Josef Jon
Thesis proposal: Are We Losing Textual Diversity to Natural Language Processing?
Sep 15, 2024



Abstract:This thesis argues that the currently widely used Natural Language Processing algorithms possibly have various limitations related to the properties of the texts they handle and produce. With the wide adoption of these tools in rapid progress, we must ask what these limitations are and what are the possible implications of integrating such tools even more deeply into our daily lives. As a testbed, we have chosen the task of Neural Machine Translation (NMT). Nevertheless, we aim for general insights and outcomes, applicable even to current Large Language Models (LLMs). We ask whether the algorithms used in NMT have inherent inductive biases that are beneficial for most types of inputs but might harm the processing of untypical texts. To explore this hypothesis, we define a set of measures to quantify text diversity based on its statistical properties, like uniformity or rhythmicity of word-level surprisal, on multiple scales (sentence, discourse, language). We then conduct a series of experiments to investigate whether NMT systems struggle with maintaining the diversity of such texts, potentially reducing the richness of the language generated by these systems, compared to human translators. We search for potential causes of these limitations rooted in training objectives and decoding algorithms. Our ultimate goal is to develop alternatives that do not enforce uniformity in the distribution of statistical properties in the output and that allow for better global planning of the translation, taking into account the intrinsic ambiguity of the translation task.
Character-level NMT and language similarity
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:We explore the effectiveness of character-level neural machine translation using Transformer architecture for various levels of language similarity and size of the training dataset on translation between Czech and Croatian, German, Hungarian, Slovak, and Spanish. We evaluate the models using automatic MT metrics and show that translation between similar languages benefits from character-level input segmentation, while for less related languages, character-level vanilla Transformer-base often lags behind subword-level segmentation. We confirm previous findings that it is possible to close the gap by finetuning the already trained subword-level models to character-level.
Negative Lexical Constraints in Neural Machine Translation
Aug 07, 2023Abstract:This paper explores negative lexical constraining in English to Czech neural machine translation. Negative lexical constraining is used to prohibit certain words or expressions in the translation produced by the neural translation model. We compared various methods based on modifying either the decoding process or the training data. The comparison was performed on two tasks: paraphrasing and feedback-based translation refinement. We also studied to which extent these methods "evade" the constraints presented to the model (usually in the dictionary form) by generating a different surface form of a given constraint.We propose a way to mitigate the issue through training with stemmed negative constraints to counter the model's ability to induce a variety of the surface forms of a word that can result in bypassing the constraint. We demonstrate that our method improves the constraining, although the problem still persists in many cases.
Breeding Machine Translations: Evolutionary approach to survive and thrive in the world of automated evaluation
May 30, 2023Abstract:We propose a genetic algorithm (GA) based method for modifying n-best lists produced by a machine translation (MT) system. Our method offers an innovative approach to improving MT quality and identifying weaknesses in evaluation metrics. Using common GA operations (mutation and crossover) on a list of hypotheses in combination with a fitness function (an arbitrary MT metric), we obtain novel and diverse outputs with high metric scores. With a combination of multiple MT metrics as the fitness function, the proposed method leads to an increase in translation quality as measured by other held-out automatic metrics. With a single metric (including popular ones such as COMET) as the fitness function, we find blind spots and flaws in the metric. This allows for an automated search for adversarial examples in an arbitrary metric, without prior assumptions on the form of such example. As a demonstration of the method, we create datasets of adversarial examples and use them to show that reference-free COMET is substantially less robust than the reference-based version.
CUNI Submission in WMT22 General Task
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:We present the CUNI-Bergamot submission for the WMT22 General translation task. We compete in English$\rightarrow$Czech direction. Our submission further explores block backtranslation techniques. Compared to the previous work, we measure performance in terms of COMET score and named entities translation accuracy. We evaluate performance of MBR decoding compared to traditional mixed backtranslation training and we show a possible synergy when using both of the techniques simultaneously. The results show that both approaches are effective means of improving translation quality and they yield even better results when combined.
CUNI systems for WMT21: Multilingual Low-Resource Translation for Indo-European Languages Shared Task
Sep 20, 2021
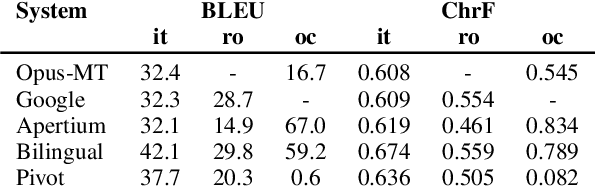
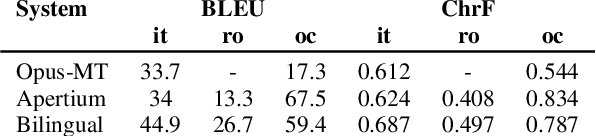
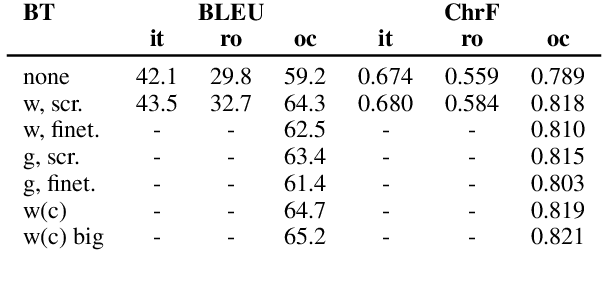
Abstract:This paper describes Charles University submission for Multilingual Low-Resource Translation for Indo-European Languages shared task at WMT21. We competed in translation from Catalan into Romanian, Italian and Occitan. Our systems are based on shared multilingual model. We show that using joint model for multiple similar language pairs improves upon translation quality in each pair. We also demonstrate that chararacter-level bilingual models are competitive for very similar language pairs (Catalan-Occitan) but less so for more distant pairs. We also describe our experiments with multi-task learning, where aside from a textual translation, the models are also trained to perform grapheme-to-phoneme conversion.
CUNI systems for WMT21: Terminology translation Shared Task
Sep 20, 2021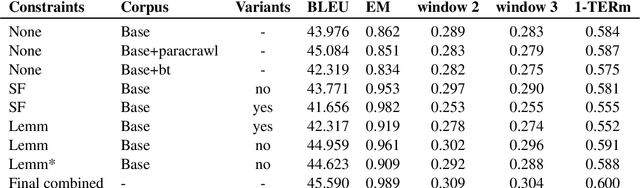
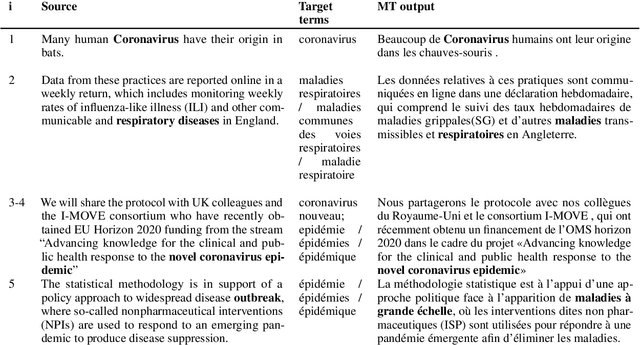
Abstract:This paper describes Charles University submission for Terminology translation Shared Task at WMT21. The objective of this task is to design a system which translates certain terms based on a provided terminology database, while preserving high overall translation quality. We competed in English-French language pair. Our approach is based on providing the desired translations alongside the input sentence and training the model to use these provided terms. We lemmatize the terms both during the training and inference, to allow the model to learn how to produce correct surface forms of the words, when they differ from the forms provided in the terminology database. Our submission ranked second in Exact Match metric which evaluates the ability of the model to produce desired terms in the translation.
End-to-End Lexically Constrained Machine Translation for Morphologically Rich Languages
Jun 24, 2021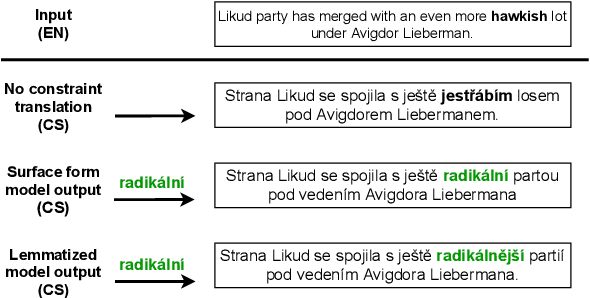
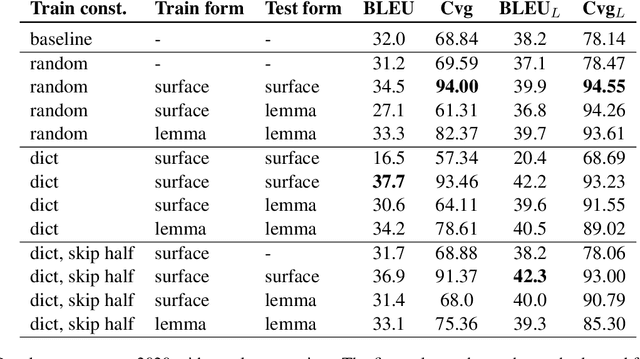
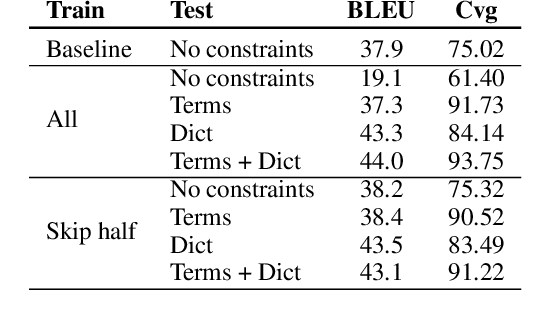
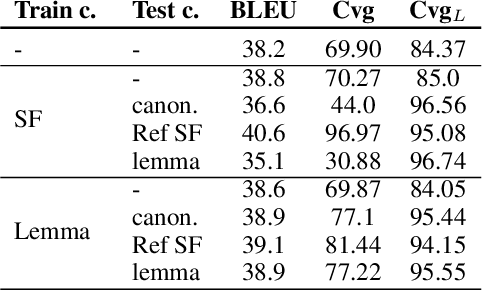
Abstract:Lexically constrained machine translation allows the user to manipulate the output sentence by enforcing the presence or absence of certain words and phrases. Although current approaches can enforce terms to appear in the translation, they often struggle to make the constraint word form agree with the rest of the generated output. Our manual analysis shows that 46% of the errors in the output of a baseline constrained model for English to Czech translation are related to agreement. We investigate mechanisms to allow neural machine translation to infer the correct word inflection given lemmatized constraints. In particular, we focus on methods based on training the model with constraints provided as part of the input sequence. Our experiments on the English-Czech language pair show that this approach improves the translation of constrained terms in both automatic and manual evaluation by reducing errors in agreement. Our approach thus eliminates inflection errors, without introducing new errors or decreasing the overall quality of the translation.
Rethinking the objectives of extractive question answering
Aug 28, 2020
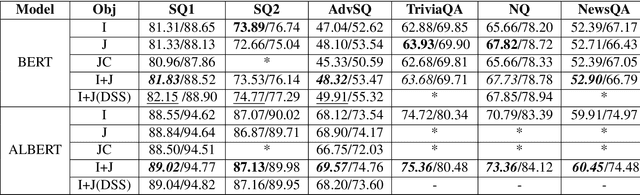


Abstract:This paper describes two generally applicable approaches towards the significant improvement of the performance of state-of-the-art extractive question answering (EQA) systems. Firstly, contrary to a common belief, it demonstrates that using the objective with independence assumption for span probability $P(a_s,a_e) = P(a_s)P(a_e)$ of span starting at position $a_s$ and ending at position $a_e$ may have adverse effects. Therefore we propose a new compound objective that models joint probability $P(a_s,a_e)$ directly, while still keeping the objective with independency assumption as an auxiliary objective. Our second approach shows the beneficial effect of distantly semi-supervised shared-normalization objective known from (Clark and Gardner, 2017). We show that normalizing over a set of documents similar to the golden passage, and marginalizing over all ground-truth answer string positions leads to the improvement of results from smaller statistical models. Our results are supported via experiments with three QA models (BidAF, BERT, ALBERT) over six datasets. The proposed approaches do not use any additional data. Our code, analysis, pretrained models, and individual results will be available online.
JokeMeter at SemEval-2020 Task 7: Convolutional humor
Aug 25, 2020



Abstract:This paper describes our system that was designed for Humor evaluation within the SemEval-2020 Task 7. The system is based on convolutional neural network architecture. We investigate the system on the official dataset, and we provide more insight to model itself to see how the learned inner features look.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge