Josh Myers-Dean
PartStickers: Generating Parts of Objects for Rapid Prototyping
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Design prototyping involves creating mockups of products or concepts to gather feedback and iterate on ideas. While prototyping often requires specific parts of objects, such as when constructing a novel creature for a video game, existing text-to-image methods tend to only generate entire objects. To address this, we propose a novel task and method of ``part sticker generation", which entails generating an isolated part of an object on a neutral background. Experiments demonstrate our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines with respect to realism and text alignment, while preserving object-level generation capabilities. We publicly share our code and models to encourage community-wide progress on this new task: https://partsticker.github.io.
SPIN: Hierarchical Segmentation with Subpart Granularity in Natural Images
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Hierarchical segmentation entails creating segmentations at varying levels of granularity. We introduce the first hierarchical semantic segmentation dataset with subpart annotations for natural images, which we call SPIN (SubPartImageNet). We also introduce two novel evaluation metrics to evaluate how well algorithms capture spatial and semantic relationships across hierarchical levels. We benchmark modern models across three different tasks and analyze their strengths and weaknesses across objects, parts, and subparts. To facilitate community-wide progress, we publicly release our dataset at https://joshmyersdean.github.io/spin/index.html.
Interpreting COVID Lateral Flow Tests' Results with Foundation Models
Apr 21, 2024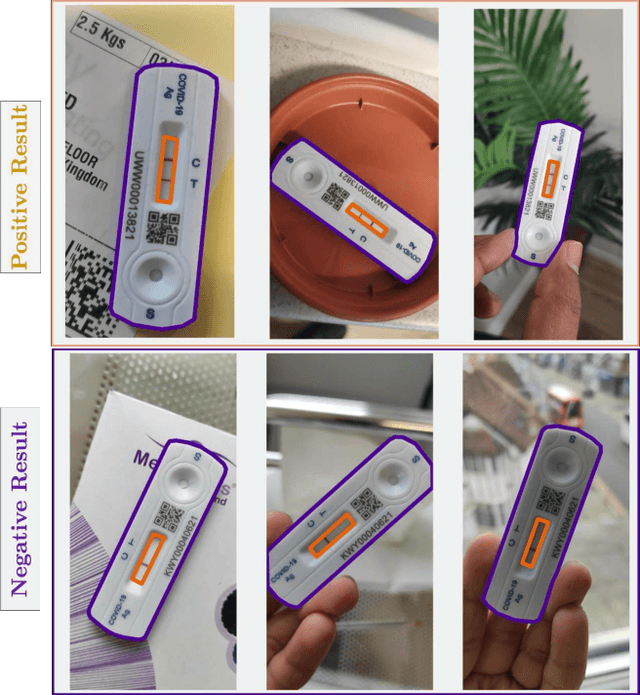
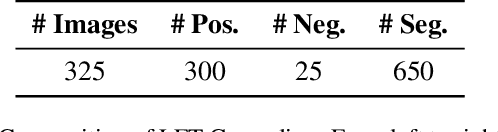
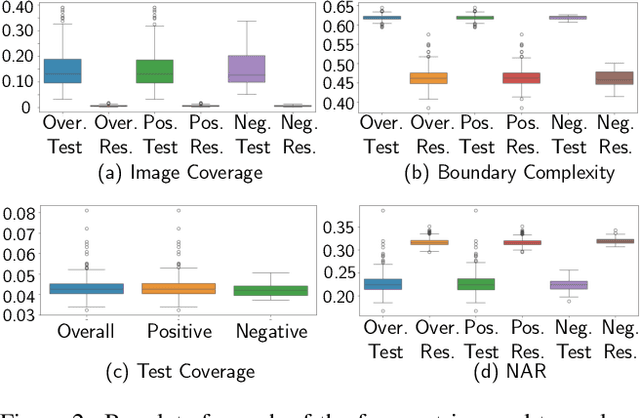
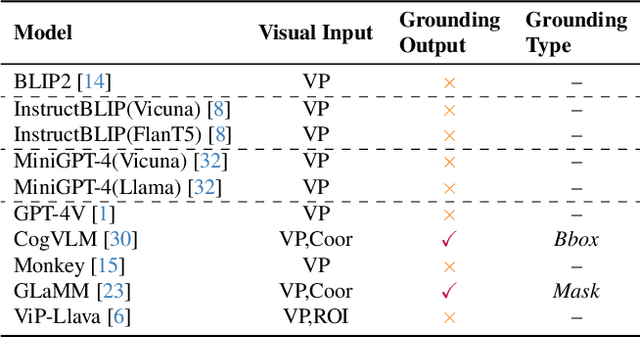
Abstract:Lateral flow tests (LFTs) enable rapid, low-cost testing for health conditions including Covid, pregnancy, HIV, and malaria. Automated readers of LFT results can yield many benefits including empowering blind people to independently learn about their health and accelerating data entry for large-scale monitoring (e.g., for pandemics such as Covid) by using only a single photograph per LFT test. Accordingly, we explore the abilities of modern foundation vision language models (VLMs) in interpreting such tests. To enable this analysis, we first create a new labeled dataset with hierarchical segmentations of each LFT test and its nested test result window. We call this dataset LFT-Grounding. Next, we benchmark eight modern VLMs in zero-shot settings for analyzing these images. We demonstrate that current VLMs frequently fail to correctly identify the type of LFT test, interpret the test results, locate the nested result window of the LFT tests, and recognize LFT tests when they partially obfuscated. To facilitate community-wide progress towards automated LFT reading, we publicly release our dataset at https://iamstuti.github.io/lft_grounding_foundation_models/.
Interactive Segmentation for Diverse Gesture Types Without Context
Jul 20, 2023Abstract:Interactive segmentation entails a human marking an image to guide how a model either creates or edits a segmentation. Our work addresses limitations of existing methods: they either only support one gesture type for marking an image (e.g., either clicks or scribbles) or require knowledge of the gesture type being employed, and require specifying whether marked regions should be included versus excluded in the final segmentation. We instead propose a simplified interactive segmentation task where a user only must mark an image, where the input can be of any gesture type without specifying the gesture type. We support this new task by introducing the first interactive segmentation dataset with multiple gesture types as well as a new evaluation metric capable of holistically evaluating interactive segmentation algorithms. We then analyze numerous interactive segmentation algorithms, including ones adapted for our novel task. While we observe promising performance overall, we also highlight areas for future improvement. To facilitate further extensions of this work, we publicly share our new dataset at https://github.com/joshmyersdean/dig.
Generalized Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation: All You Need is Fine-Tuning
Dec 21, 2021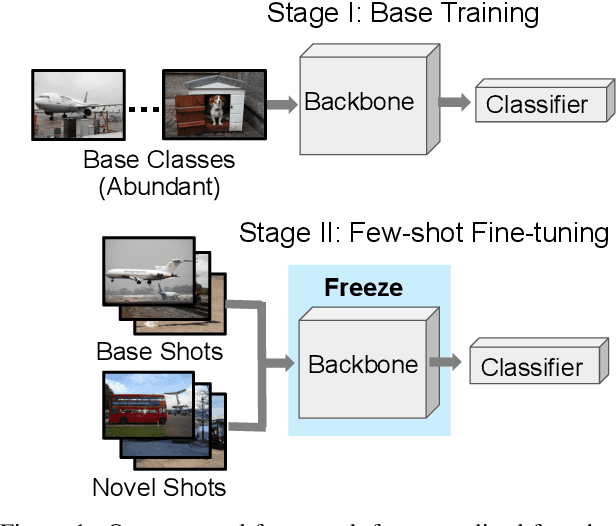
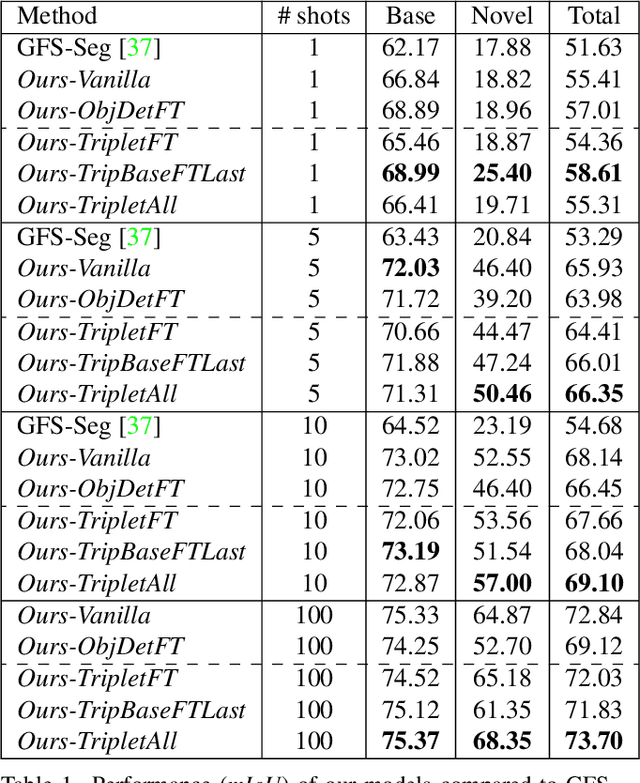
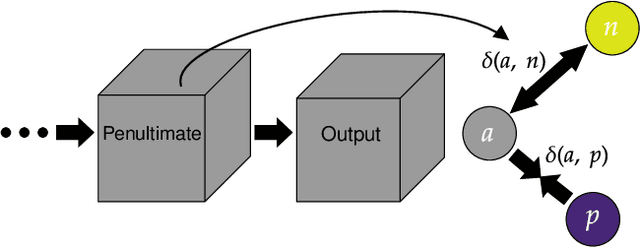
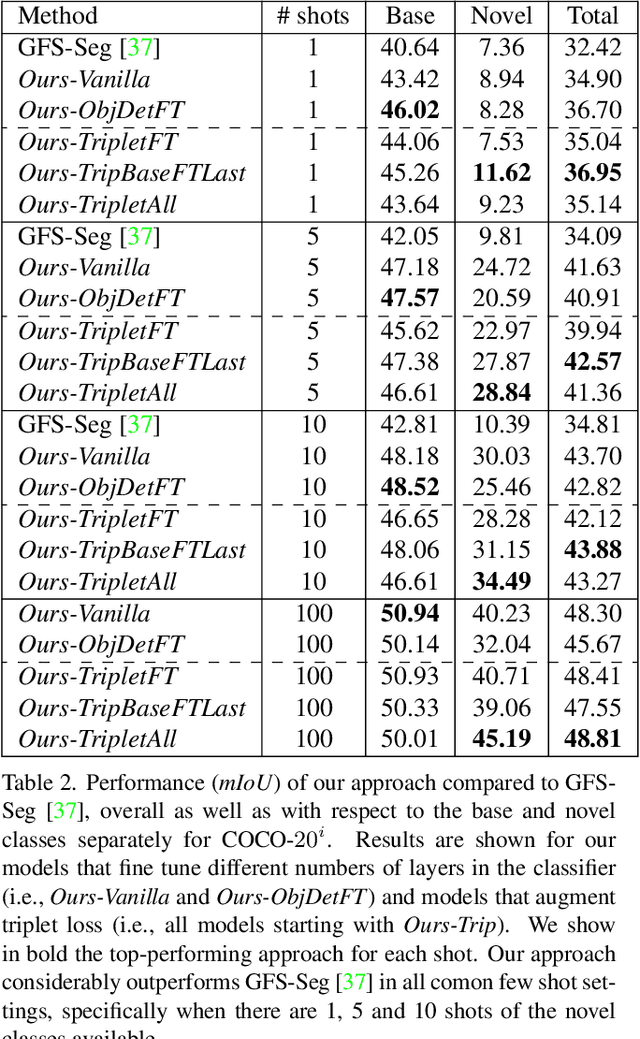
Abstract:Generalized few-shot semantic segmentation was introduced to move beyond only evaluating few-shot segmentation models on novel classes to include testing their ability to remember base classes. While all approaches currently are based on meta-learning, they perform poorly and saturate in learning after observing only a few shots. We propose the first fine-tuning solution, and demonstrate that it addresses the saturation problem while achieving state-of-art results on two datasets, PASCAL-$5^i$ and COCO-$20^i$. We also show it outperforms existing methods whether fine-tuning multiple final layers or only the final layer. Finally, we present a triplet loss regularization that shows how to redistribute the balance of performance between novel and base categories so that there is a smaller gap between them.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge