacks. Yet, in reality, we find that attacks often affect only a subset of users who are vulnerable. These perturbations of indiscriminate magnitude make it difficult to balance effective protection for vulnerable users without degrading recommendation quality for those who are not affected. To address this issue, our research delves into understanding user vulnerability. Considering that poisoning attacks pollute the training data, we note that the higher degree to which a recommender system fits users' training data correlates with an increased likelihood of users incorporating attack information, indicating their vulnerability. Leveraging these insights, we introduce the Vulnerability-aware Adversarial Training (VAT), designed to defend against poisoning attacks in recommender systems. VAT employs a novel vulnerability-aware function to estimate users' vulnerability based on the degree to which the system fits them. Guided by this estimation, VAT applies perturbations of adaptive magnitude to each user, not only reducing the success ratio of attacks but also preserving, and potentially enhancing, the quality of recommendations. Comprehensive experiments confirm VAT's superior defensive capabilities across different recommendation models and against various types of attacks.
Accelerating the Surrogate Retraining for Poisoning Attacks against Recommender Systems
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the vulnerability of recommender systems to data poisoning attacks, where adversaries inject carefully crafted fake user interactions into the training data of recommenders to promote target items. Current attack methods involve iteratively retraining a surrogate recommender on the poisoned data with the latest fake users to optimize the attack. However, this repetitive retraining is highly time-consuming, hindering the efficient assessment and optimization of fake users. To mitigate this computational bottleneck and develop a more effective attack in an affordable time, we analyze the retraining process and find that a change in the representation of one user/item will cause a cascading effect through the user-item interaction graph. Under theoretical guidance, we introduce \emph{Gradient Passing} (GP), a novel technique that explicitly passes gradients between interacted user-item pairs during backpropagation, thereby approximating the cascading effect and accelerating retraining. With just a single update, GP can achieve effects comparable to multiple original training iterations. Under the same number of retraining epochs, GP enables a closer approximation of the surrogate recommender to the victim. This more accurate approximation provides better guidance for optimizing fake users, ultimately leading to enhanced data poisoning attacks. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of our proposed GP.
LoRec: Large Language Model for Robust Sequential Recommendation against Poisoning Attacks
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:Sequential recommender systems stand out for their ability to capture users' dynamic interests and the patterns of item-to-item transitions. However, the inherent openness of sequential recommender systems renders them vulnerable to poisoning attacks, where fraudulent users are injected into the training data to manipulate learned patterns. Traditional defense strategies predominantly depend on predefined assumptions or rules extracted from specific known attacks, limiting their generalizability to unknown attack types. To solve the above problems, considering the rich open-world knowledge encapsulated in Large Language Models (LLMs), our research initially focuses on the capabilities of LLMs in the detection of unknown fraudulent activities within recommender systems, a strategy we denote as LLM4Dec. Empirical evaluations demonstrate the substantial capability of LLMs in identifying unknown fraudsters, leveraging their expansive, open-world knowledge. Building upon this, we propose the integration of LLMs into defense strategies to extend their effectiveness beyond the confines of known attacks. We propose LoRec, an advanced framework that employs LLM-Enhanced Calibration to strengthen the robustness of sequential recommender systems against poisoning attacks. LoRec integrates an LLM-enhanced CalibraTor (LCT) that refines the training process of sequential recommender systems with knowledge derived from LLMs, applying a user-wise reweighting to diminish the impact of fraudsters injected by attacks. By incorporating LLMs' open-world knowledge, the LCT effectively converts the limited, specific priors or rules into a more general pattern of fraudsters, offering improved defenses against poisoning attacks. Our comprehensive experiments validate that LoRec, as a general framework, significantly strengthens the robustness of sequential recommender systems.
Robust Recommender System: A Survey and Future Directions
Sep 05, 2023



Abstract:With the rapid growth of information, recommender systems have become integral for providing personalized suggestions and overcoming information overload. However, their practical deployment often encounters "dirty" data, where noise or malicious information can lead to abnormal recommendations. Research on improving recommender systems' robustness against such dirty data has thus gained significant attention. This survey provides a comprehensive review of recent work on recommender systems' robustness. We first present a taxonomy to organize current techniques for withstanding malicious attacks and natural noise. We then explore state-of-the-art methods in each category, including fraudster detection, adversarial training, certifiable robust training against malicious attacks, and regularization, purification, self-supervised learning against natural noise. Additionally, we summarize evaluation metrics and common datasets used to assess robustness. We discuss robustness across varying recommendation scenarios and its interplay with other properties like accuracy, interpretability, privacy, and fairness. Finally, we delve into open issues and future research directions in this emerging field. Our goal is to equip readers with a holistic understanding of robust recommender systems and spotlight pathways for future research and development.
DyTed: Disentangling Temporal Invariance and Fluctuations in Dynamic Graph Representation Learning
Oct 19, 2022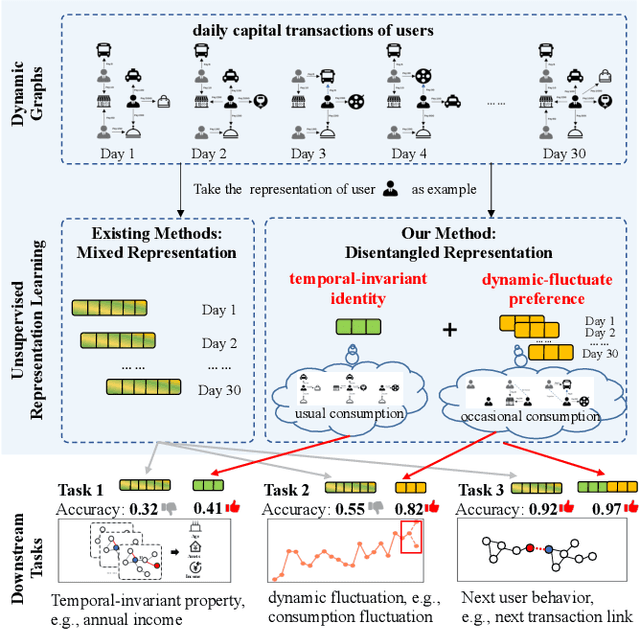
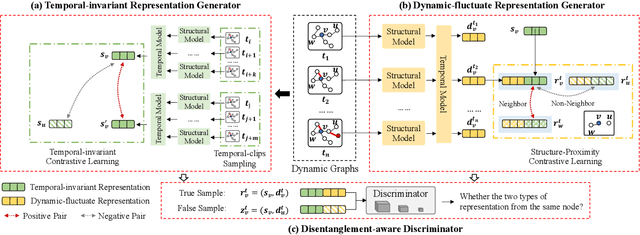
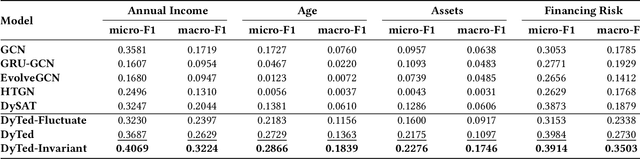
Abstract:Unsupervised representation learning for dynamic graphs has attracted a lot of research attention in recent years. Compared with static graphs, dynamic graphs are the integrative reflection of both the temporal-invariant or stable characteristics of nodes and the dynamic-fluctuate preference changing with time. However, existing dynamic graph representation learning methods generally confound these two types of information into a shared representation space, which may lead to poor explanation, less robustness, and a limited ability when applied to different downstream tasks. Taking the real dynamic graphs of daily capital transactions on Tencent as an example, the learned representation of the state-of-the-art method achieves only 32% accuracy in predicting temporal-invariant characteristics of users like annual income. In this paper, we introduce a novel temporal invariance-fluctuation disentangled representation learning framework for dynamic graphs, namely DyTed. In particular, we propose a temporal-invariant representation generator and a dynamic-fluctuate representation generator with carefully designed pretext tasks to identify the two types of representations in dynamic graphs. To further enhance the disentanglement or separation, we propose a disentanglement-aware discriminator under an adversarial learning framework. Extensive experiments on Tencent and five commonly used public datasets demonstrate that the different parts of our disentangled representation can achieve state-of-the-art performance on various downstream tasks, as well as be more robust against noise, and is a general framework that can further improve existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge