Kai Konen
Style Vectors for Steering Generative Large Language Model
Feb 02, 2024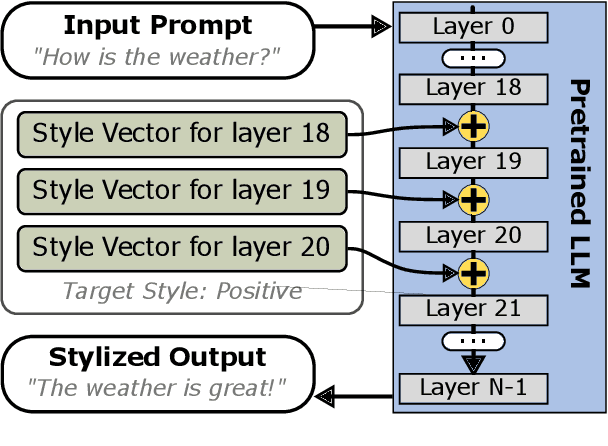
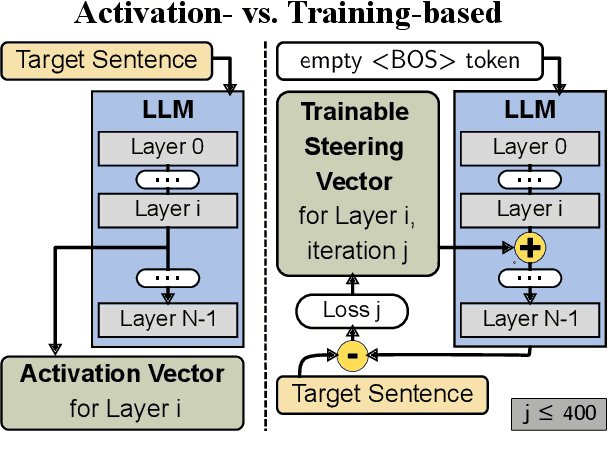
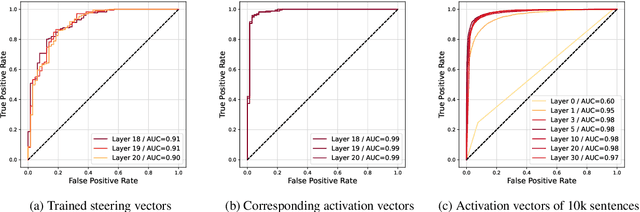
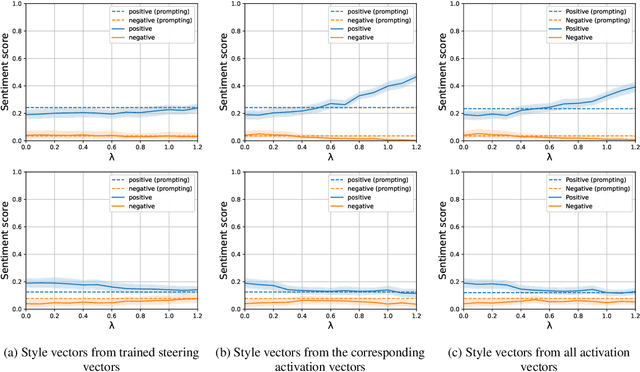
Abstract:This research explores strategies for steering the output of large language models (LLMs) towards specific styles, such as sentiment, emotion, or writing style, by adding style vectors to the activations of hidden layers during text generation. We show that style vectors can be simply computed from recorded layer activations for input texts in a specific style in contrast to more complex training-based approaches. Through a series of experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of activation engineering using such style vectors to influence the style of generated text in a nuanced and parameterisable way, distinguishing it from prompt engineering. The presented research constitutes a significant step towards developing more adaptive and effective AI-empowered interactive systems.
Decentralized Deep Reinforcement Learning for a Distributed and Adaptive Locomotion Controller of a Hexapod Robot
May 21, 2020
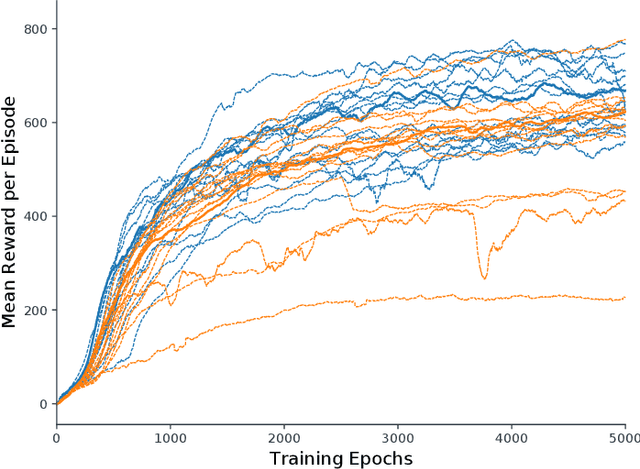
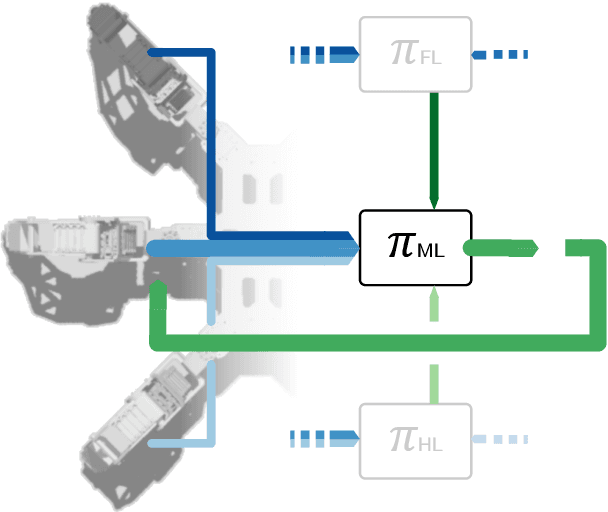
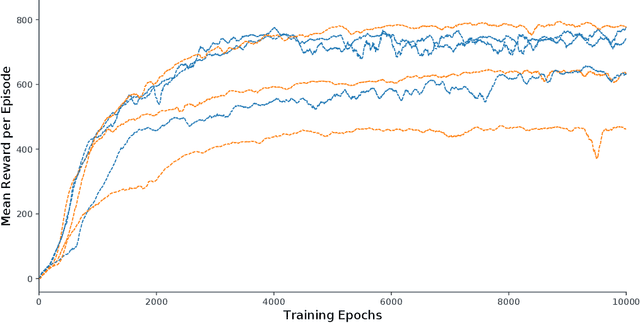
Abstract:Locomotion is a prime example for adaptive behavior in animals and biological control principles have inspired control architectures for legged robots. While machine learning has been successfully applied to many tasks in recent years, Deep Reinforcement Learning approaches still appear to struggle when applied to real world robots in continuous control tasks and in particular do not appear as robust solutions that can handle uncertainties well. Therefore, there is a new interest in incorporating biological principles into such learning architectures. While inducing a hierarchical organization as found in motor control has shown already some success, we here propose a decentralized organization as found in insect motor control for coordination of different legs. A decentralized and distributed architecture is introduced on a simulated hexapod robot and the details of the controller are learned through Deep Reinforcement Learning. We first show that such a concurrent local structure is able to learn better walking behavior. Secondly, that the simpler organization is learned faster compared to holistic approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge