Junehyoung Kwon
DIAL: Dense Image-text ALignment for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Sep 24, 2024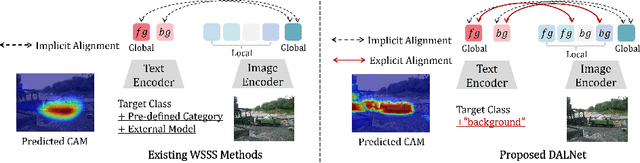
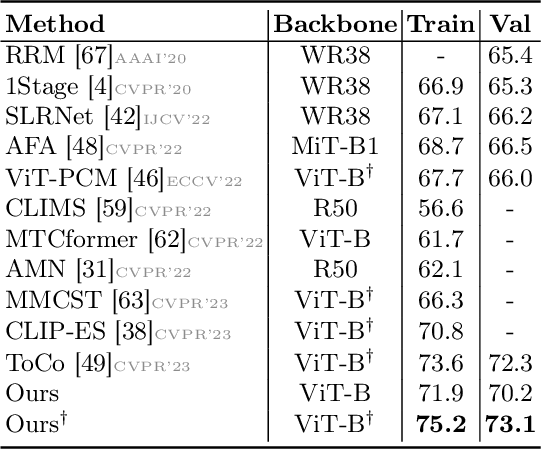
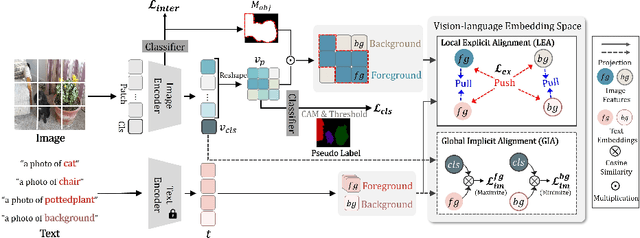
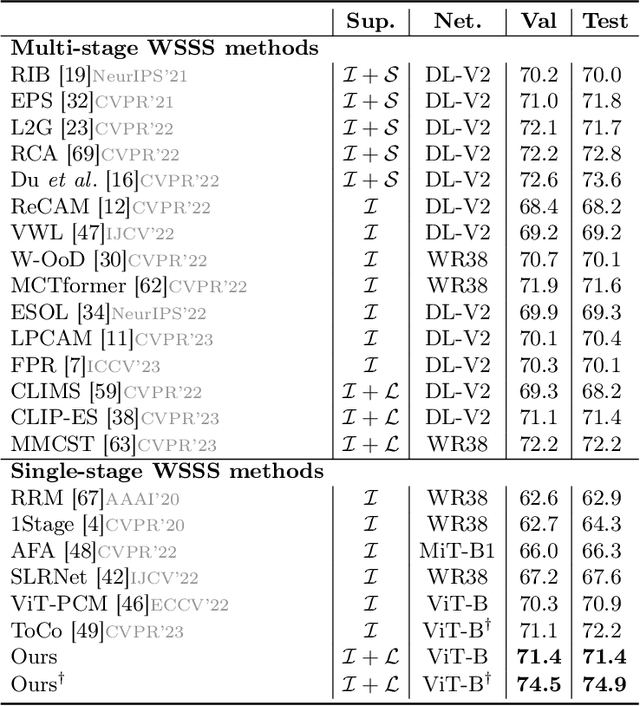
Abstract:Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) approaches typically rely on class activation maps (CAMs) for initial seed generation, which often fail to capture global context due to limited supervision from image-level labels. To address this issue, we introduce DALNet, Dense Alignment Learning Network that leverages text embeddings to enhance the comprehensive understanding and precise localization of objects across different levels of granularity. Our key insight is to employ a dual-level alignment strategy: (1) Global Implicit Alignment (GIA) to capture global semantics by maximizing the similarity between the class token and the corresponding text embeddings while minimizing the similarity with background embeddings, and (2) Local Explicit Alignment (LEA) to improve object localization by utilizing spatial information from patch tokens. Moreover, we propose a cross-contrastive learning approach that aligns foreground features between image and text modalities while separating them from the background, encouraging activation in missing regions and suppressing distractions. Through extensive experiments on the PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets, we demonstrate that DALNet significantly outperforms state-of-the-art WSSS methods. Our approach, in particular, allows for more efficient end-to-end process as a single-stage method.
VolDoGer: LLM-assisted Datasets for Domain Generalization in Vision-Language Tasks
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:Domain generalizability is a crucial aspect of a deep learning model since it determines the capability of the model to perform well on data from unseen domains. However, research on the domain generalizability of deep learning models for vision-language tasks remains limited, primarily because of the lack of required datasets. To address these challenges, we propose VolDoGer: Vision-Language Dataset for Domain Generalization, a dedicated dataset designed for domain generalization that addresses three vision-language tasks: image captioning, visual question answering, and visual entailment. We constructed VolDoGer by extending LLM-based data annotation techniques to vision-language tasks, thereby alleviating the burden of recruiting human annotators. We evaluated the domain generalizability of various models, ranging from fine-tuned models to a recent multimodal large language model, through VolDoGer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge