Ka Chun Shum
Color Alignment in Diffusion
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have shown great promise in synthesizing visually appealing images. However, it remains challenging to condition the synthesis at a fine-grained level, for instance, synthesizing image pixels following some generic color pattern. Existing image synthesis methods often produce contents that fall outside the desired pixel conditions. To address this, we introduce a novel color alignment algorithm that confines the generative process in diffusion models within a given color pattern. Specifically, we project diffusion terms, either imagery samples or latent representations, into a conditional color space to align with the input color distribution. This strategy simplifies the prediction in diffusion models within a color manifold while still allowing plausible structures in generated contents, thus enabling the generation of diverse contents that comply with the target color pattern. Experimental results demonstrate our state-of-the-art performance in conditioning and controlling of color pixels, while maintaining on-par generation quality and diversity in comparison with regular diffusion models.
StyleCity: Large-Scale 3D Urban Scenes Stylization with Vision-and-Text Reference via Progressive Optimization
Apr 16, 2024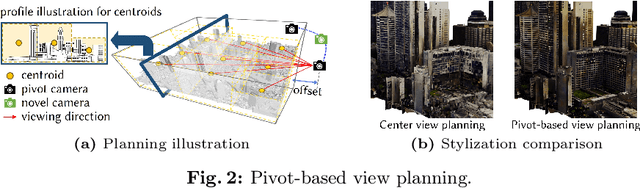



Abstract:Creating large-scale virtual urban scenes with variant styles is inherently challenging. To facilitate prototypes of virtual production and bypass the need for complex materials and lighting setups, we introduce the first vision-and-text-driven texture stylization system for large-scale urban scenes, StyleCity. Taking an image and text as references, StyleCity stylizes a 3D textured mesh of a large-scale urban scene in a semantics-aware fashion and generates a harmonic omnidirectional sky background. To achieve that, we propose to stylize a neural texture field by transferring 2D vision-and-text priors to 3D globally and locally. During 3D stylization, we progressively scale the planned training views of the input 3D scene at different levels in order to preserve high-quality scene content. We then optimize the scene style globally by adapting the scale of the style image with the scale of the training views. Moreover, we enhance local semantics consistency by the semantics-aware style loss which is crucial for photo-realistic stylization. Besides texture stylization, we further adopt a generative diffusion model to synthesize a style-consistent omnidirectional sky image, which offers a more immersive atmosphere and assists the semantic stylization process. The stylized neural texture field can be baked into an arbitrary-resolution texture, enabling seamless integration into conventional rendering pipelines and significantly easing the virtual production prototyping process. Extensive experiments demonstrate our stylized scenes' superiority in qualitative and quantitative performance and user preferences.
Advances in 3D Neural Stylization: A Survey
Nov 30, 2023

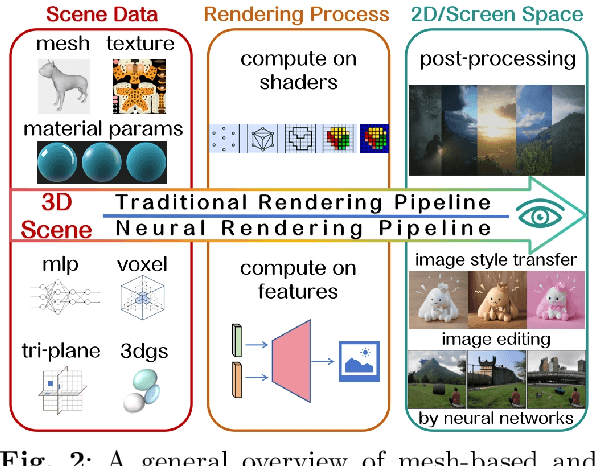

Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence provides a novel way of producing digital art in styles. The expressive power of neural networks enables the realm of visual style transfer methods, which can be used to edit images, videos, and 3D data to make them more artistic and diverse. This paper reports on recent advances in neural stylization for 3D data. We provide a taxonomy for neural stylization by considering several important design choices, including scene representation, guidance data, optimization strategies, and output styles. Building on such taxonomy, our survey first revisits the background of neural stylization on 2D images, and then provides in-depth discussions on recent neural stylization methods for 3D data, where we also provide a mini-benchmark on artistic stylization methods. Based on the insights gained from the survey, we then discuss open challenges, future research, and potential applications and impacts of neural stylization.
Language-driven Object Fusion into Neural Radiance Fields with Pose-Conditioned Dataset Updates
Sep 25, 2023



Abstract:Neural radiance field is an emerging rendering method that generates high-quality multi-view consistent images from a neural scene representation and volume rendering. Although neural radiance field-based techniques are robust for scene reconstruction, their ability to add or remove objects remains limited. This paper proposes a new language-driven approach for object manipulation with neural radiance fields through dataset updates. Specifically, to insert a new foreground object represented by a set of multi-view images into a background radiance field, we use a text-to-image diffusion model to learn and generate combined images that fuse the object of interest into the given background across views. These combined images are then used for refining the background radiance field so that we can render view-consistent images containing both the object and the background. To ensure view consistency, we propose a dataset updates strategy that prioritizes radiance field training with camera views close to the already-trained views prior to propagating the training to remaining views. We show that under the same dataset updates strategy, we can easily adapt our method for object insertion using data from text-to-3D models as well as object removal. Experimental results show that our method generates photorealistic images of the edited scenes, and outperforms state-of-the-art methods in 3D reconstruction and neural radiance field blending.
Conditional 360-degree Image Synthesis for Immersive Indoor Scene Decoration
Jul 18, 2023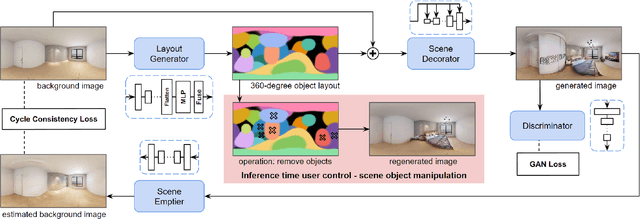
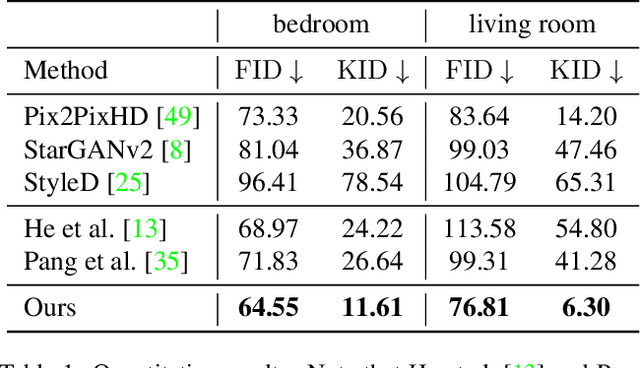
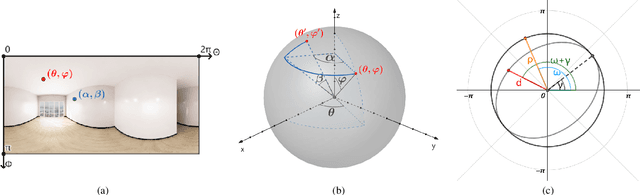
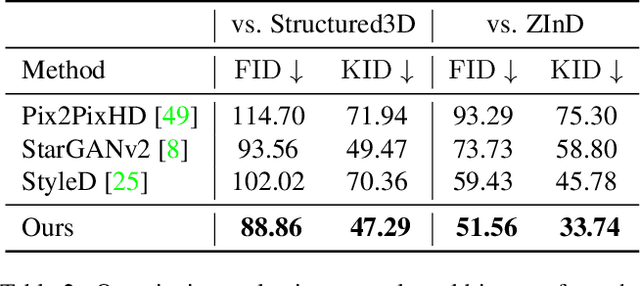
Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of conditional scene decoration for 360-degree images. Our method takes a 360-degree background photograph of an indoor scene and generates decorated images of the same scene in the panorama view. To do this, we develop a 360-aware object layout generator that learns latent object vectors in the 360-degree view to enable a variety of furniture arrangements for an input 360-degree background image. We use this object layout to condition a generative adversarial network to synthesize images of an input scene. To further reinforce the generation capability of our model, we develop a simple yet effective scene emptier that removes the generated furniture and produces an emptied scene for our model to learn a cyclic constraint. We train the model on the Structure3D dataset and show that our model can generate diverse decorations with controllable object layout. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Structure3D dataset and generalizes well to the Zillow indoor scene dataset. Our user study confirms the immersive experiences provided by the realistic image quality and furniture layout in our generation results. Our implementation will be made available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge