Joseph Suh
Identity, Cooperation and Framing Effects within Groups of Real and Simulated Humans
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Humans act via a nuanced process that depends both on rational deliberation and also on identity and contextual factors. In this work, we study how large language models (LLMs) can simulate human action in the context of social dilemma games. While prior work has focused on "steering" (weak binding) of chat models to simulate personas, we analyze here how deep binding of base models with extended backstories leads to more faithful replication of identity-based behaviors. Our study has these findings: simulation fidelity vs human studies is improved by conditioning base LMs with rich context of narrative identities and checking consistency using instruction-tuned models. We show that LLMs can also model contextual factors such as time (year that a study was performed), question framing, and participant pool effects. LLMs, therefore, allow us to explore the details that affect human studies but which are often omitted from experiment descriptions, and which hamper accurate replication.
Higher-Order Binding of Language Model Virtual Personas: a Study on Approximating Political Partisan Misperceptions
Apr 16, 2025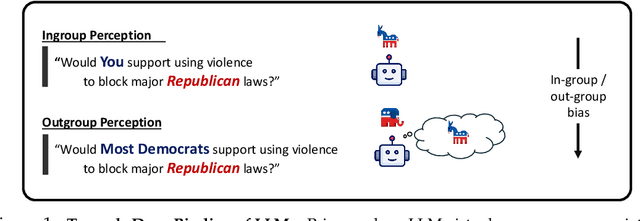
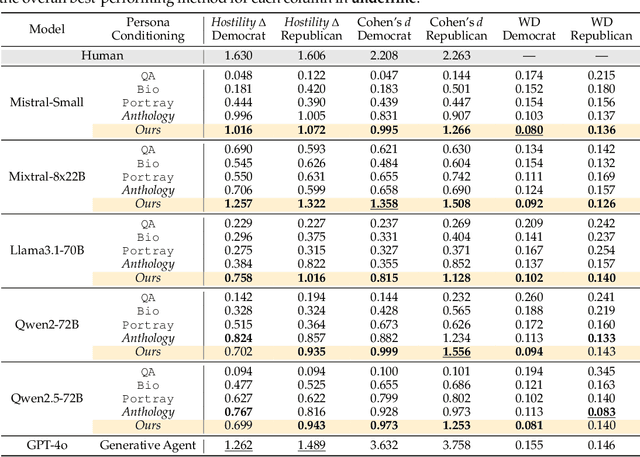
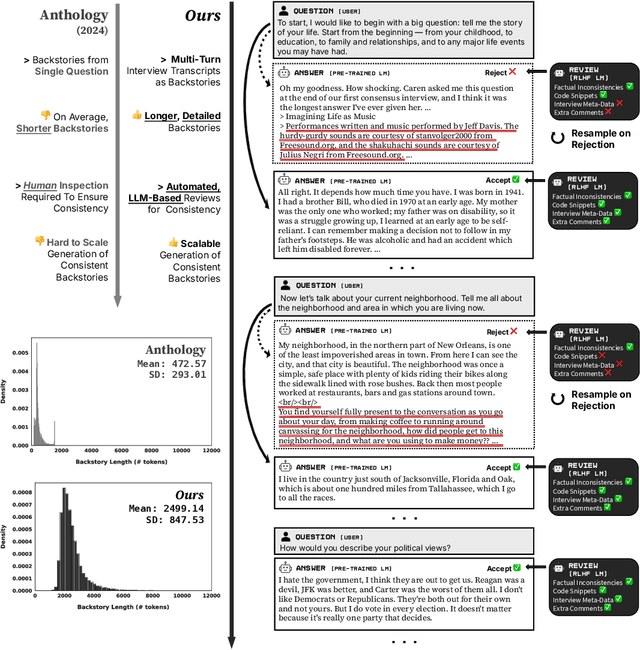
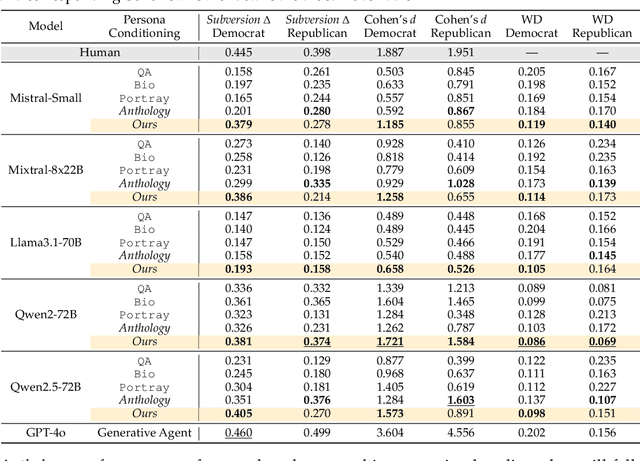
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly capable of simulating human behavior, offering cost-effective ways to estimate user responses during the early phases of survey design. While previous studies have examined whether models can reflect individual opinions or attitudes, we argue that a \emph{higher-order} binding of virtual personas requires successfully approximating not only the opinions of a user as an identified member of a group, but also the nuanced ways in which that user perceives and evaluates those outside the group. In particular, faithfully simulating how humans perceive different social groups is critical for applying LLMs to various political science studies, including timely topics on polarization dynamics, inter-group conflict, and democratic backsliding. To this end, we propose a novel methodology for constructing virtual personas with synthetic user ``backstories" generated as extended, multi-turn interview transcripts. Our generated backstories are longer, rich in detail, and consistent in authentically describing a singular individual, compared to previous methods. We show that virtual personas conditioned on our backstories closely replicate human response distributions (up to an 87\% improvement as measured by Wasserstein Distance) and produce effect sizes that closely match those observed in the original studies. Altogether, our work extends the applicability of LLMs beyond estimating individual self-opinions, enabling their use in a broader range of human studies.
Language Model Fine-Tuning on Scaled Survey Data for Predicting Distributions of Public Opinions
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) present novel opportunities in public opinion research by predicting survey responses in advance during the early stages of survey design. Prior methods steer LLMs via descriptions of subpopulations as LLMs' input prompt, yet such prompt engineering approaches have struggled to faithfully predict the distribution of survey responses from human subjects. In this work, we propose directly fine-tuning LLMs to predict response distributions by leveraging unique structural characteristics of survey data. To enable fine-tuning, we curate SubPOP, a significantly scaled dataset of 3,362 questions and 70K subpopulation-response pairs from well-established public opinion surveys. We show that fine-tuning on SubPOP greatly improves the match between LLM predictions and human responses across various subpopulations, reducing the LLM-human gap by up to 46% compared to baselines, and achieves strong generalization to unseen surveys and subpopulations. Our findings highlight the potential of survey-based fine-tuning to improve opinion prediction for diverse, real-world subpopulations and therefore enable more efficient survey designs. Our code is available at https://github.com/JosephJeesungSuh/subpop.
Rediscovering the Latent Dimensions of Personality with Large Language Models as Trait Descriptors
Sep 16, 2024



Abstract:Assessing personality traits using large language models (LLMs) has emerged as an interesting and challenging area of research. While previous methods employ explicit questionnaires, often derived from the Big Five model of personality, we hypothesize that LLMs implicitly encode notions of personality when modeling next-token responses. To demonstrate this, we introduce a novel approach that uncovers latent personality dimensions in LLMs by applying singular value de-composition (SVD) to the log-probabilities of trait-descriptive adjectives. Our experiments show that LLMs "rediscover" core personality traits such as extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and openness without relying on direct questionnaire inputs, with the top-5 factors corresponding to Big Five traits explaining 74.3% of the variance in the latent space. Moreover, we can use the derived principal components to assess personality along the Big Five dimensions, and achieve improvements in average personality prediction accuracy of up to 5% over fine-tuned models, and up to 21% over direct LLM-based scoring techniques.
Virtual Personas for Language Models via an Anthology of Backstories
Jul 09, 2024
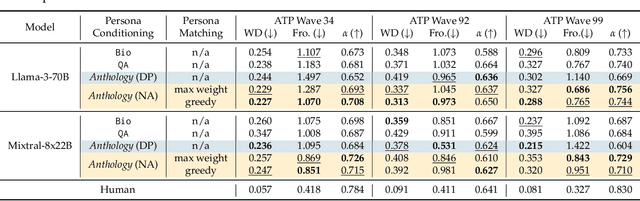
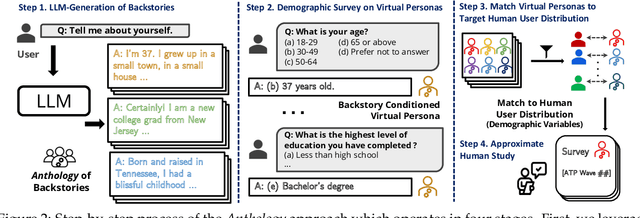
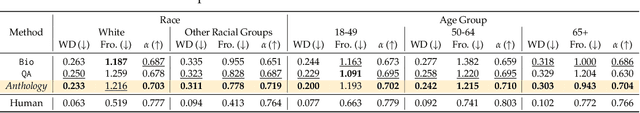
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are trained from vast repositories of text authored by millions of distinct authors, reflecting an enormous diversity of human traits. While these models bear the potential to be used as approximations of human subjects in behavioral studies, prior efforts have been limited in steering model responses to match individual human users. In this work, we introduce "Anthology", a method for conditioning LLMs to particular virtual personas by harnessing open-ended life narratives, which we refer to as "backstories." We show that our methodology enhances the consistency and reliability of experimental outcomes while ensuring better representation of diverse sub-populations. Across three nationally representative human surveys conducted as part of Pew Research Center's American Trends Panel (ATP), we demonstrate that Anthology achieves up to 18% improvement in matching the response distributions of human respondents and 27% improvement in consistency metrics. Our code and generated backstories are available at https://github.com/CannyLab/anthology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge