Joost J. C. Verhoeff
Decision making in cancer: Causal questions require causal answers
Sep 15, 2022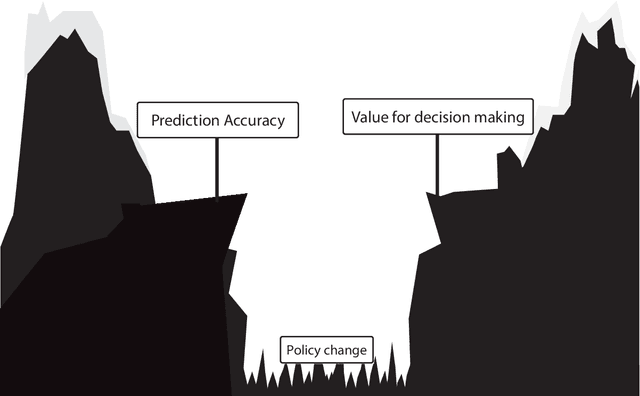
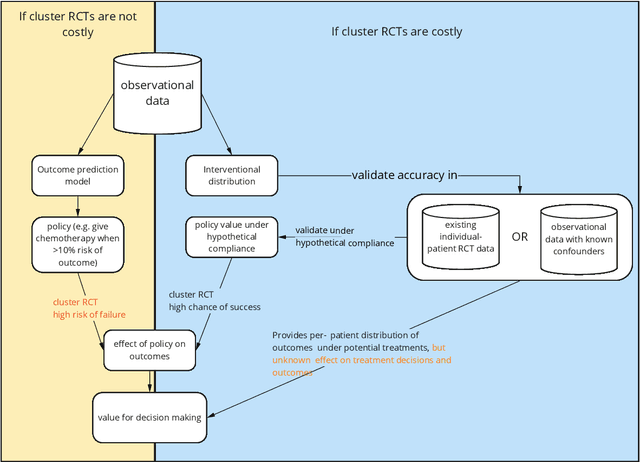
Abstract:Treatment decisions in cancer care are guided by treatment effect estimates from randomized controlled trials (RCTs). RCTs estimate the average effect of one treatment versus another in a certain population. However, treatments may not be equally effective for every patient in a population. Knowing the effectiveness of treatments tailored to specific patient and tumor characteristics would enable individualized treatment decisions. Getting tailored treatment effects by averaging outcomes in different patient subgroups in RCTs requires an unfeasible number of patients to have sufficient statistical power in all relevant subgroups for all possible treatments. The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) recommends that researchers develop outcome prediction models (OPMs) in an effort to individualize treatment decisions. OPMs sometimes called risk models or prognosis models, use patient and tumor characteristics to predict a patient outcome such as overall survival. The assumption is that the predictions are useful for treatment decisions using rules such as "prescribe chemotherapy only if the OPM predicts the patient has a high risk of recurrence". Recognizing the importance of reliable predictions, the AJCC published a checklist for OPMs to ensure dependable OPM prediction accuracy in the patient population for which the OPM was designed. However, accurate outcome predictions do not imply that these predictions yield good treatment decisions. In this perspective, we show that OPM rely on a fixed treatment policy which implies that OPM that were found to accurately predict outcomes in validation studies can still lead to patient harm when used to inform treatment decisions. We then give guidance on how to develop models that are useful for individualized treatment decisions and how to evaluate whether a model has value for decision-making.
Automatic Online Quality Control of Synthetic CTs
Nov 12, 2019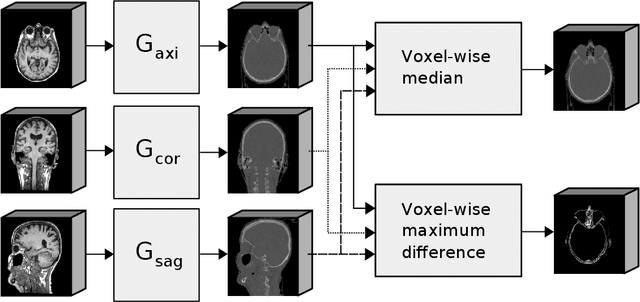
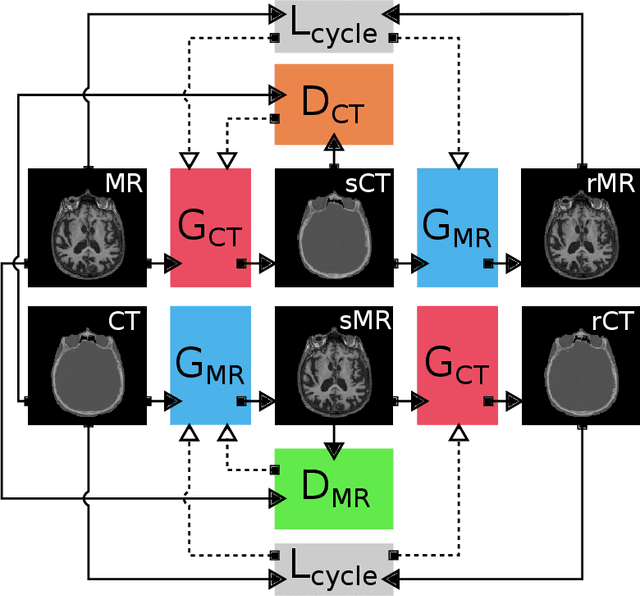
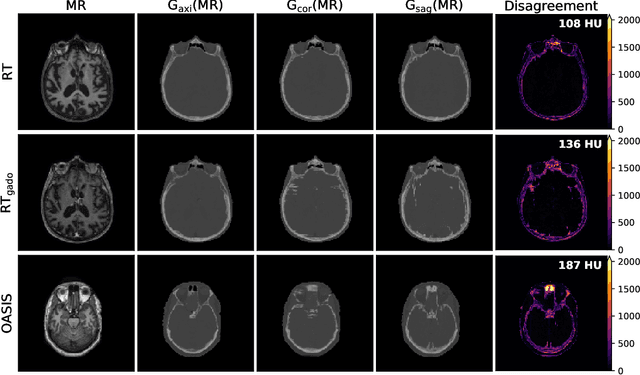
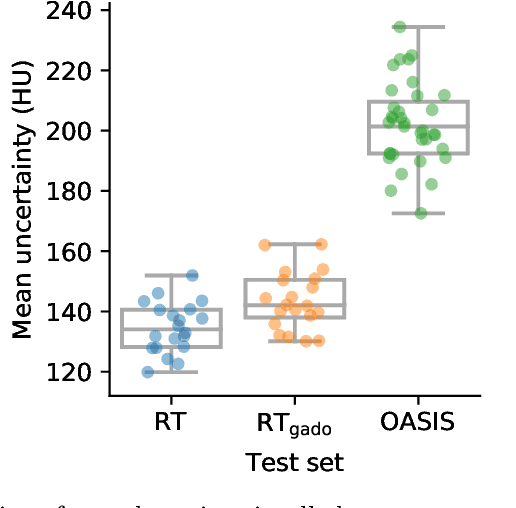
Abstract:Accurate MR-to-CT synthesis is a requirement for MR-only workflows in radiotherapy (RT) treatment planning. In recent years, deep learning-based approaches have shown impressive results in this field. However, to prevent downstream errors in RT treatment planning, it is important that deep learning models are only applied to data for which they are trained and that generated synthetic CT (sCT) images do not contain severe errors. For this, a mechanism for online quality control should be in place. In this work, we use an ensemble of sCT generators and assess their disagreement as a measure of uncertainty of the results. We show that this uncertainty measure can be used for two kinds of online quality control. First, to detect input images that are outside the expected distribution of MR images. Second, to identify sCT images that were generated from suitable MR images but potentially contain errors. Such automatic online quality control for sCT generation is likely to become an integral part of MR-only RT workflows.
Exploiting Clinically Available Delineations for CNN-based Segmentation in Radiotherapy Treatment Planning
Nov 12, 2019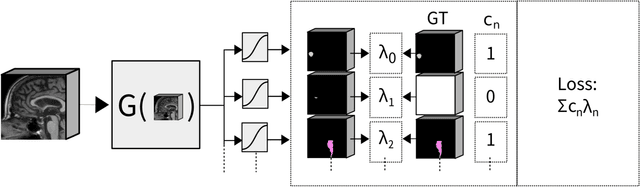
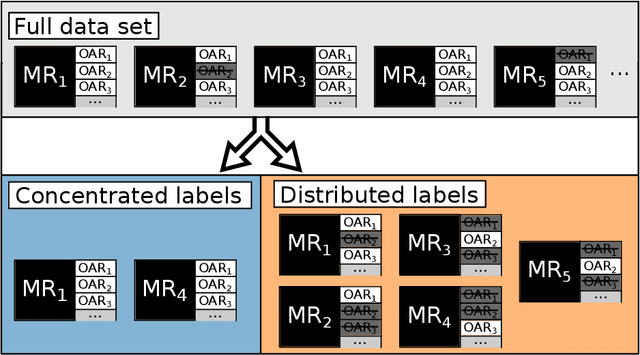
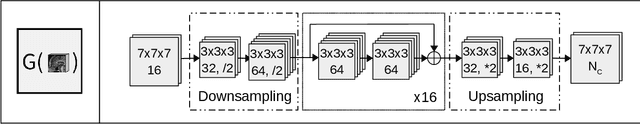
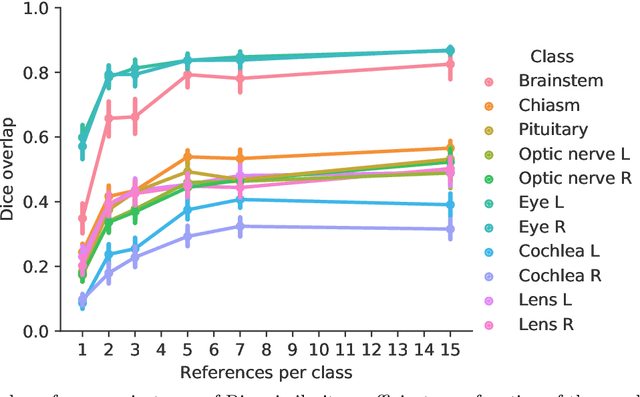
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been widely and successfully used for medical image segmentation. However, CNNs are typically considered to require large numbers of dedicated expert-segmented training volumes, which may be limiting in practice. This work investigates whether clinically obtained segmentations which are readily available in picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) could provide a possible source of data to train a CNN for segmentation of organs-at-risk (OARs) in radiotherapy treatment planning. In such data, delineations of structures deemed irrelevant to the target clinical use may be lacking. To overcome this issue, we use multi-label instead of multi-class segmentation. We empirically assess how many clinical delineations would be sufficient to train a CNN for the segmentation of OARs and find that increasing the training set size beyond a limited number of images leads to sharply diminishing returns. Moreover, we find that by using multi-label segmentation, missing structures in the reference standard do not have a negative effect on overall segmentation accuracy. These results indicate that segmentations obtained in a clinical workflow can be used to train an accurate OAR segmentation model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge