Kaijin Xu
Deep Learning System to Screen Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia
Feb 21, 2020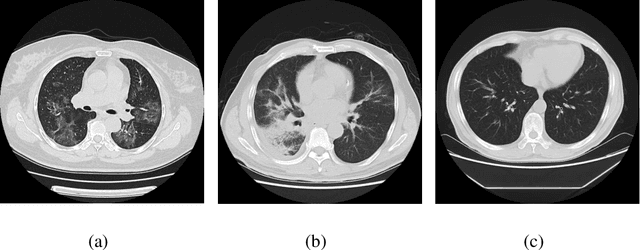
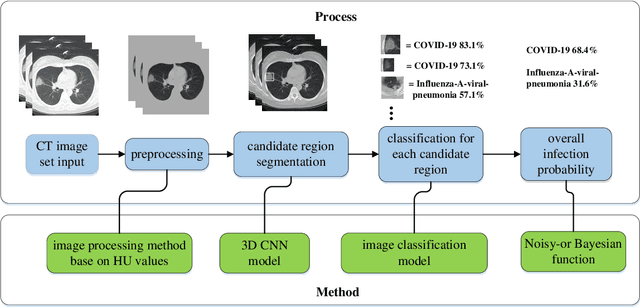
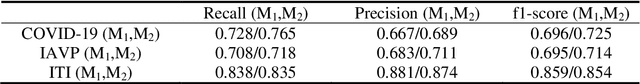
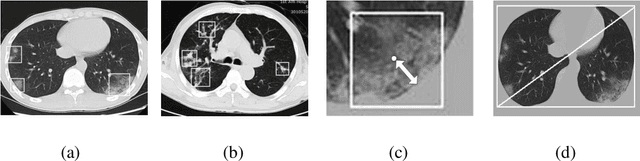
Abstract:We found that the real time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) detection of viral RNA from sputum or nasopharyngeal swab has a relatively low positive rate in the early stage to determine COVID-19 (named by the World Health Organization). The manifestations of computed tomography (CT) imaging of COVID-19 had their own characteristics, which are different from other types of viral pneumonia, such as Influenza-A viral pneumonia. Therefore, clinical doctors call for another early diagnostic criteria for this new type of pneumonia as soon as possible.This study aimed to establish an early screening model to distinguish COVID-19 pneumonia from Influenza-A viral pneumonia and healthy cases with pulmonary CT images using deep learning techniques. The candidate infection regions were first segmented out using a 3-dimensional deep learning model from pulmonary CT image set. These separated images were then categorized into COVID-19, Influenza-A viral pneumonia and irrelevant to infection groups, together with the corresponding confidence scores using a location-attention classification model. Finally the infection type and total confidence score of this CT case were calculated with Noisy-or Bayesian function.The experiments result of benchmark dataset showed that the overall accuracy was 86.7 % from the perspective of CT cases as a whole.The deep learning models established in this study were effective for the early screening of COVID-19 patients and demonstrated to be a promising supplementary diagnostic method for frontline clinical doctors.
A Deep Learning System That Generates Quantitative CT Reports for Diagnosing Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Oct 05, 2019
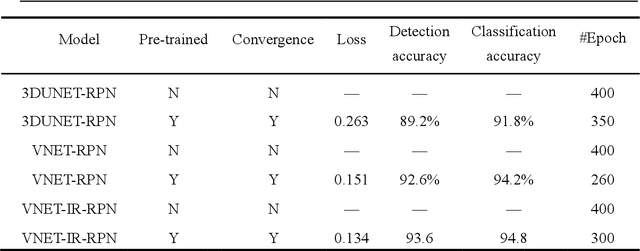
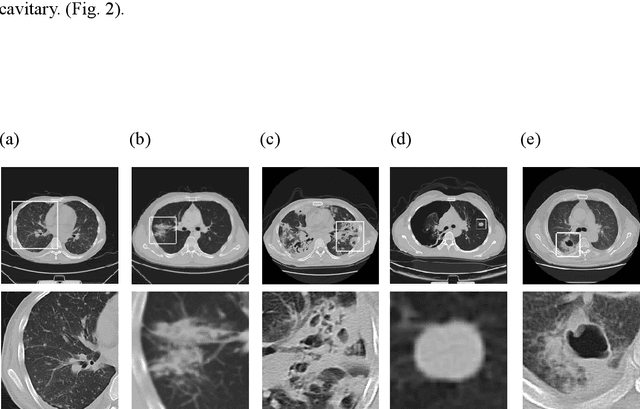
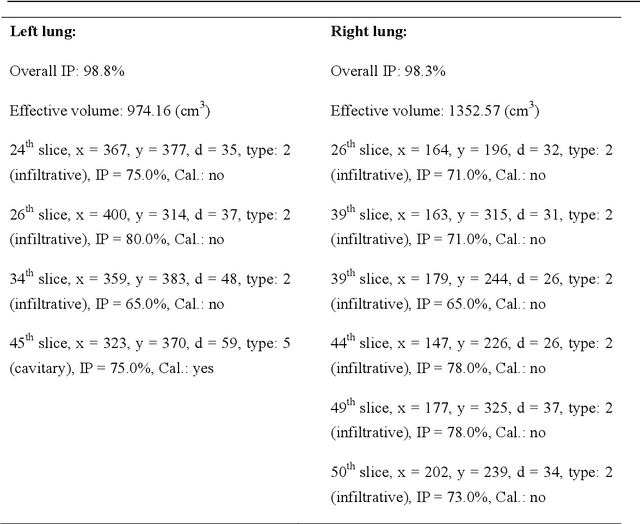
Abstract:We developed a deep learning model-based system to automatically generate a quantitative Computed Tomography (CT) diagnostic report for Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) cases.501 CT imaging datasets from 223 patients with active PTB were collected, and another 501 cases from a healthy population served as negative samples.2884 lesions of PTB were carefully labeled and classified manually by professional radiologists.Three state-of-the-art 3D convolution neural network (CNN) models were trained and evaluated in the inspection of PTB CT images. Transfer learning method was also utilized during this process. The best model was selected to annotate the spatial location of lesions and classify them into miliary, infiltrative, caseous, tuberculoma and cavitary types simultaneously.Then the Noisy-Or Bayesian function was used to generate an overall infection probability.Finally, a quantitative diagnostic report was exported.The results showed that the recall and precision rates, from the perspective of a single lesion region of PTB, were 85.9% and 89.2% respectively. The overall recall and precision rates,from the perspective of one PTB case, were 98.7% and 93.7%, respectively. Moreover, the precision rate of the PTB lesion type classification was 90.9%.The new method might serve as an effective reference for decision making by clinical doctors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge