Kai Herz
Magnetic Resonance Center, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tübingen, Germany, Department of Biomedical Magnetic Resonance, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
Accelerated and Quantitative 3D Semisolid MT/CEST Imaging using a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN-CEST)
Jul 22, 2022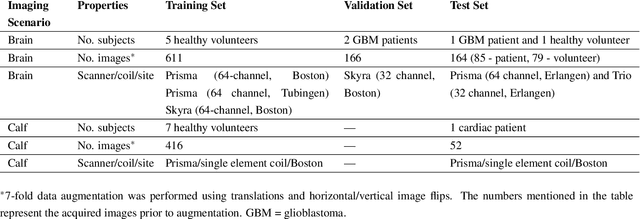
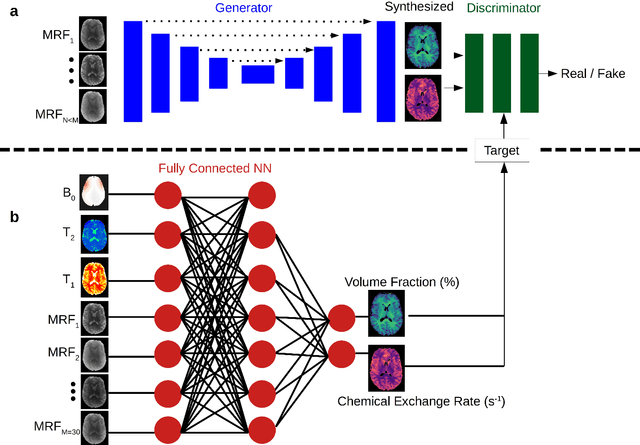
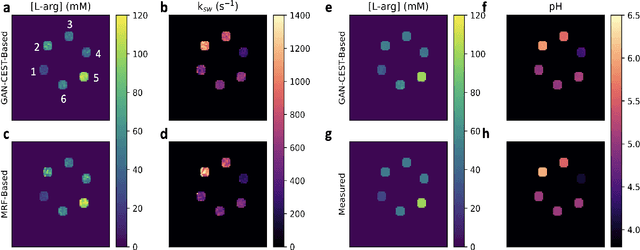
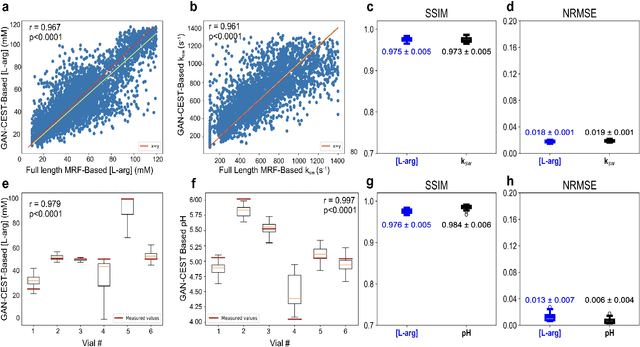
Abstract:Purpose: To substantially shorten the acquisition time required for quantitative 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) and semisolid magnetization transfer (MT) imaging and allow for rapid chemical exchange parameter map reconstruction. Methods: Three-dimensional CEST and MT magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) datasets of L-arginine phantoms, whole-brains, and calf muscles from healthy volunteers, cancer patients, and cardiac patients were acquired using 3T clinical scanners at 3 different sites, using 3 different scanner models and coils. A generative adversarial network supervised framework (GAN-CEST) was then designed and trained to learn the mapping from a reduced input data space to the quantitative exchange parameter space, while preserving perceptual and quantitative content. Results: The GAN-CEST 3D acquisition time was 42-52 seconds, 70% shorter than CEST-MRF. The quantitative reconstruction of the entire brain took 0.8 seconds. An excellent agreement was observed between the ground truth and GAN-based L-arginine concentration and pH values (Pearson's r > 0.97, NRMSE < 1.5%). GAN-CEST images from a brain-tumor subject yielded a semi-solid volume fraction and exchange rate NRMSE of 3.8$\pm$1.3% and 4.6$\pm$1.3%, respectively, and SSIM of 96.3$\pm$1.6% and 95.0$\pm$2.4%, respectively. The mapping of the calf-muscle exchange parameters in a cardiac patient, yielded NRMSE < 7% and SSIM > 94% for the semi-solid exchange parameters. In regions with large susceptibility artifacts, GAN-CEST has demonstrated improved performance and reduced noise compared to MRF. Conclusion: GAN-CEST can substantially reduce the acquisition time for quantitative semisolid MT/CEST mapping, while retaining performance even when facing pathologies and scanner models that were not available during training.
snapshot CEST++ : the next snapshot CEST for fast whole-brain APTw imaging at 3T
Jul 01, 2022
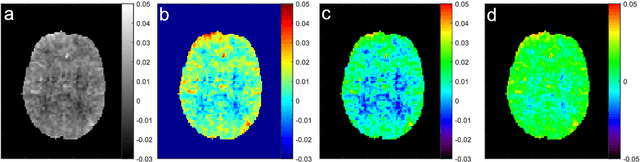
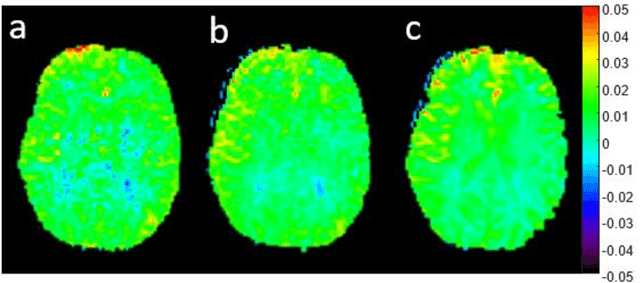
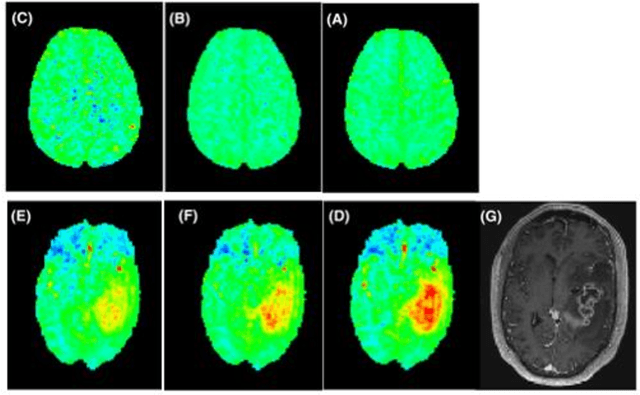
Abstract:CEST suffers from two main problems long acquisitin times or restricted coverage as well as incoherent protocol settings. In this paper we give suggestions on how to optimise your protocol settings fro CEST and present one setting for APT CEST. To increase the coverage while keeping the acquisition time constant we suggest using a spatial temporal Compressed Sensing approach. Finally, 1.8mm isotropic whole brain APT CEST maps can be acquired in a little bit less than 2min with a fully integrated online reconstruction. This will pave the way to an even further clinical use of CEST.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge